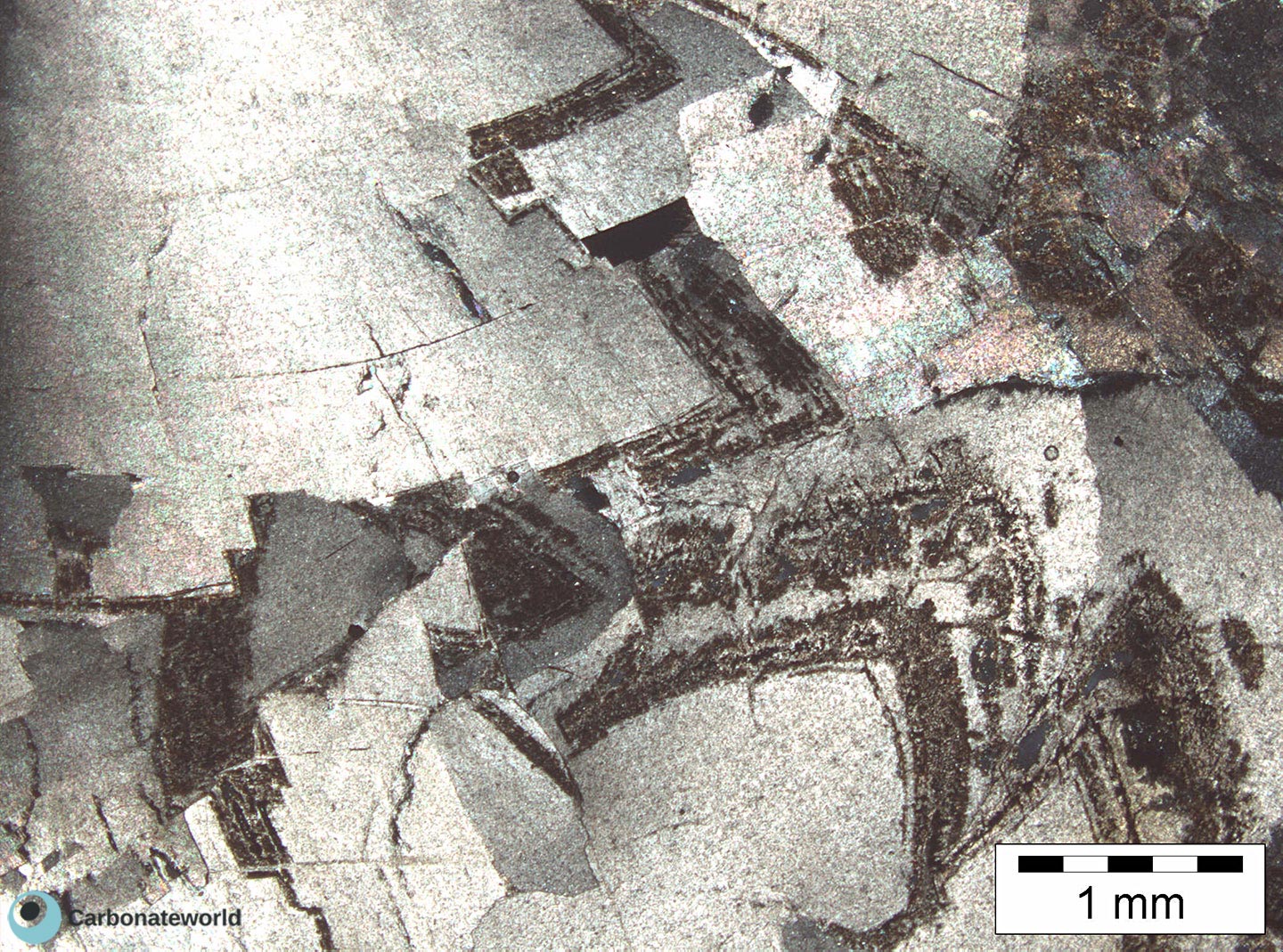
Dolomitization 1
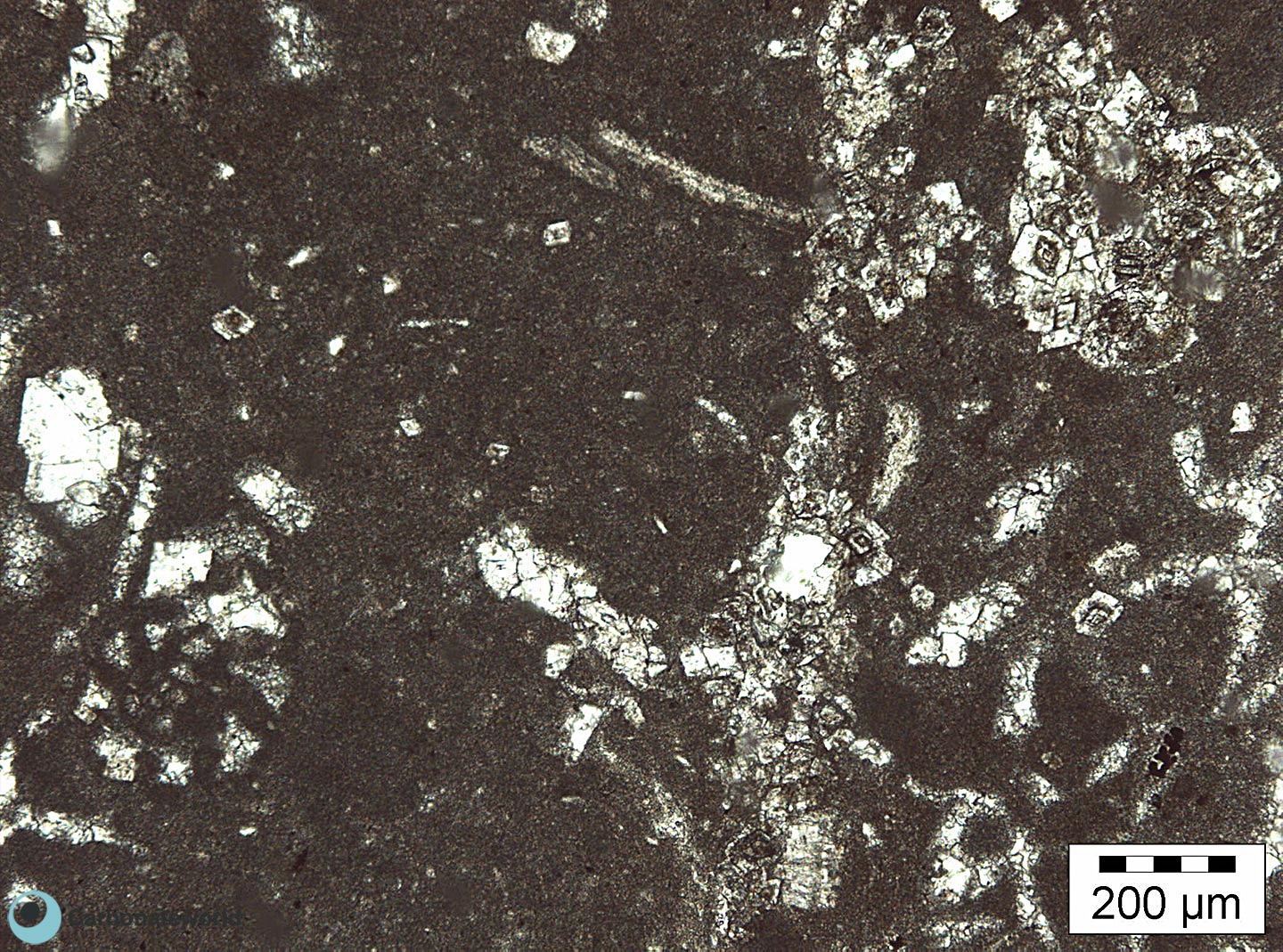
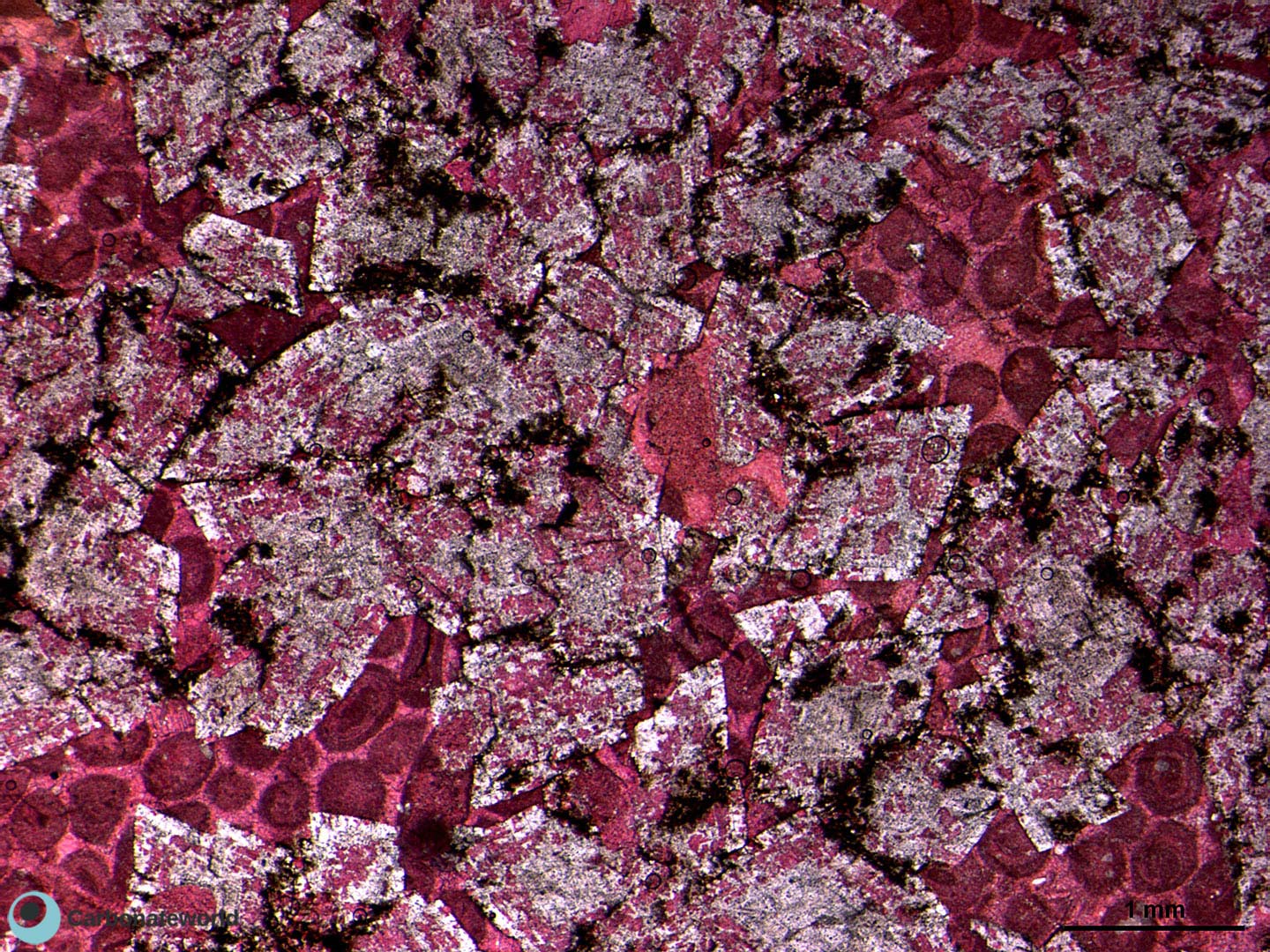
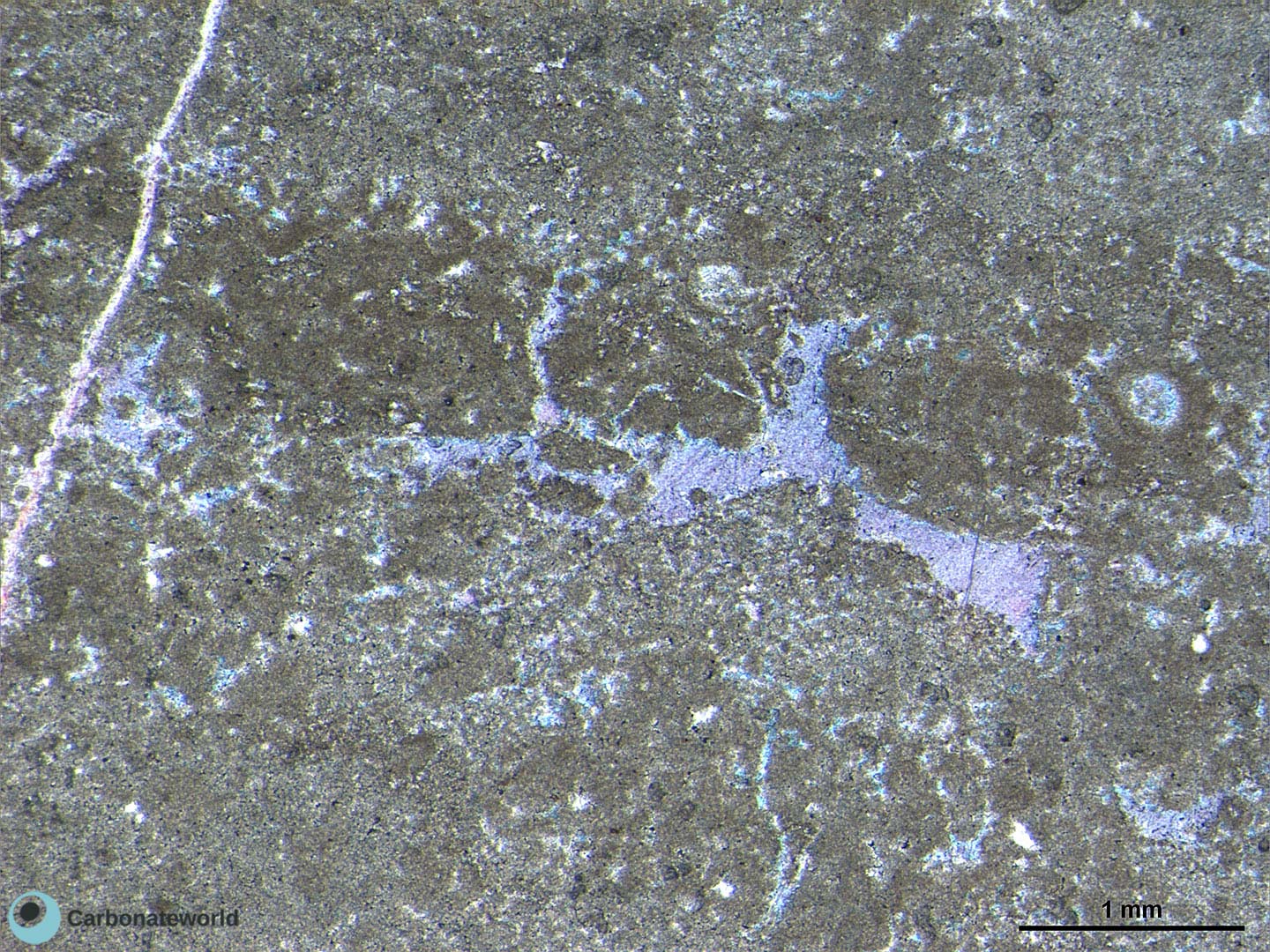
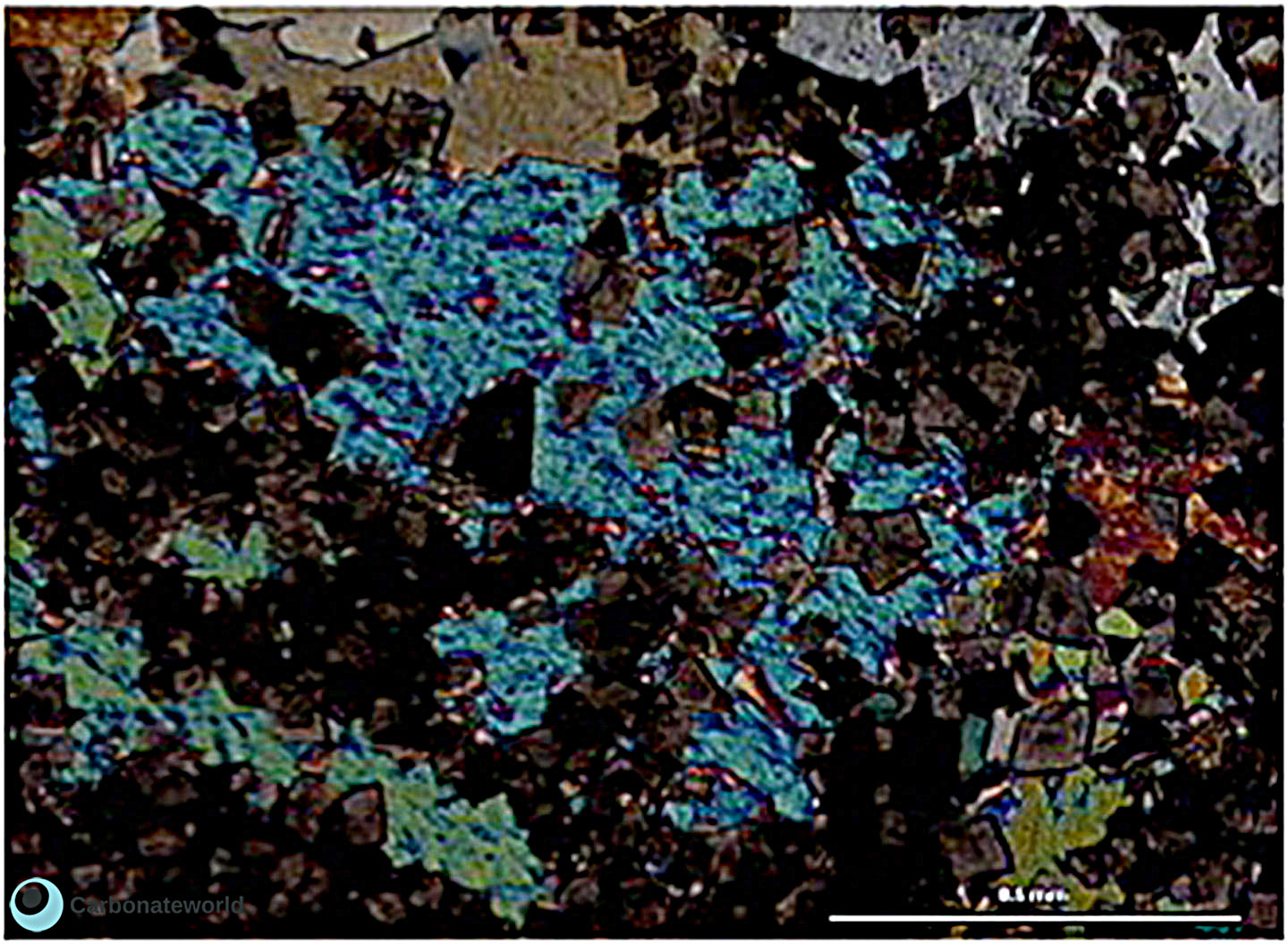
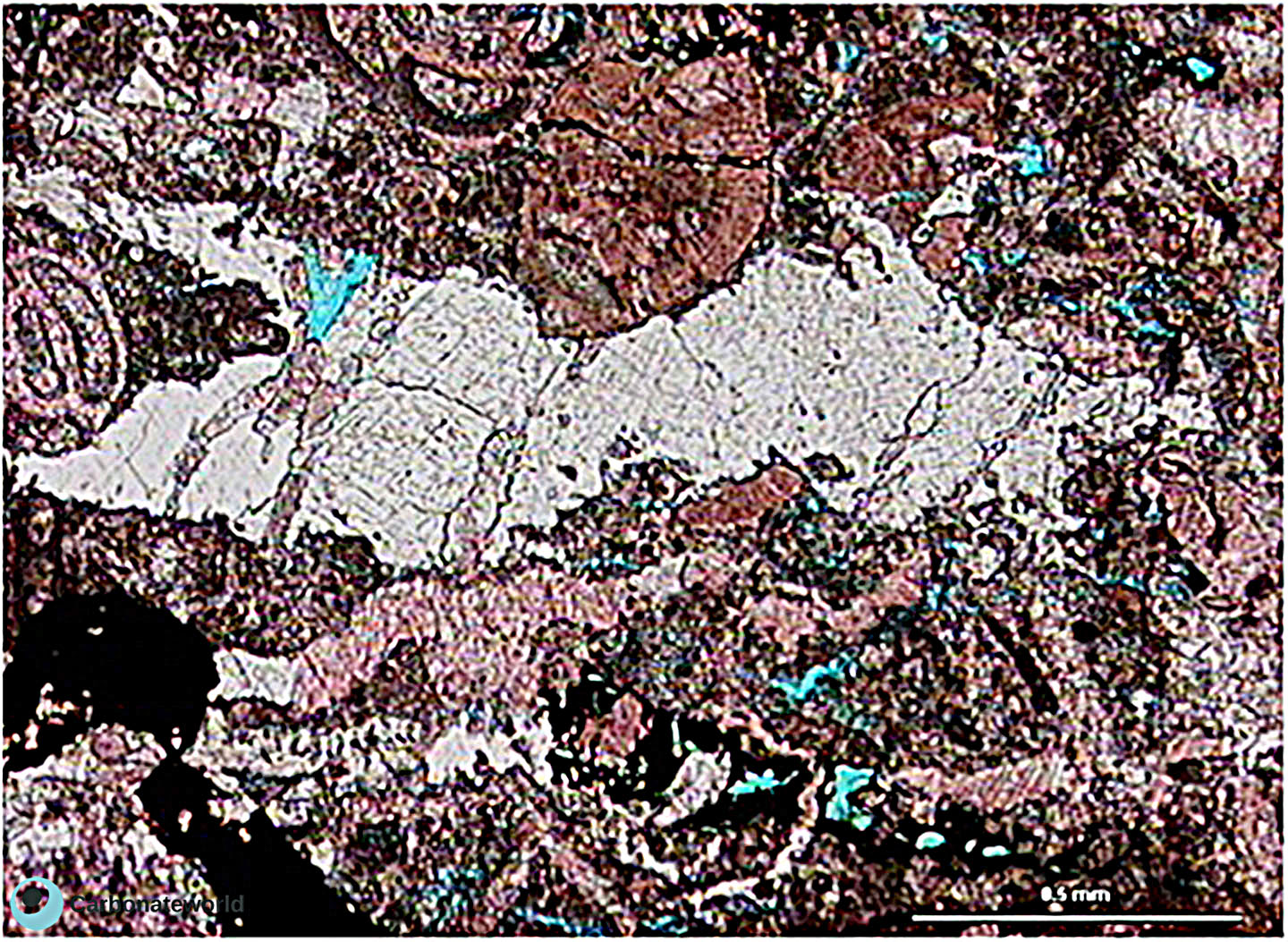
1. Euhedral Dolomite
Idiotopic mosaic (planar-e euhedral) of fabric replacive non selective dolomite (grey). The dolomite rhombic crystals are evident because unstained by alizarin red whereas the host rock is an ooidal grainstone stained in pink because it consists of non ferroan calcite. Burial ferroan calcite cement occludes the interparticle space (blue staining with K ferricyanide).
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
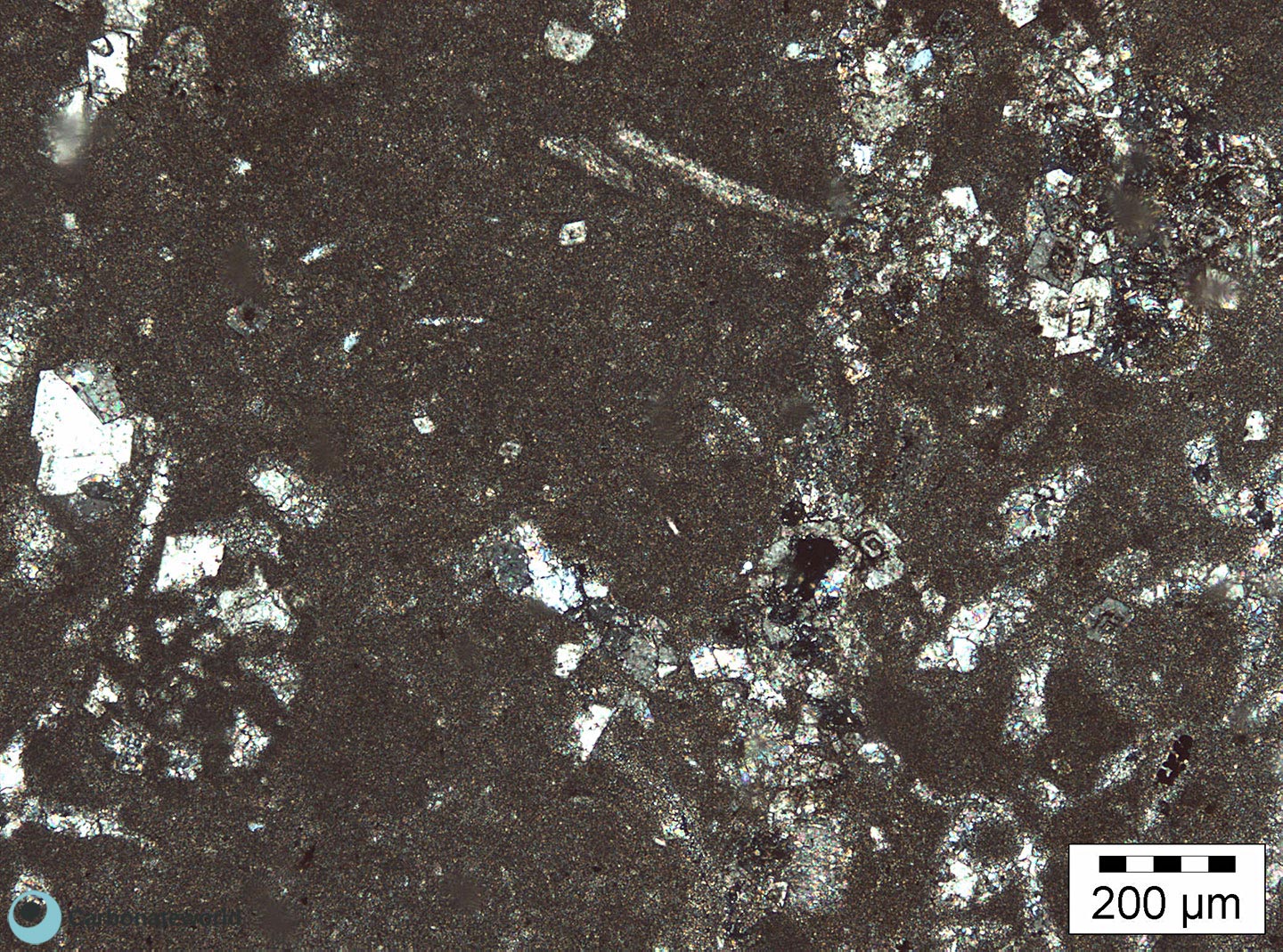
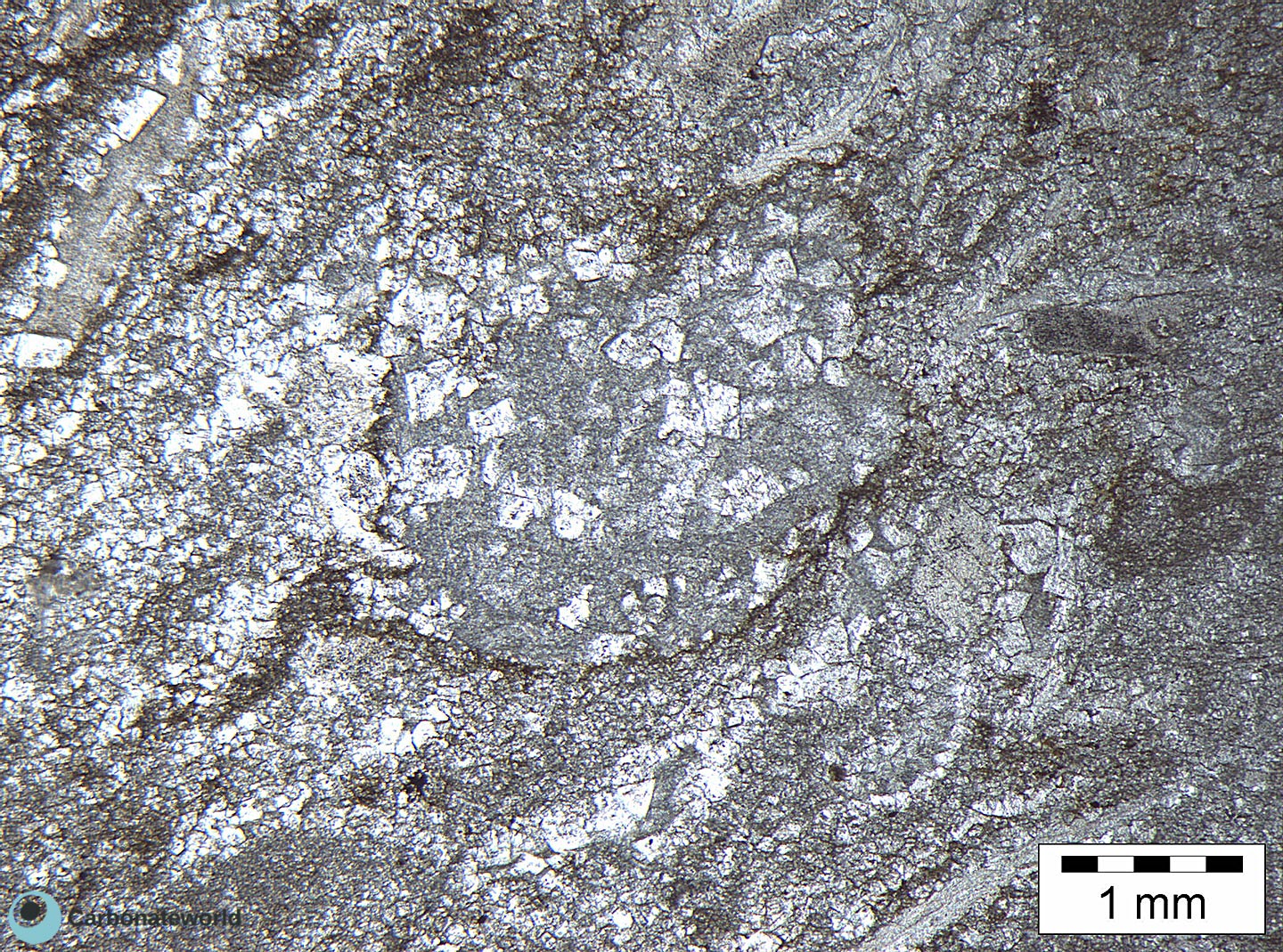
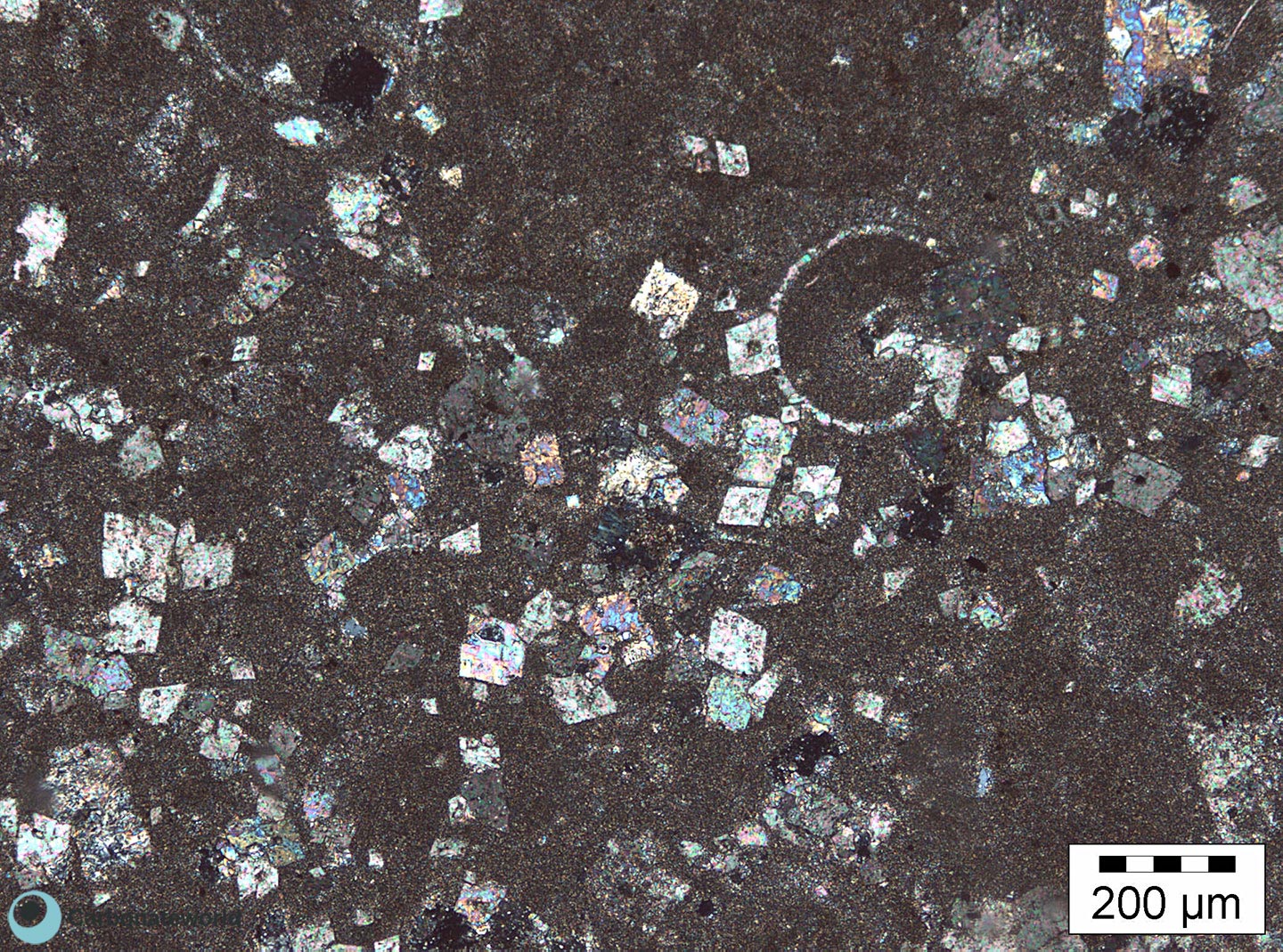
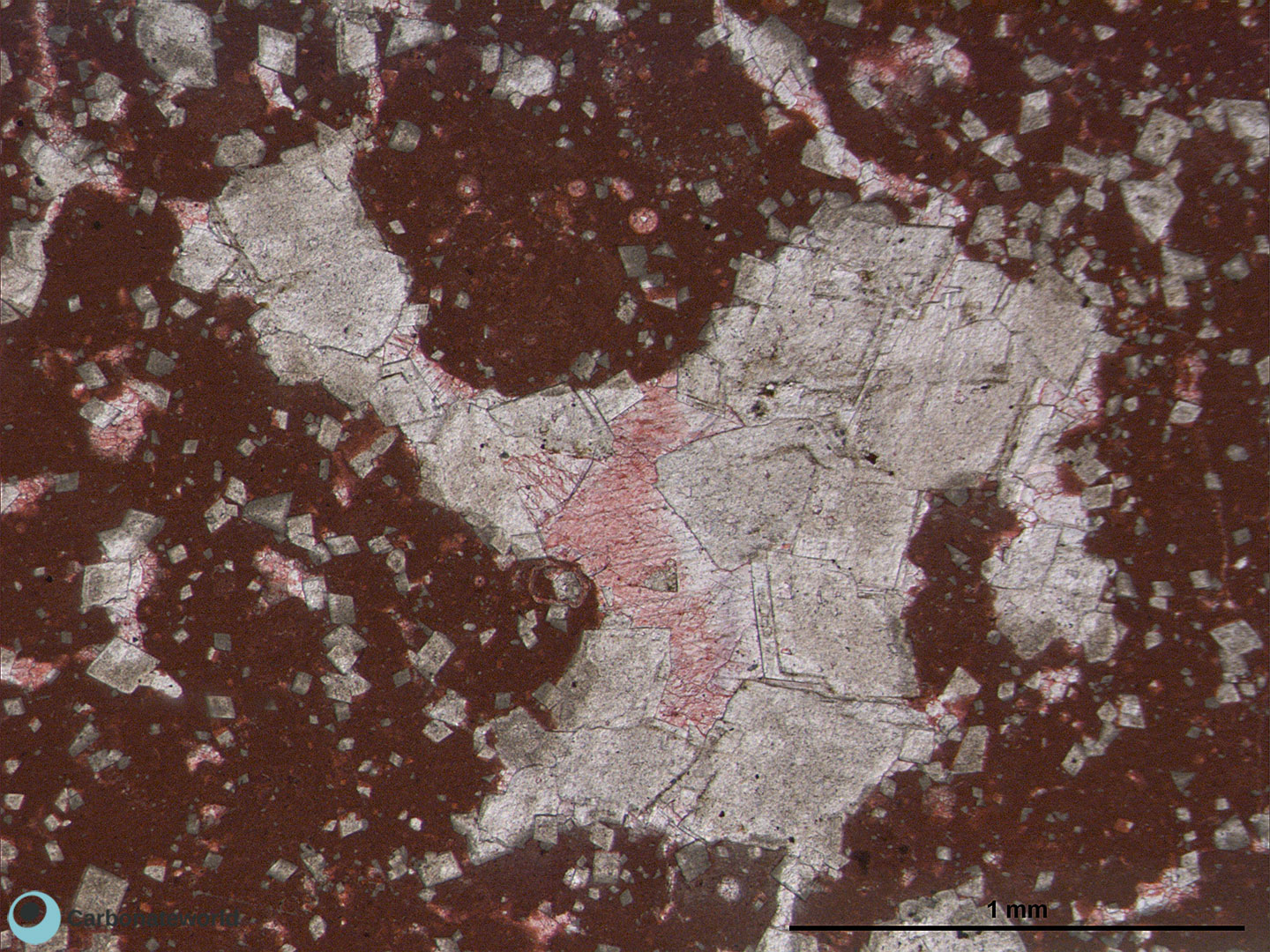
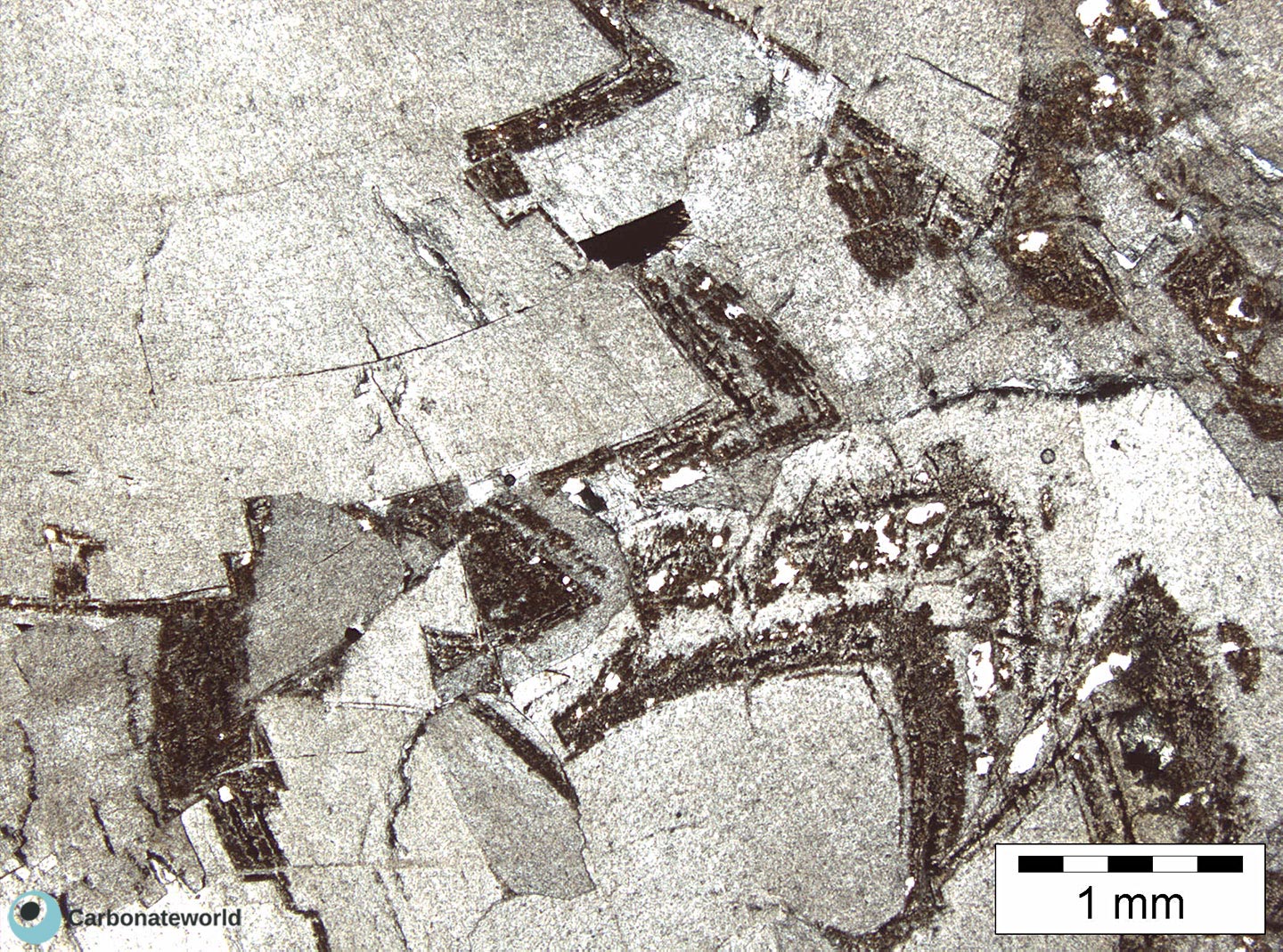
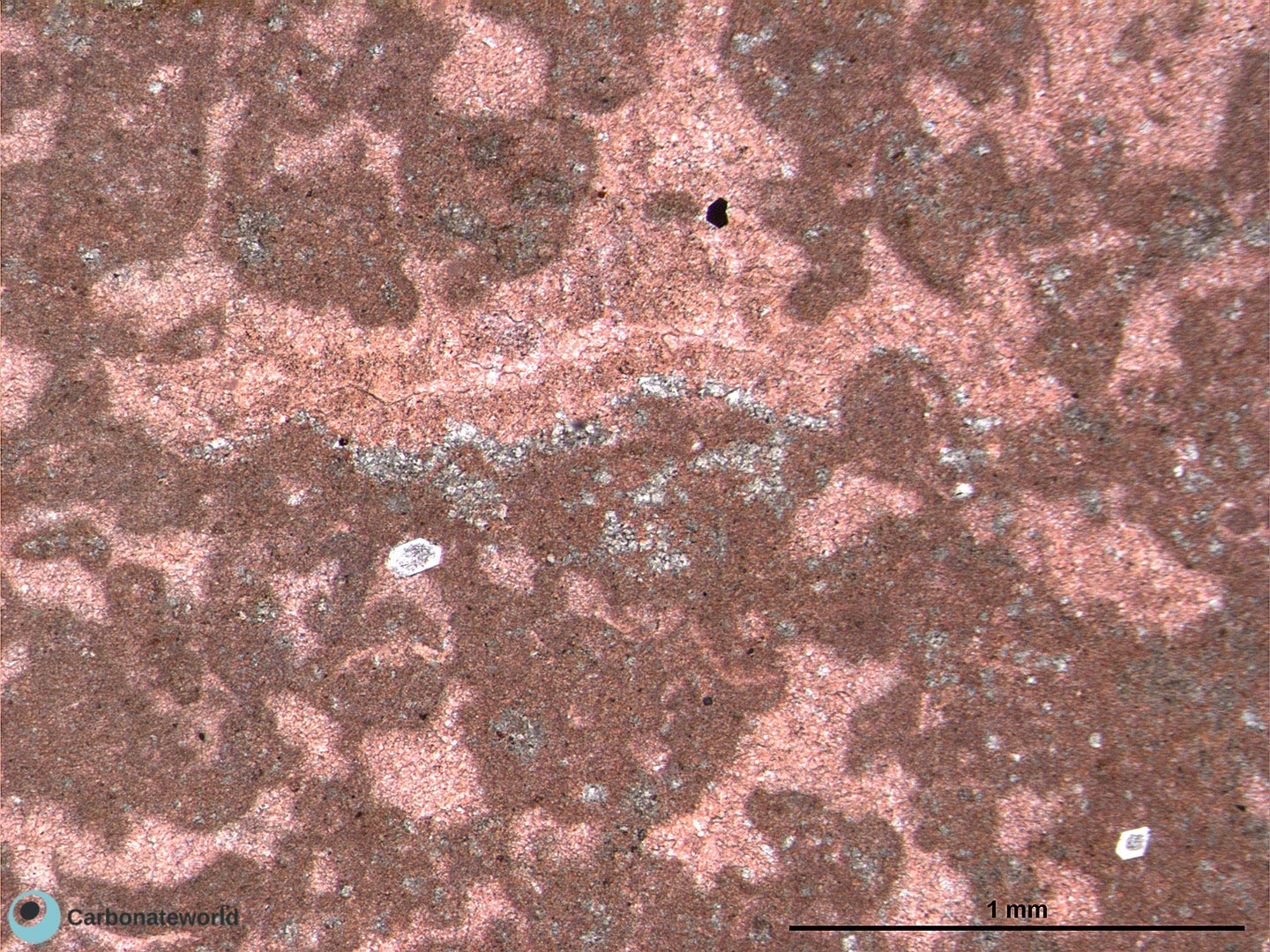
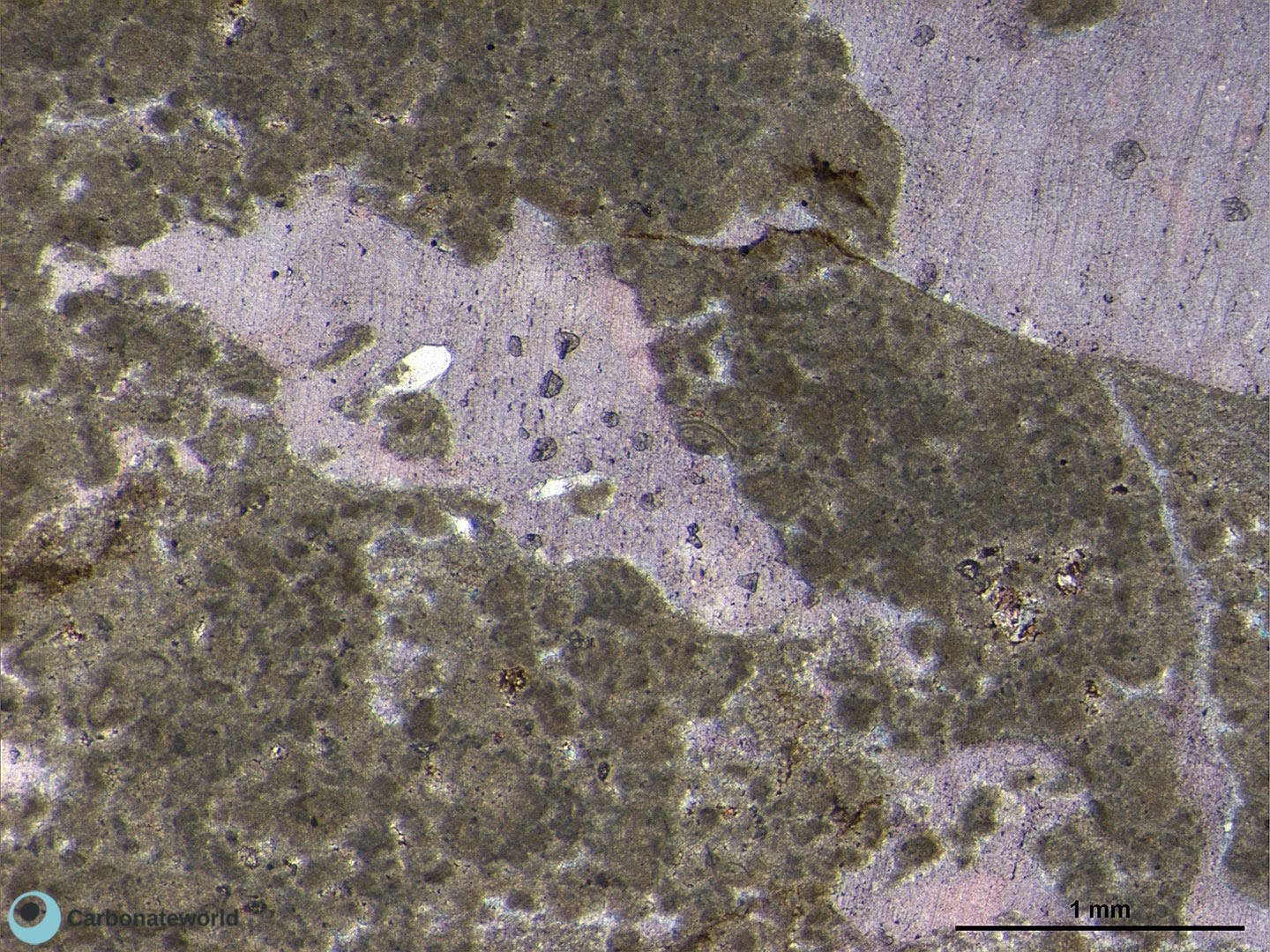
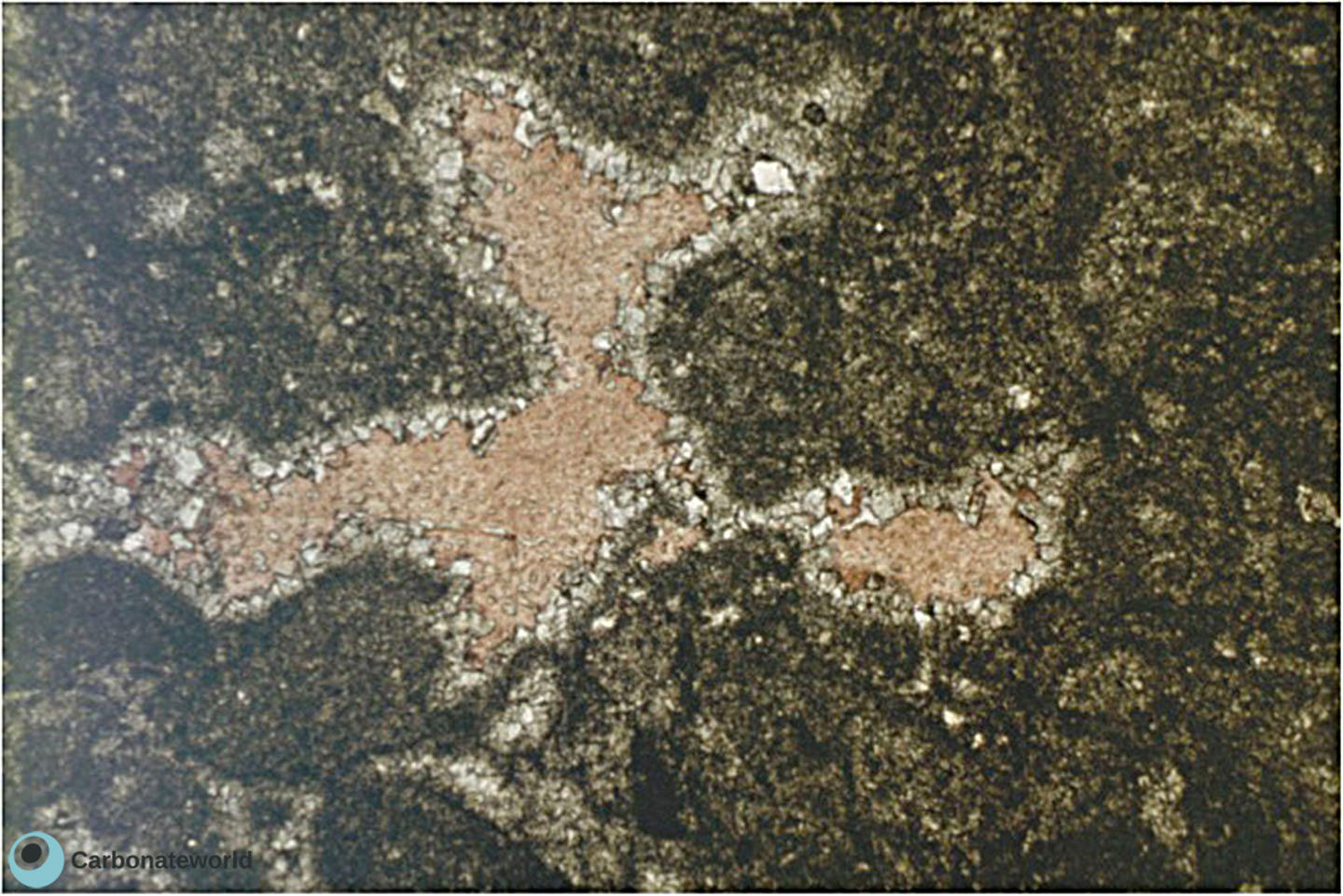
2. Dolomitization Timing
Detail of previous image with idiotopic mosaic (planar-e euhedral) of fabric replacive non selective dolomite (grey, unstained by alizarin red). The dolomite rhombs appear broken where they had developed at grain contact. Dolomitization seems to have occurred before burial mechanical compaction.
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
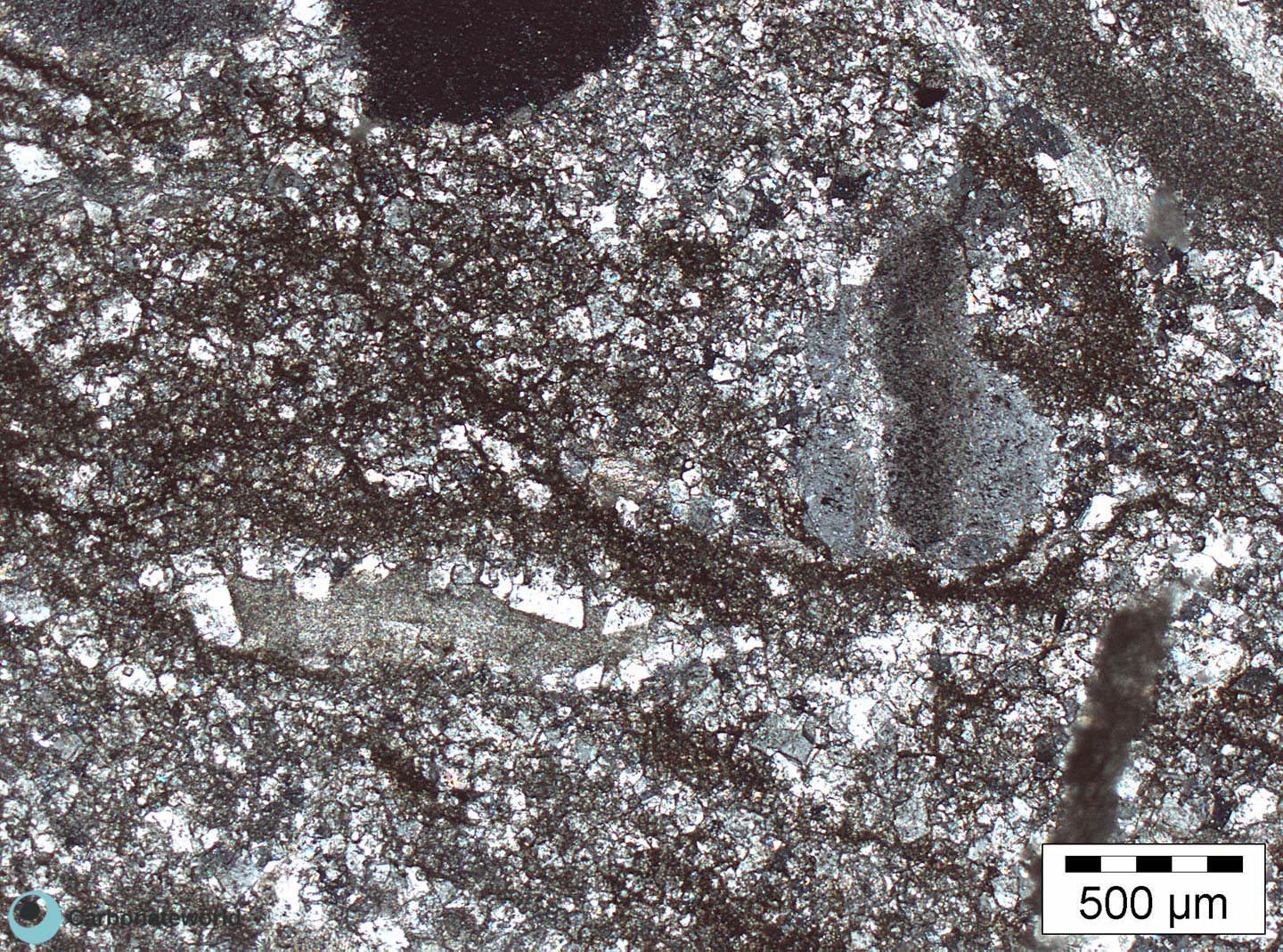
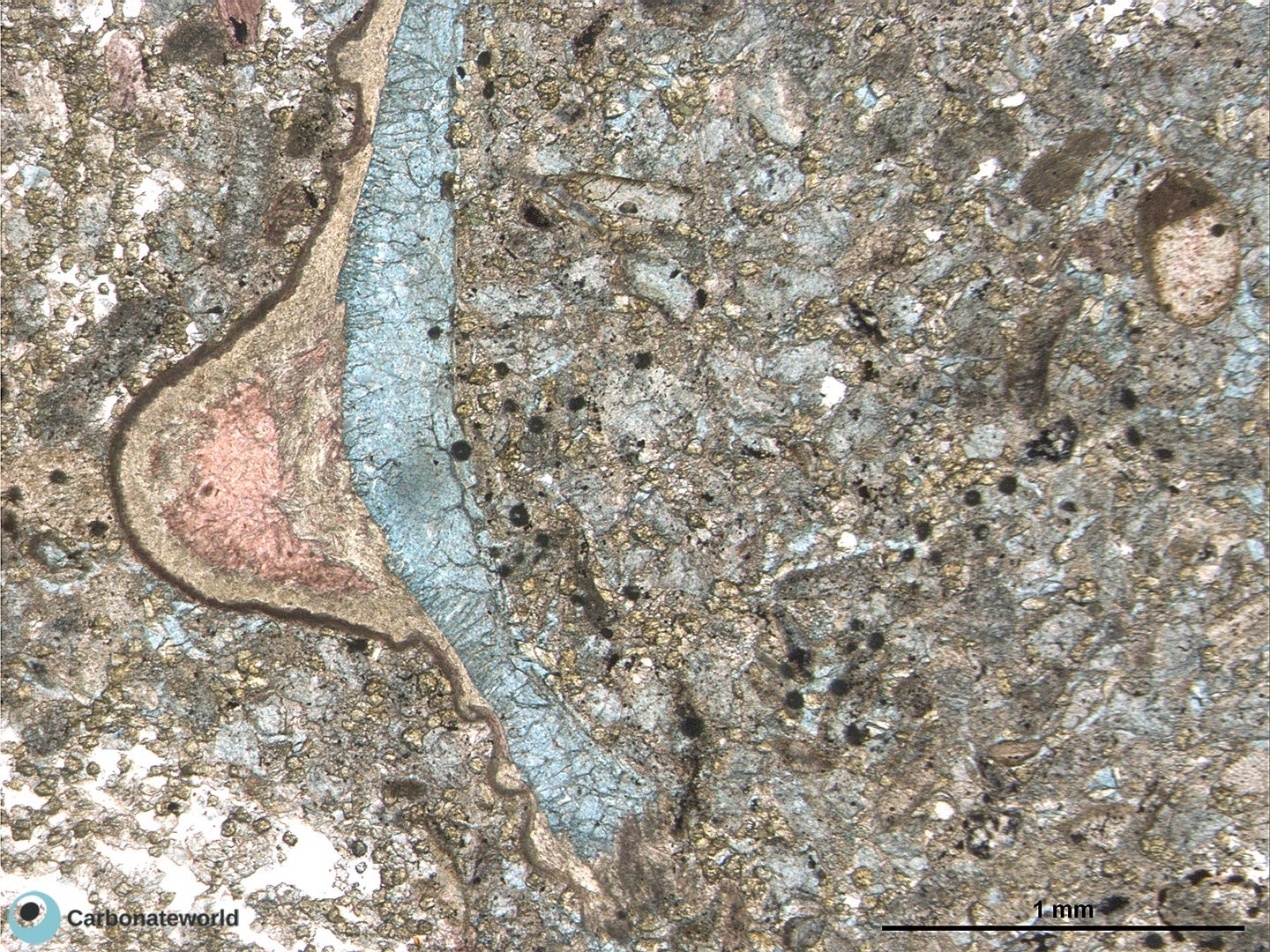
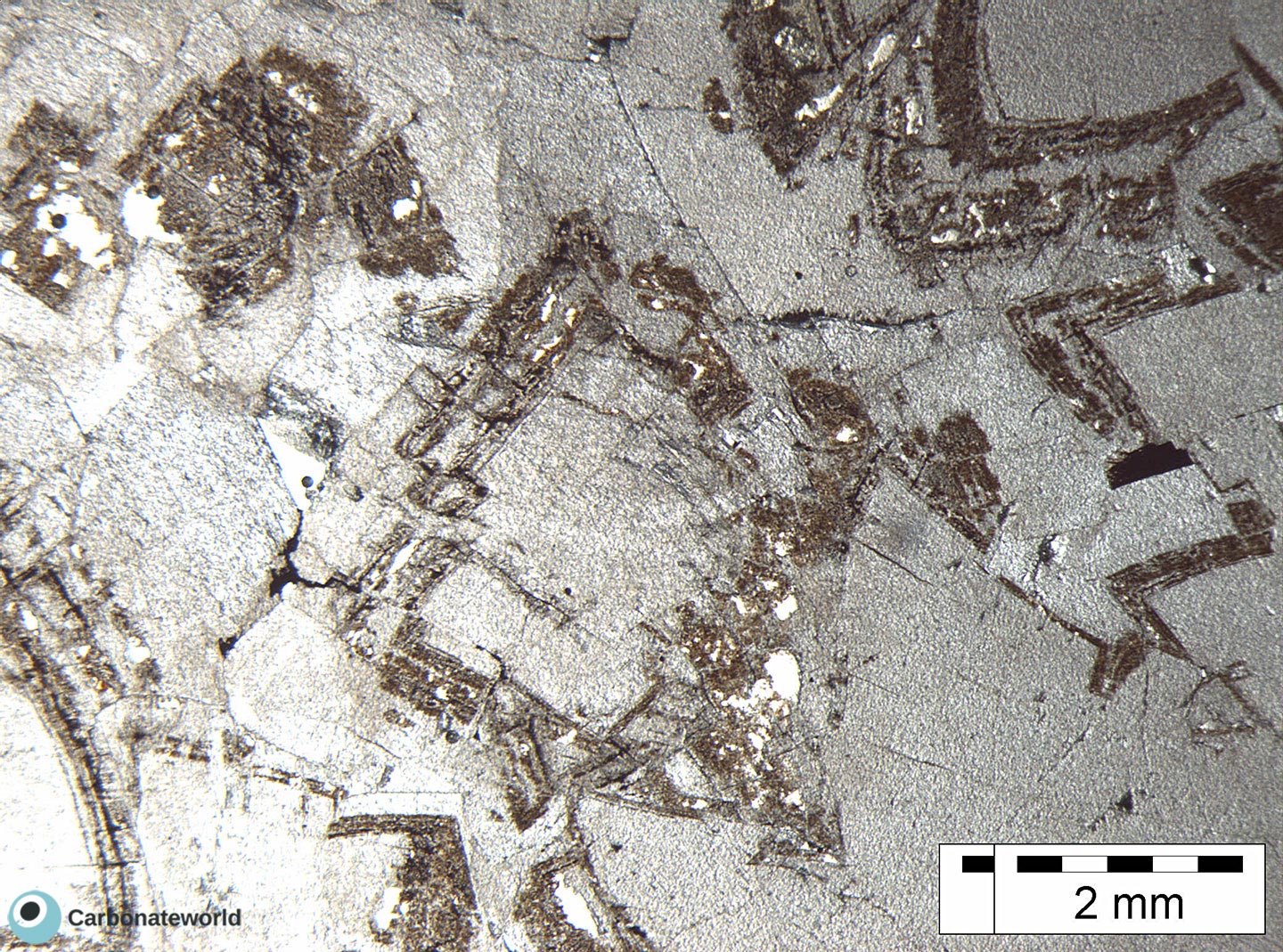
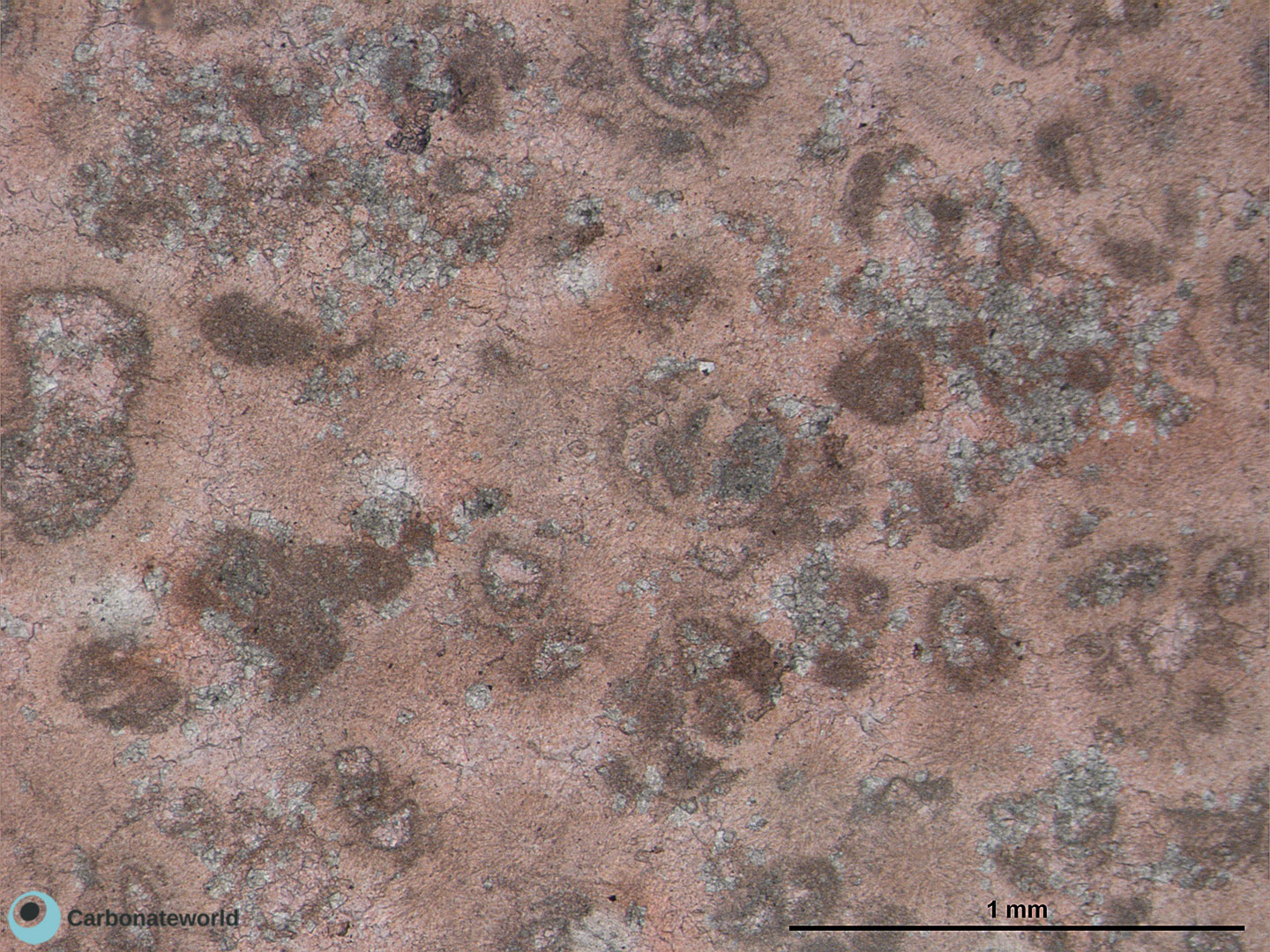
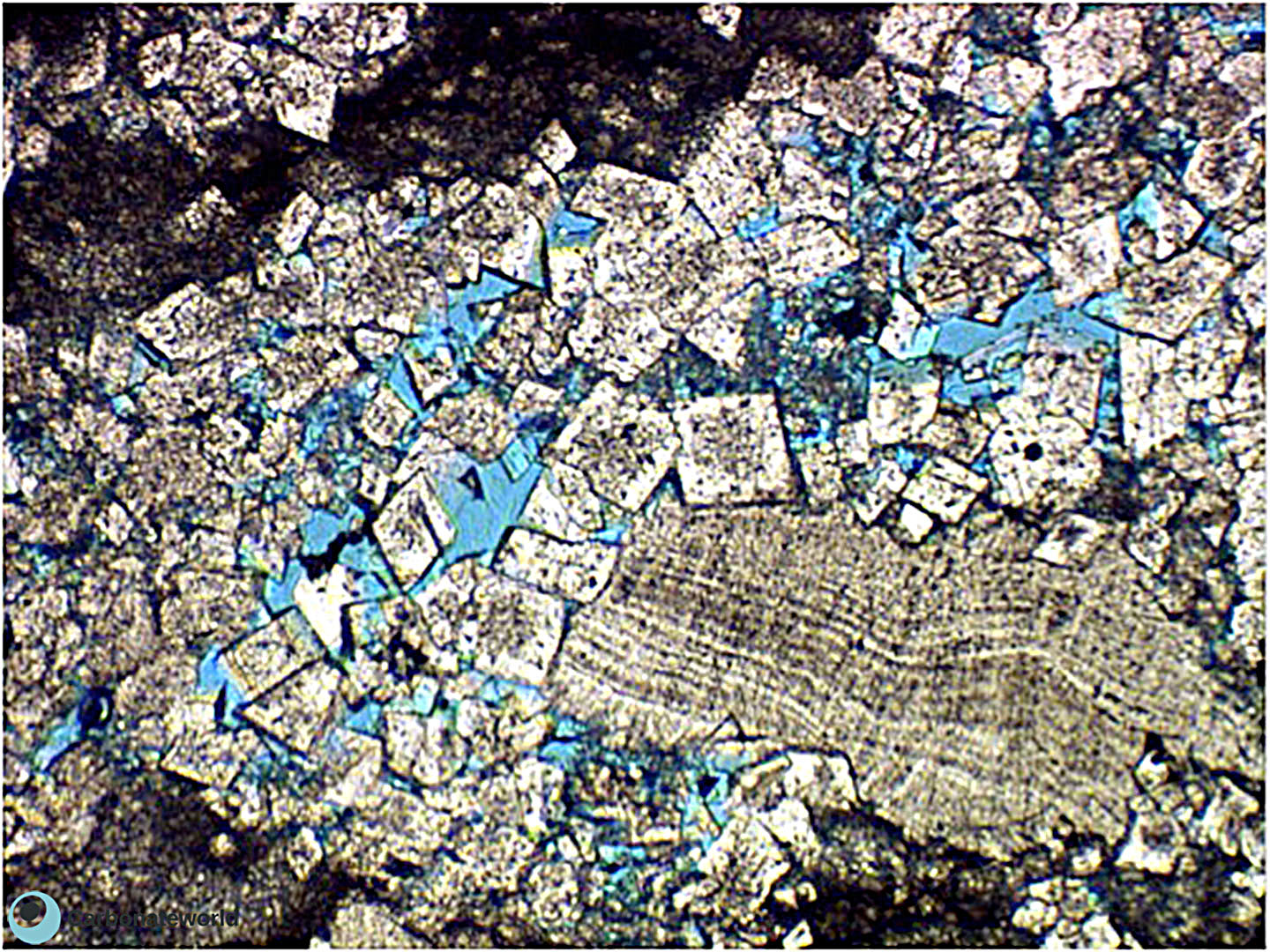
3. Zoned Dolomite
Idiotopic mosaic (planar-e euhedral) of fabric replacive non selective dolomite (grey). Burial ferroan calcite cement occludes the interparticle space (blue staining with K ferricyanide) and precipitated following an irregular rim of non ferroan equant calcite of possible meteoric phreatic origin. Dolomite rhombs show zoned subparallel growth line with likely variable composition.
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
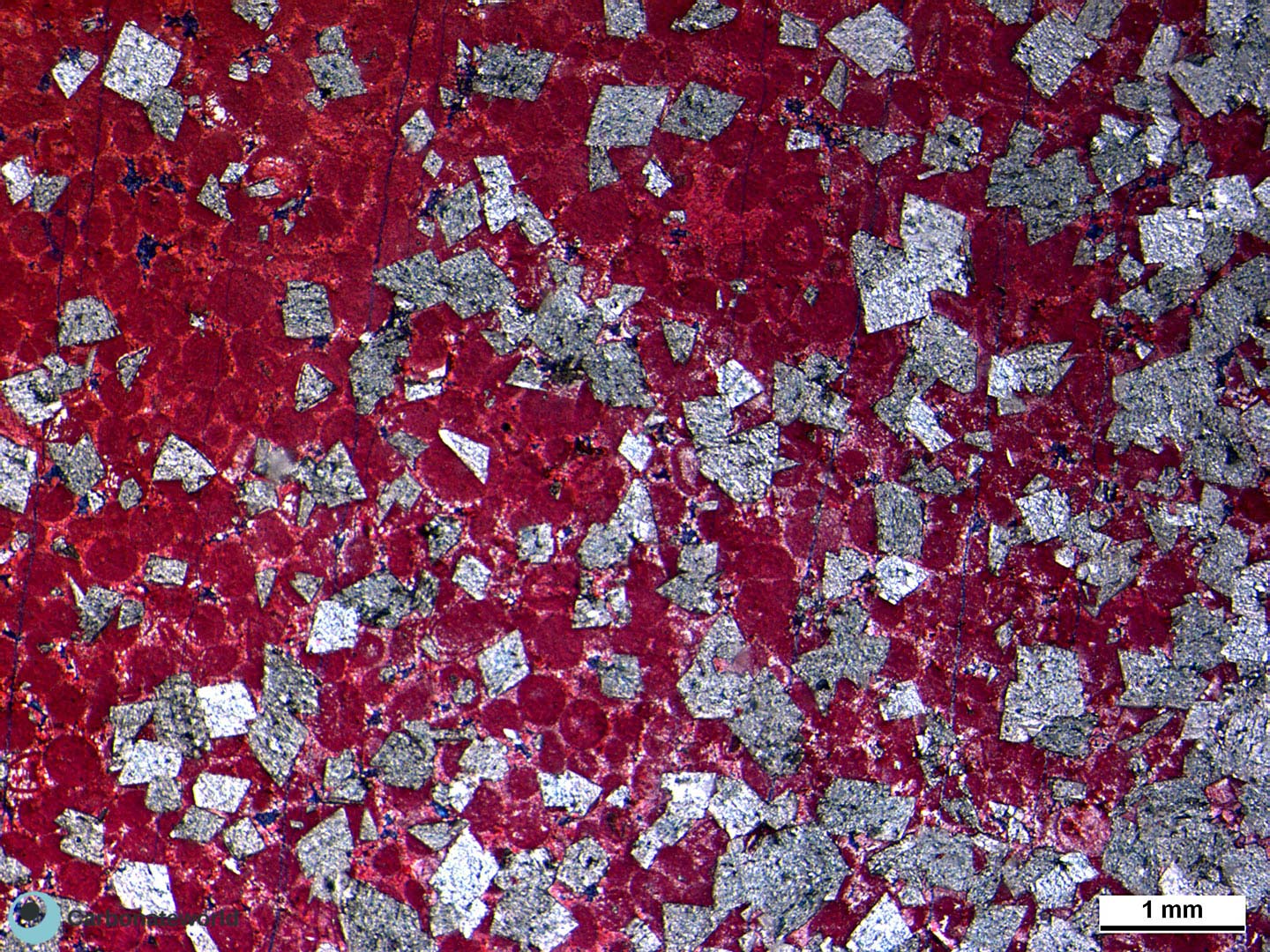
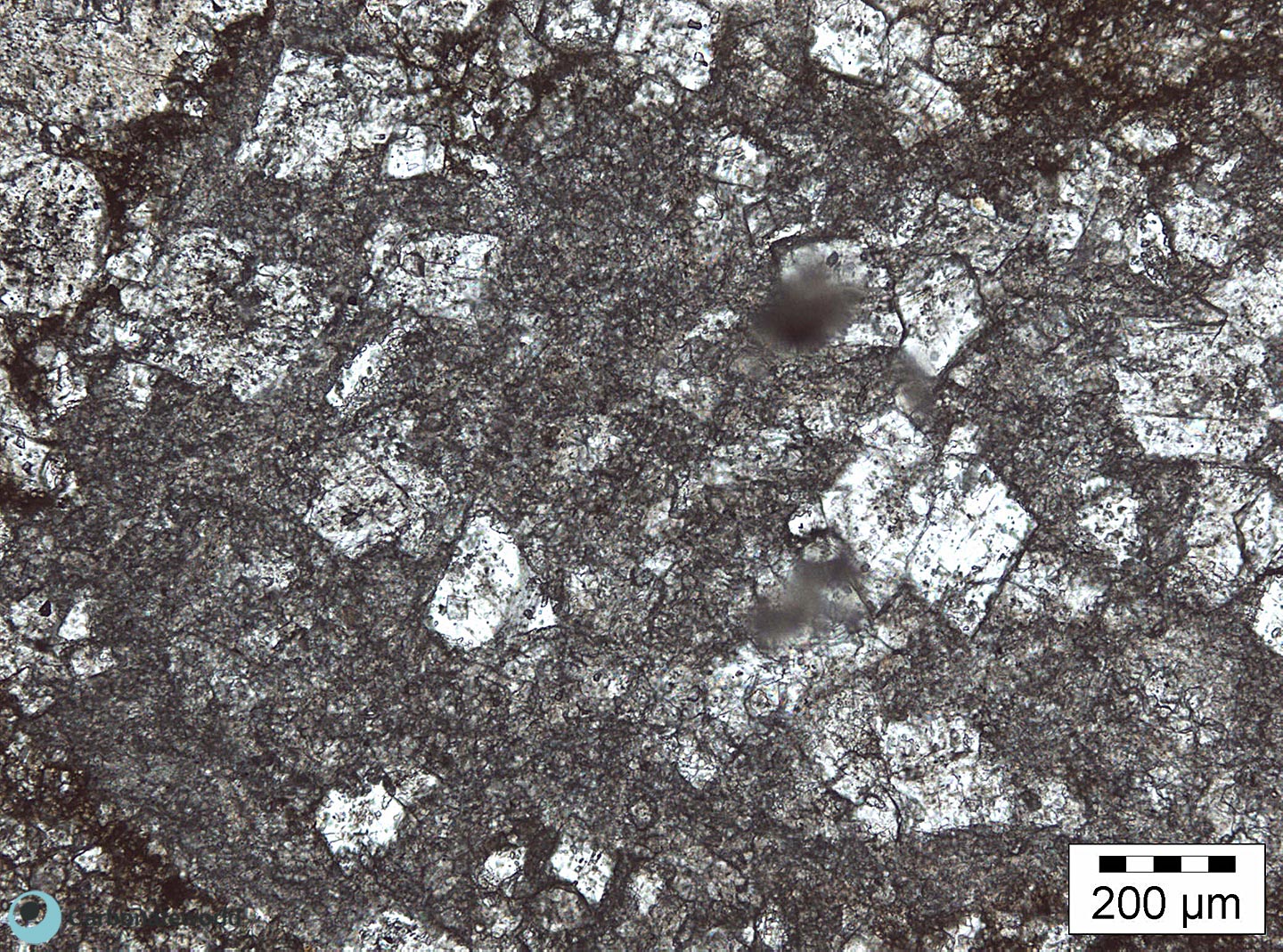
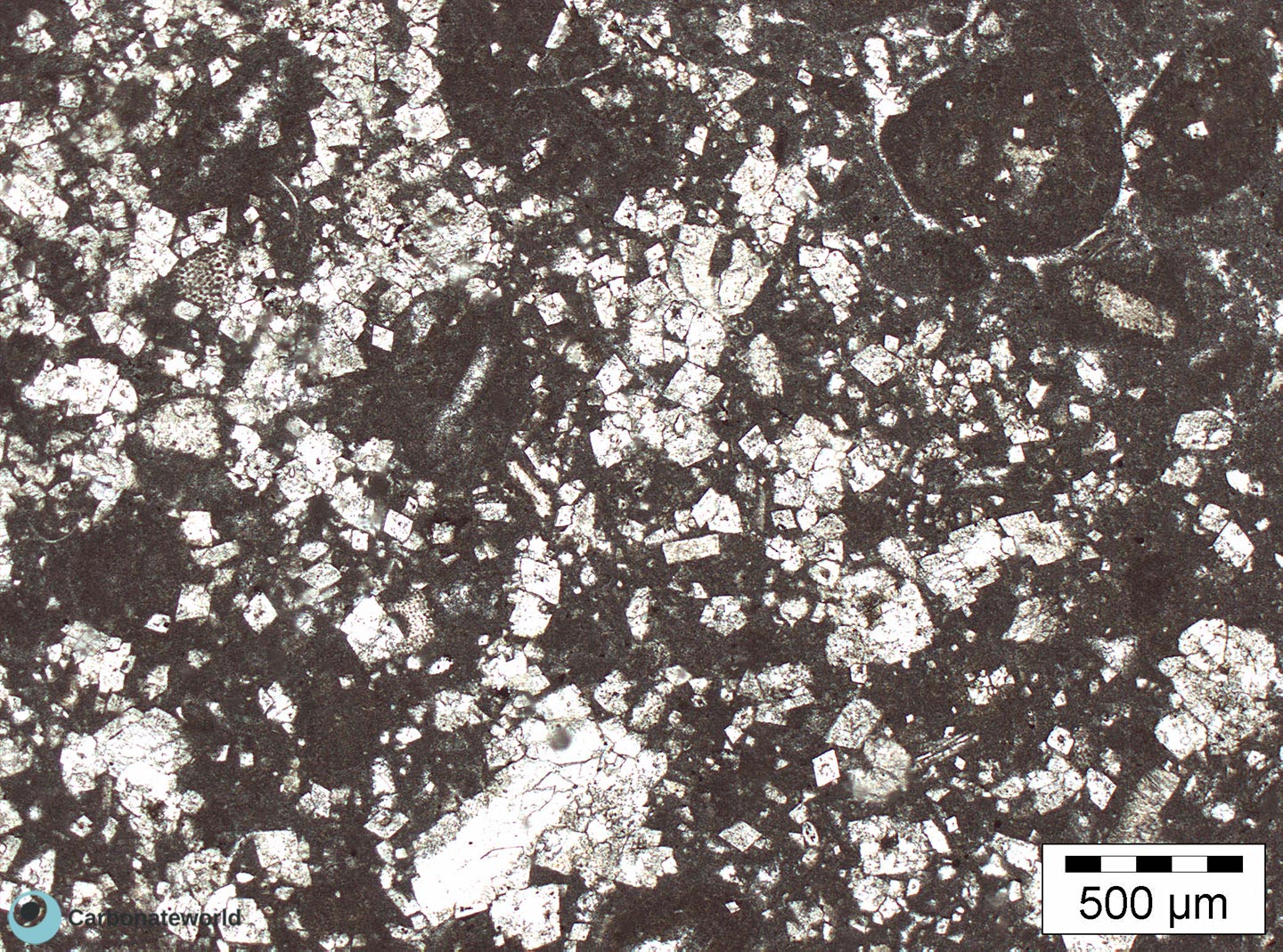
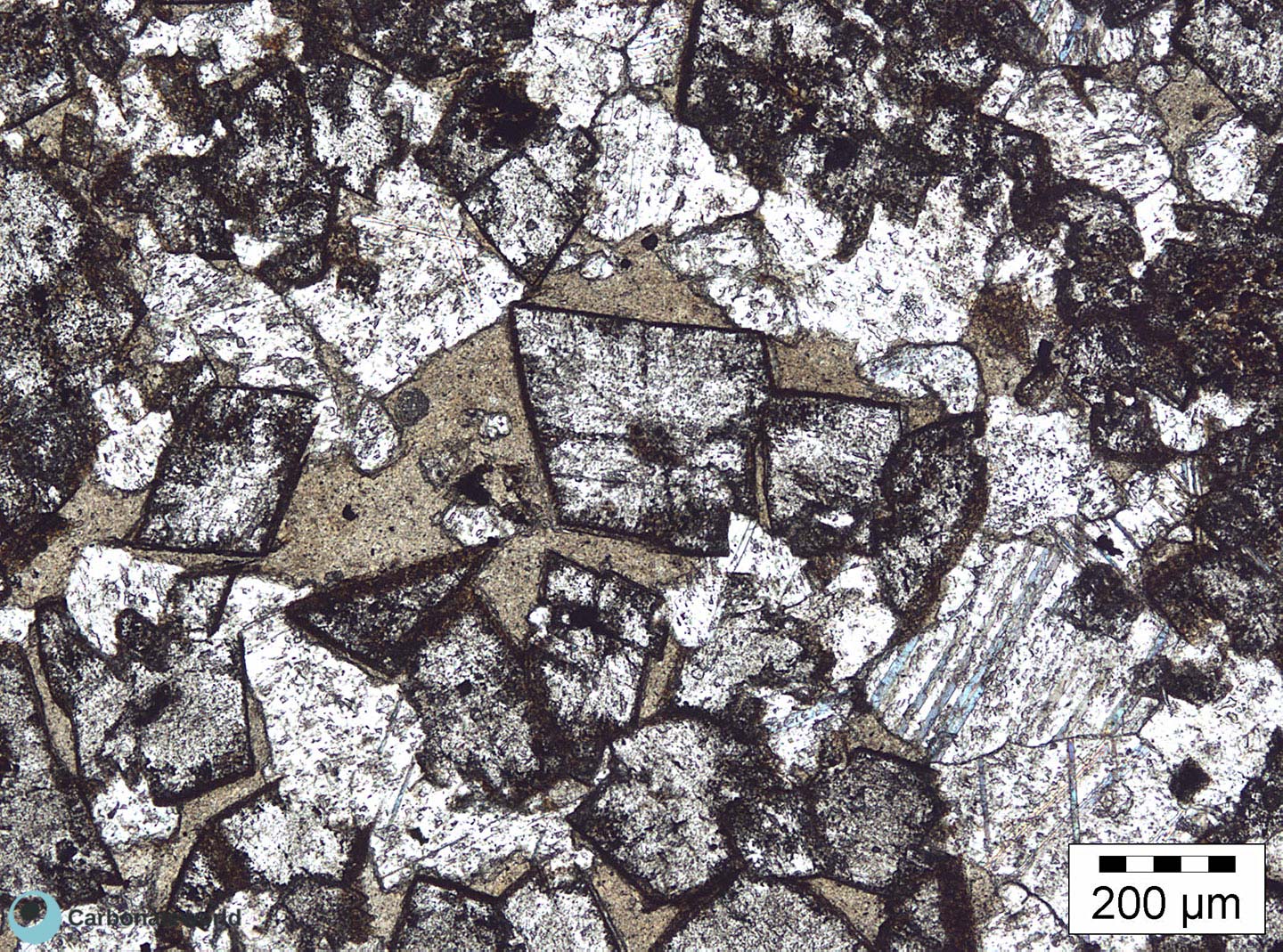
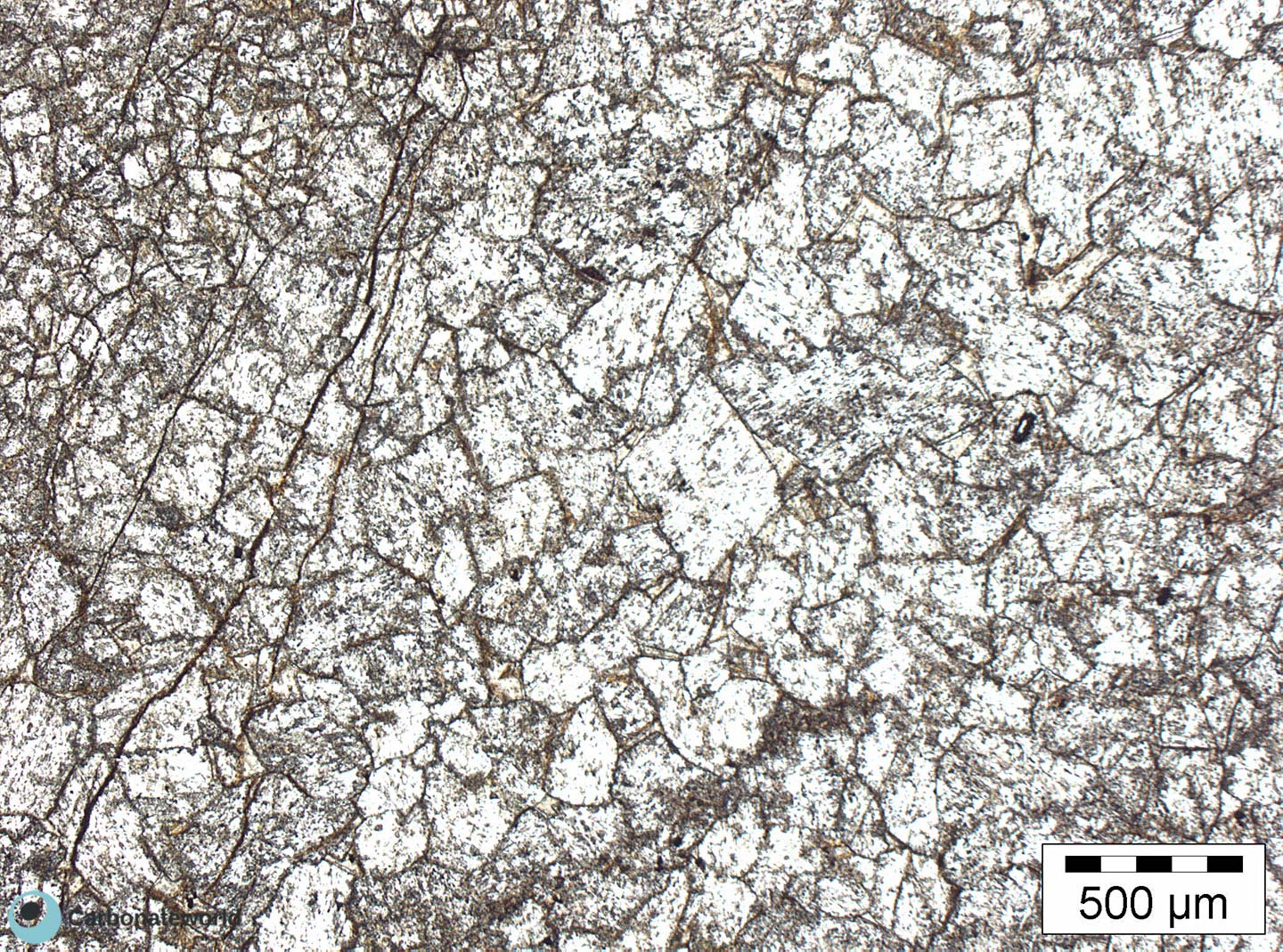
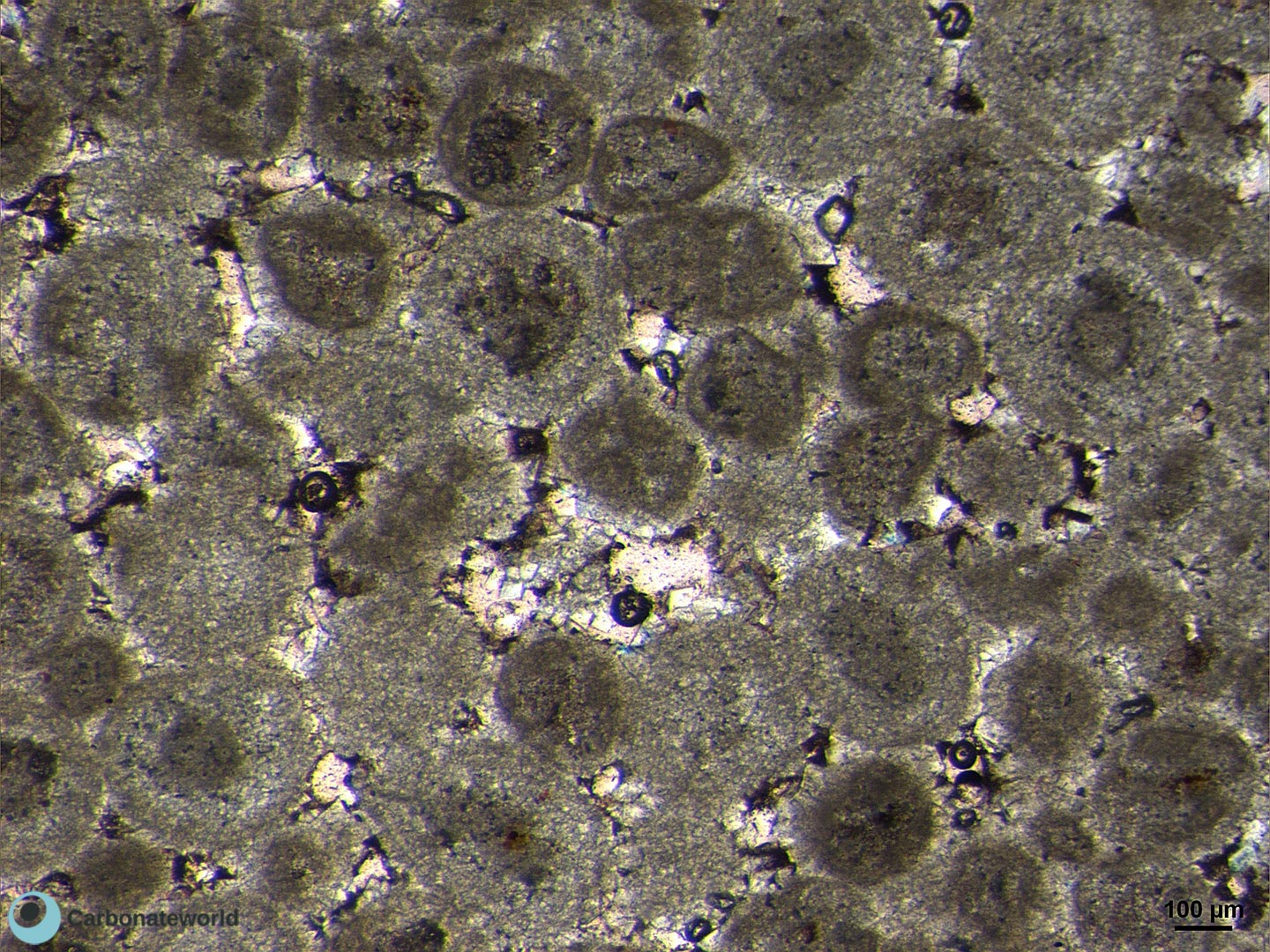
4. Euhedral/Subhedral Dolomite
Idiotopic to hypidiotopic mosaic (planar-e to planar-s) of fabric replacive non selective dolomite (grey). The dolomite rhombs are evident because unstained by alizarin red whereas the host rock is an ooidal grainstone stained in pink because it consists of non ferroan calcite.
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
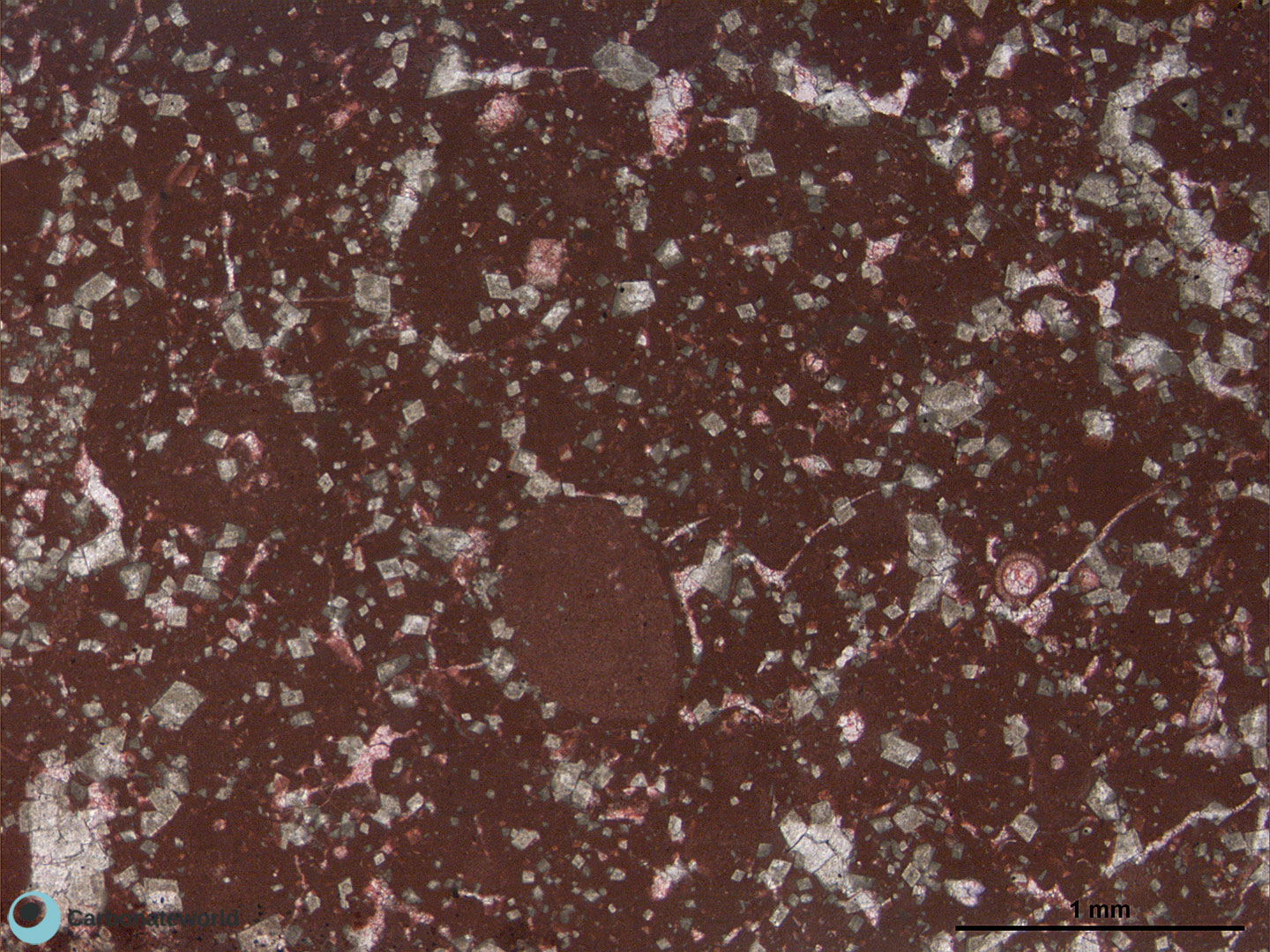
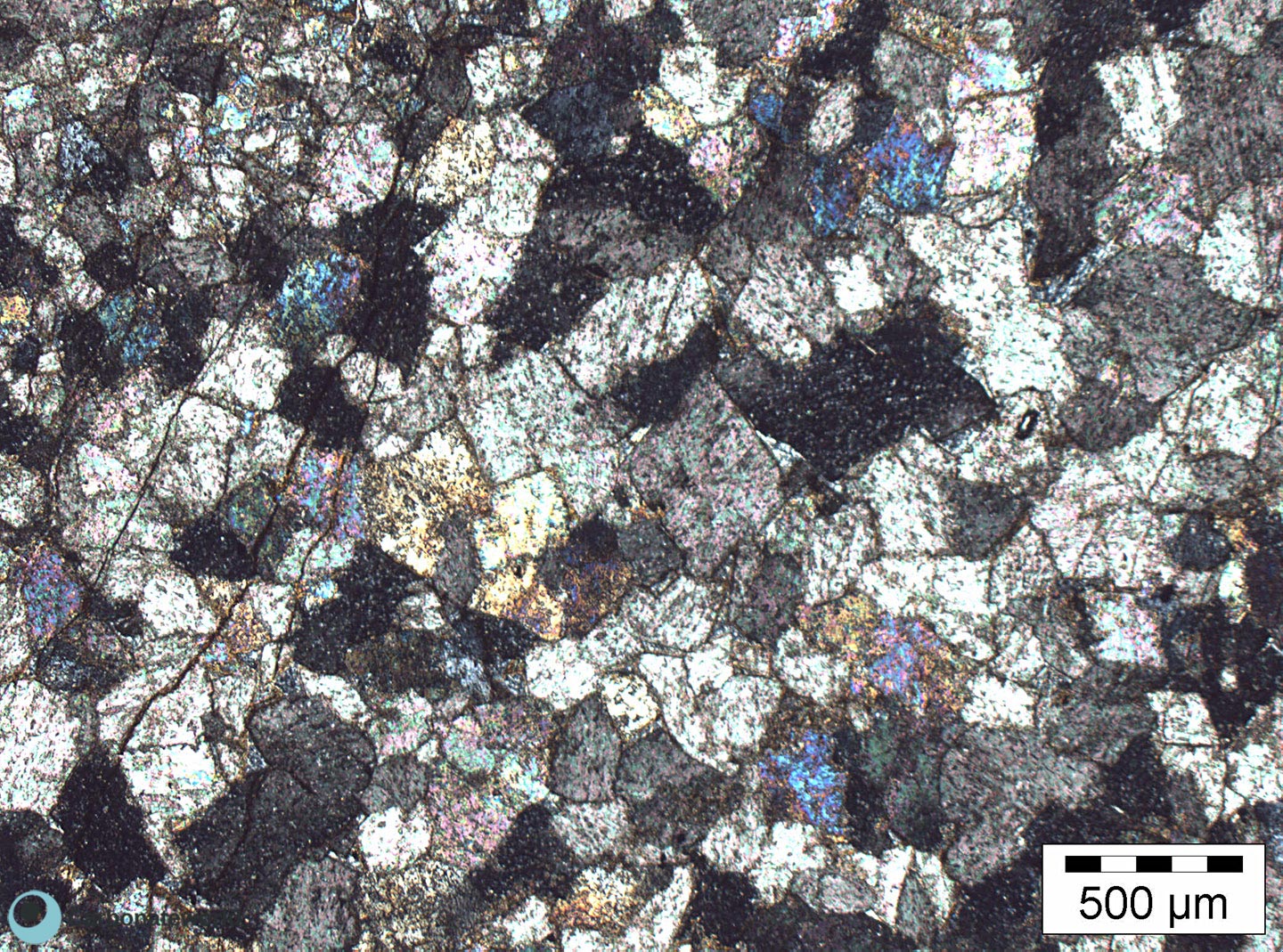
5. Subhedral Dolomite
Hypidiotopic mosaic (planar-s subhedral) of fabric replacive non selective dolomite (grey). The dolomite rhombs are evident because unstained by alizarin red whereas the host rock is an ooidal grainstone stained in pink because of its non ferroan calcite composition.
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
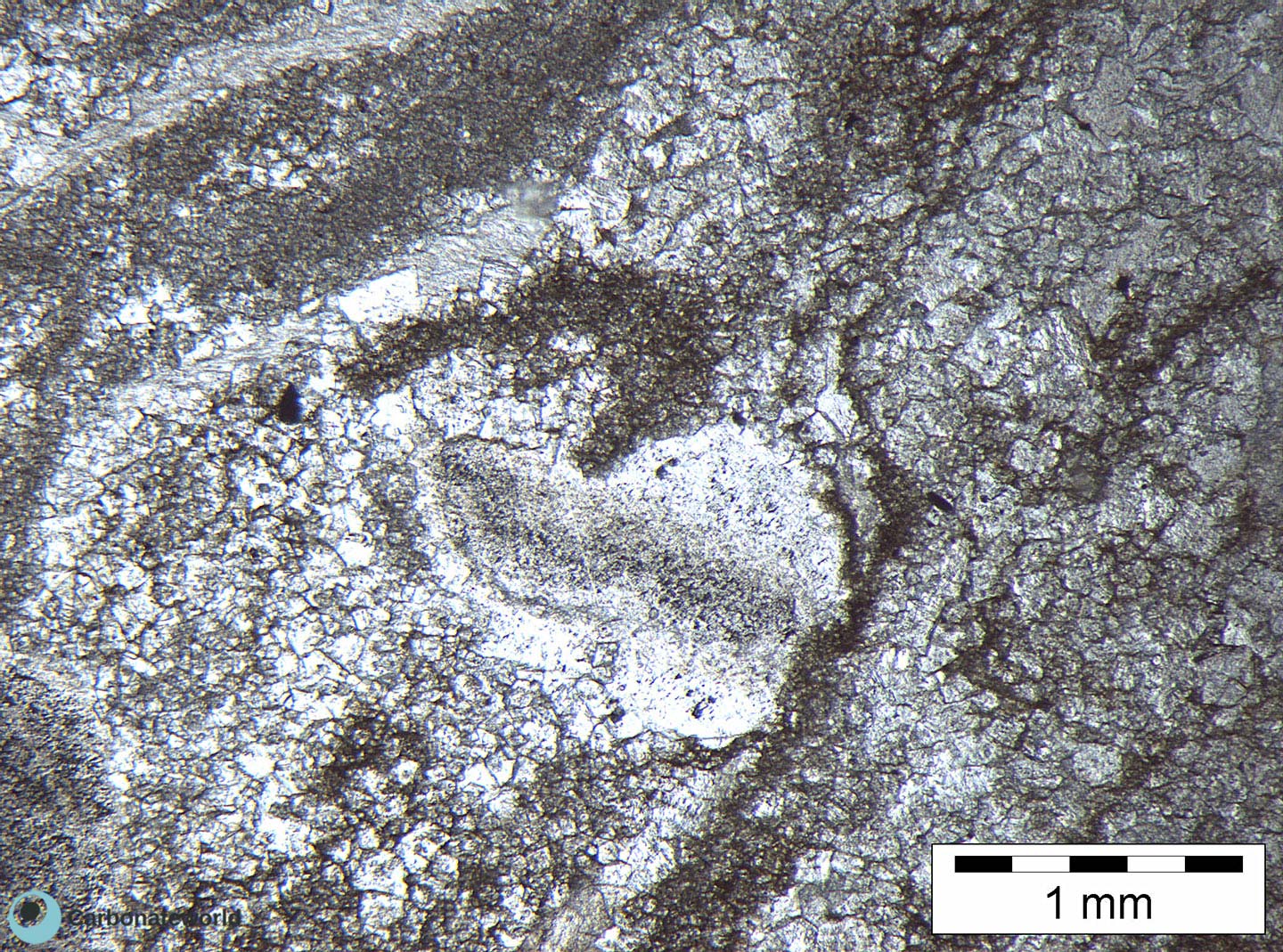
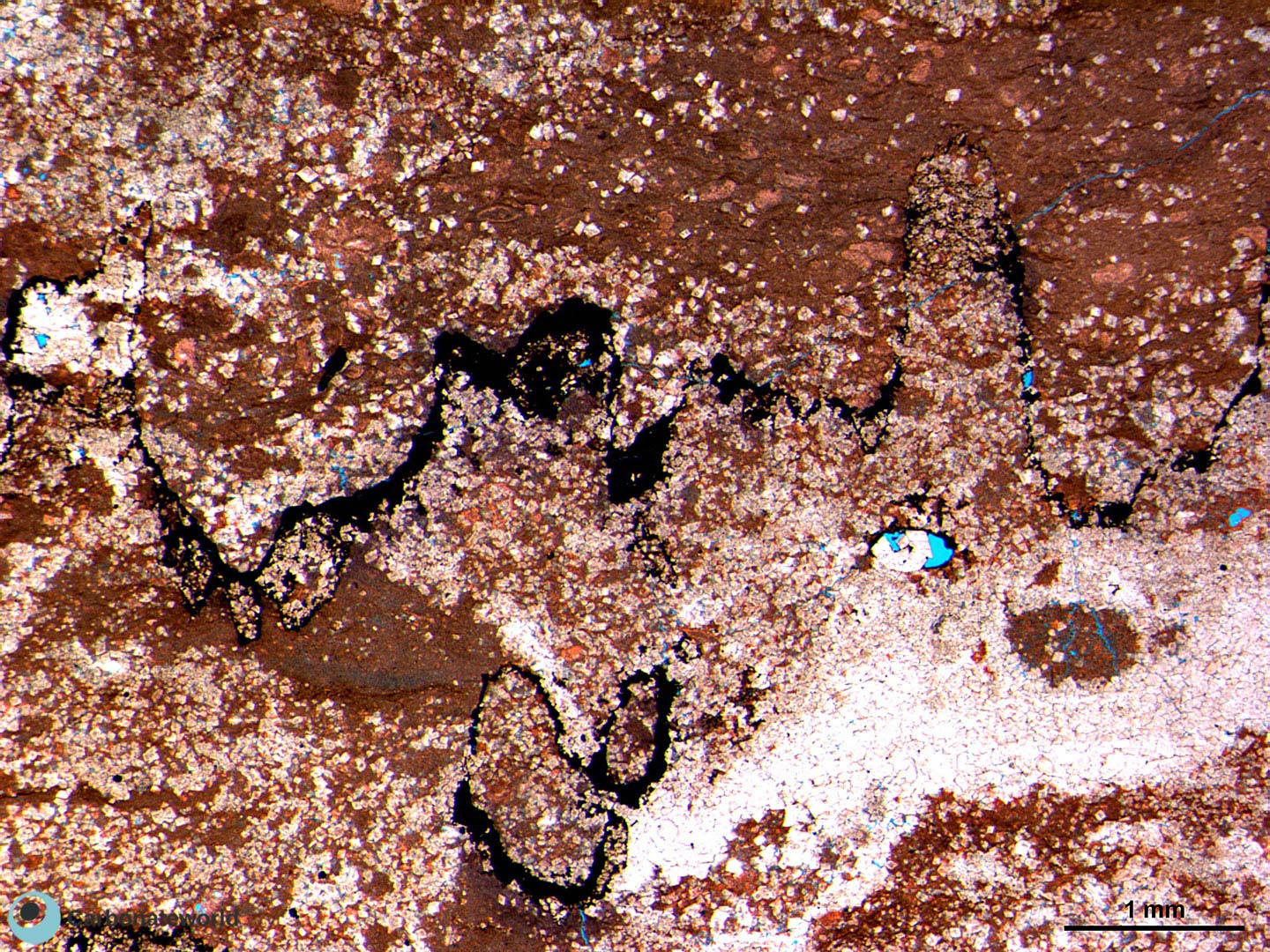
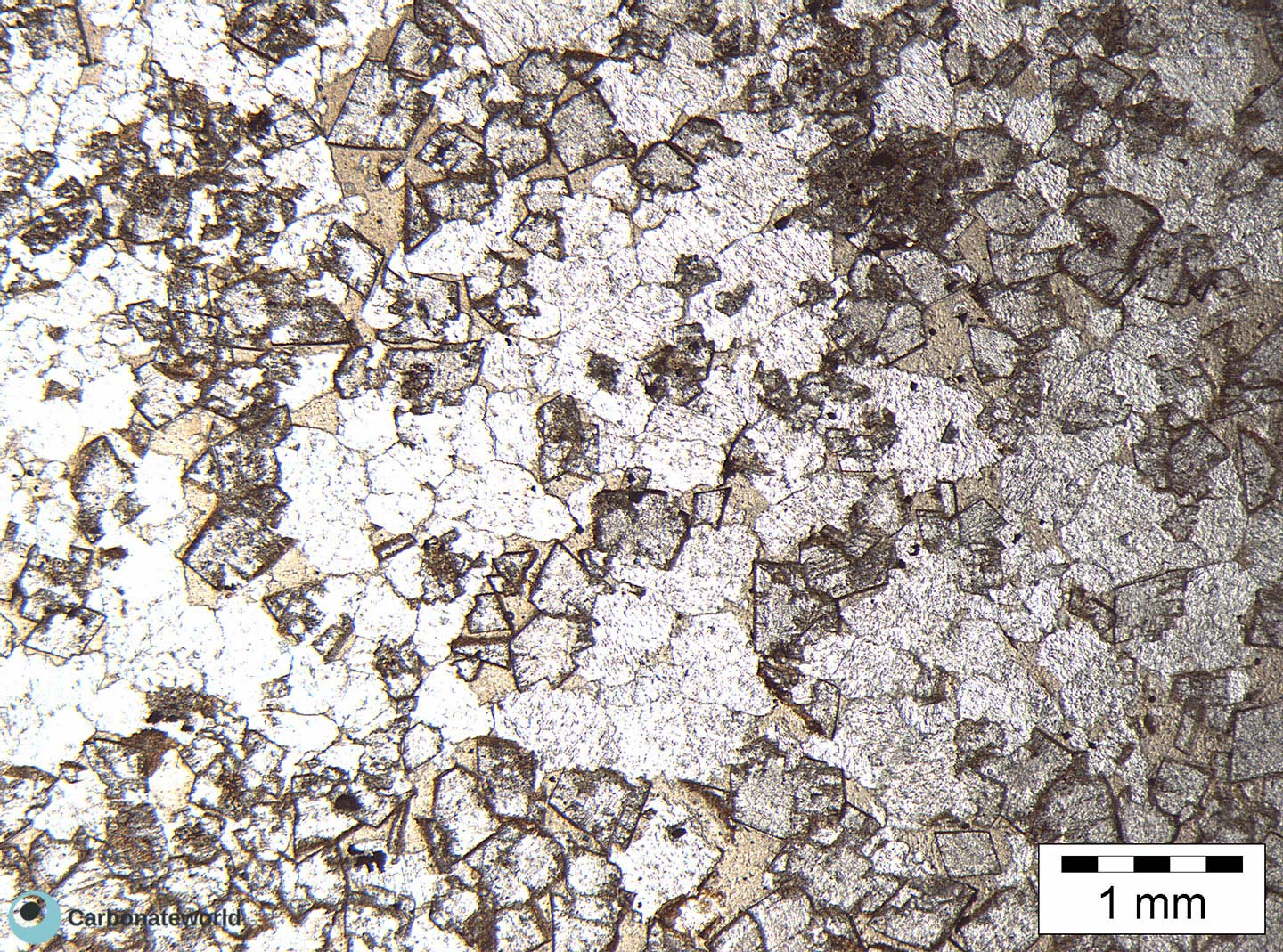
6. Euhedral Dolomite
Skeletal packstone with a bivalve shell affected by micro-boring and coated by a micrite envelope. In the centre, two rhombic crystals of dolomite show evidence of corrosion.
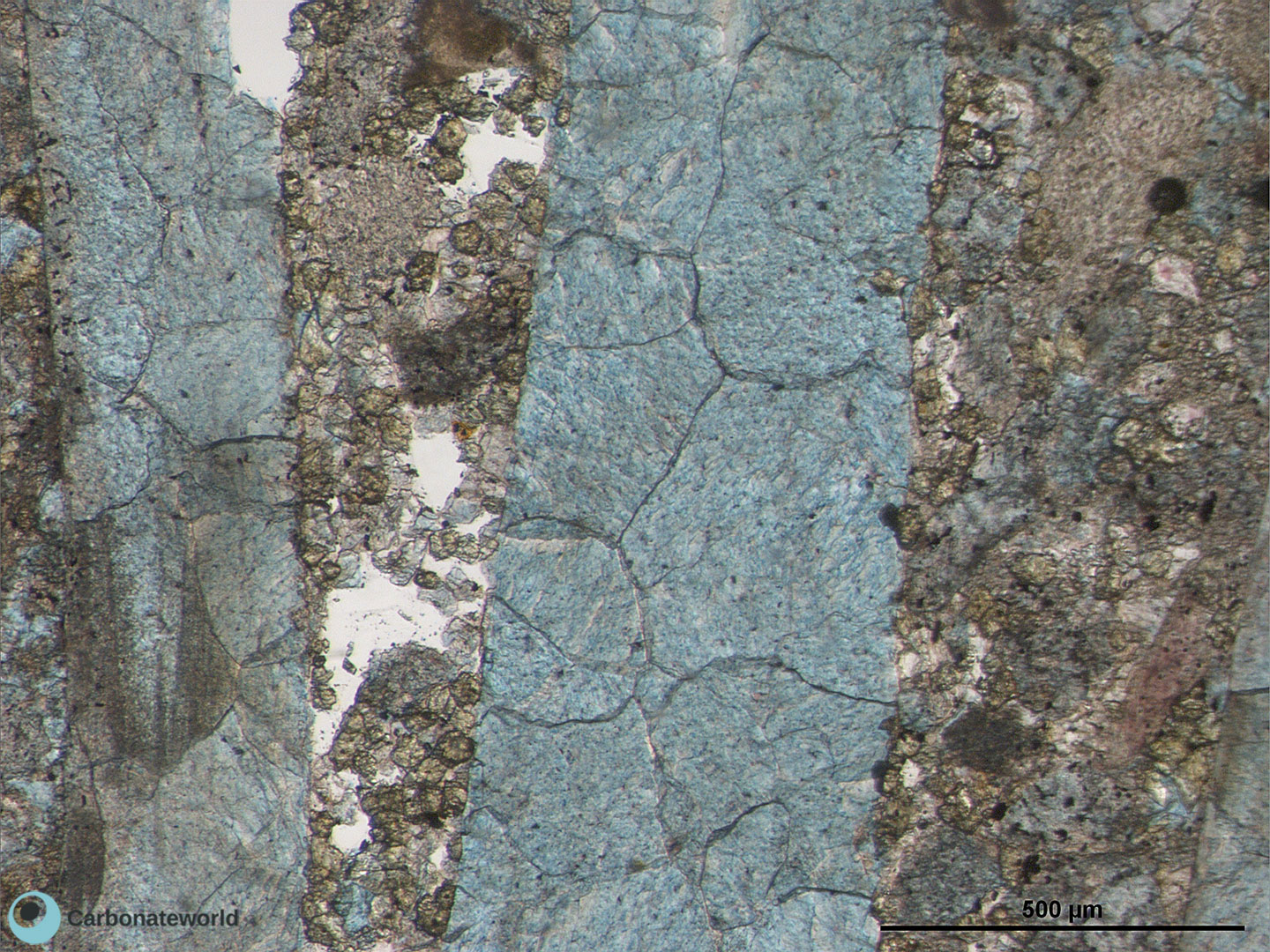
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
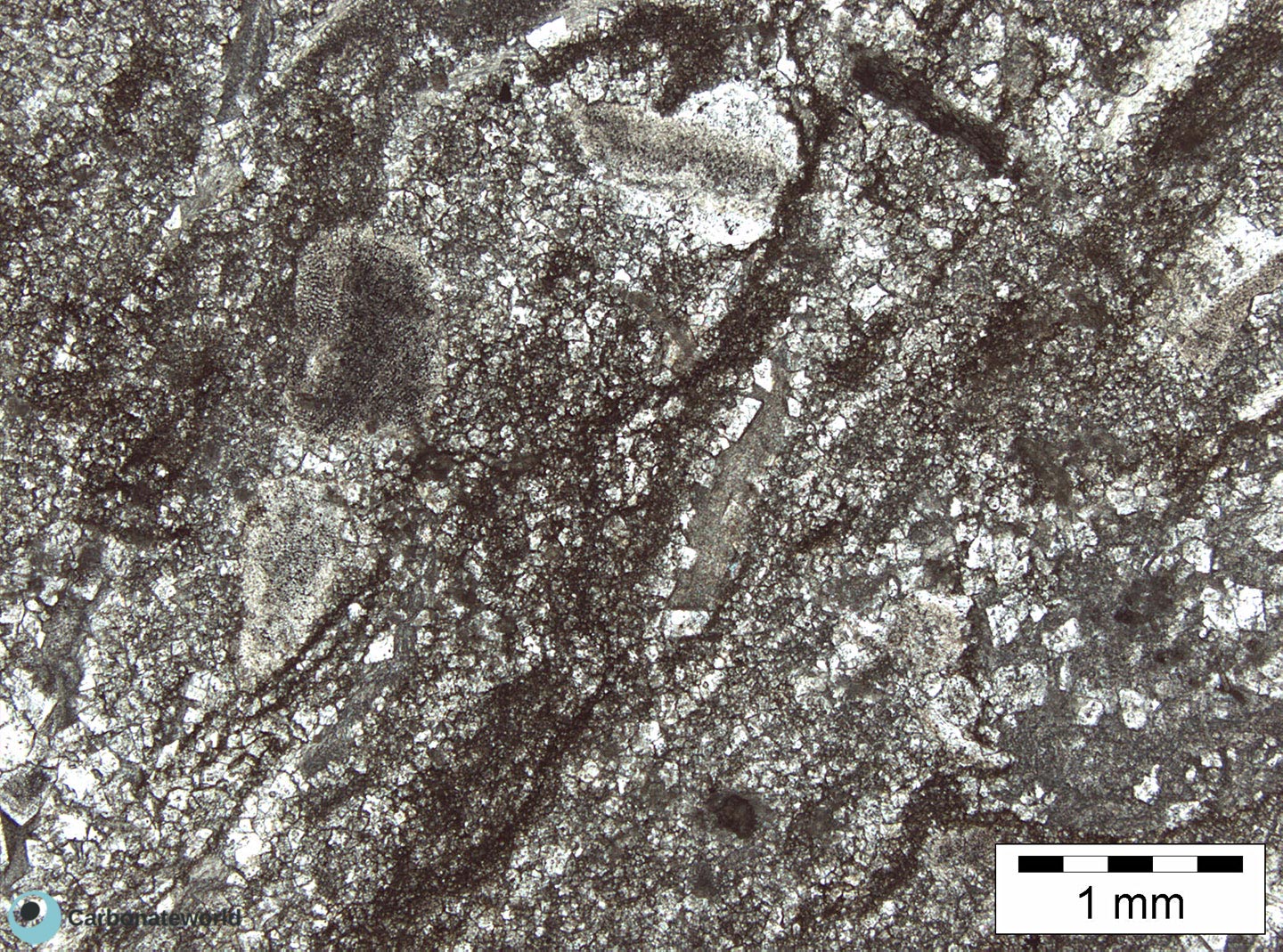
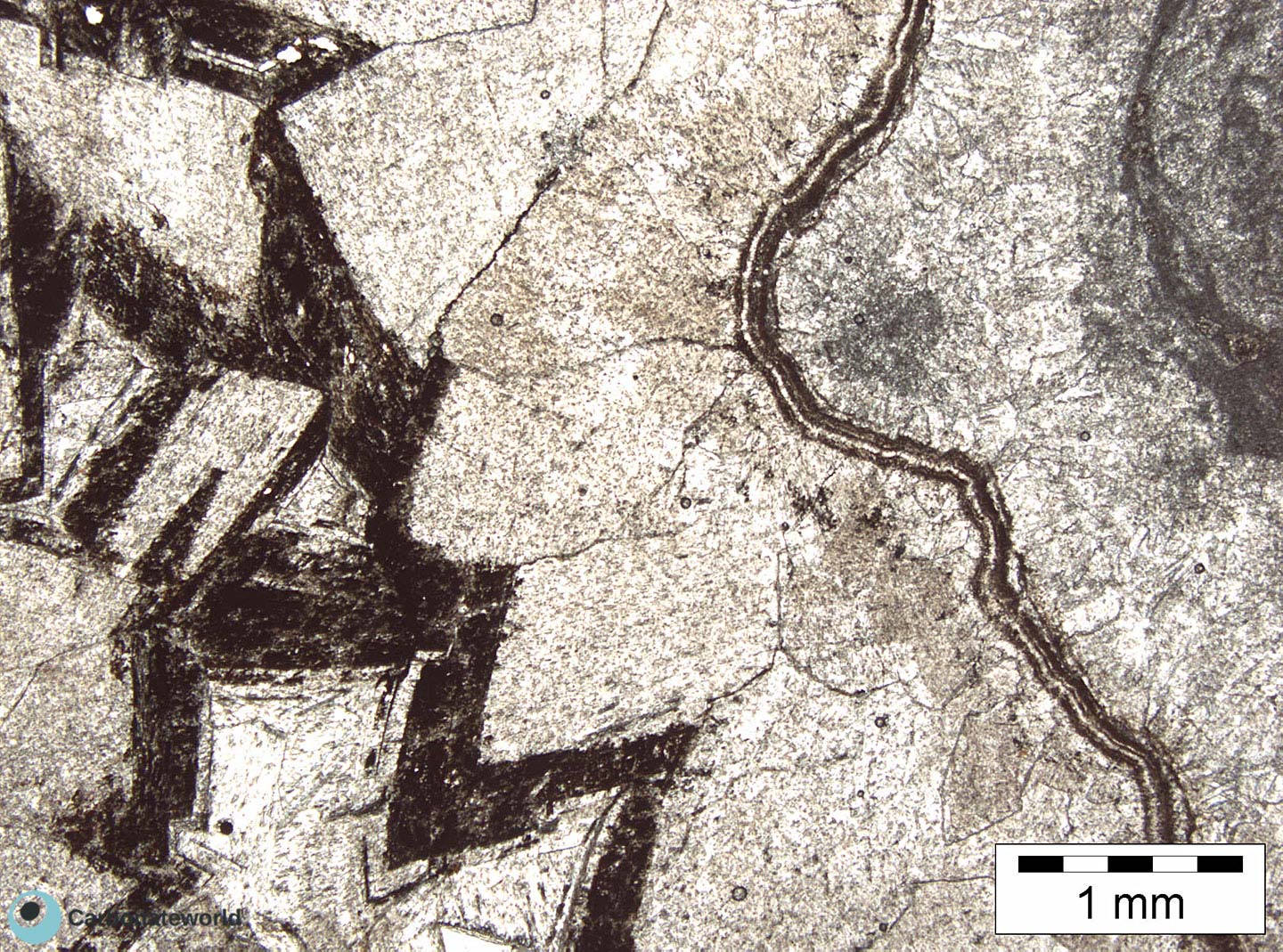
7. Zoned Dolomite
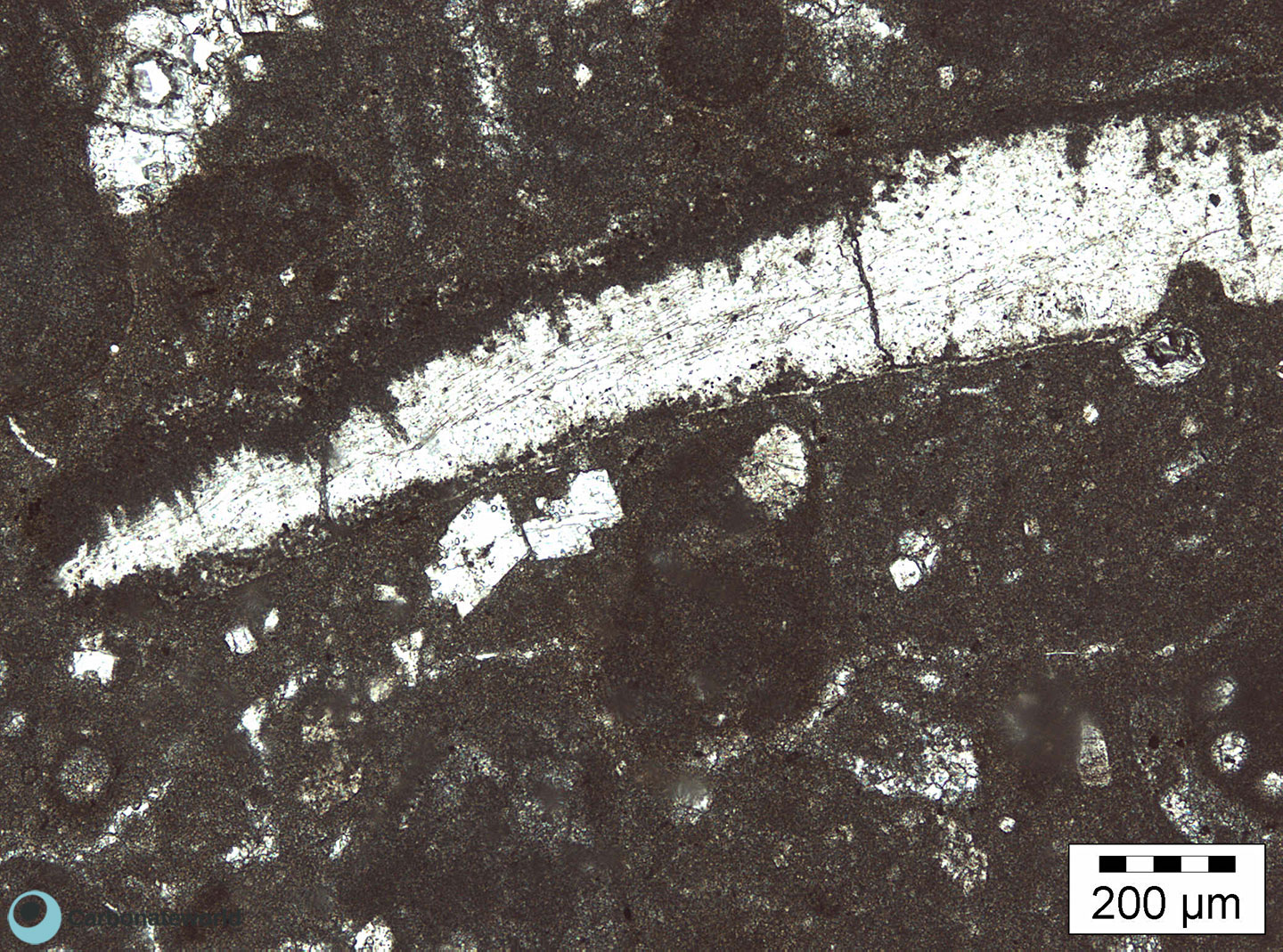
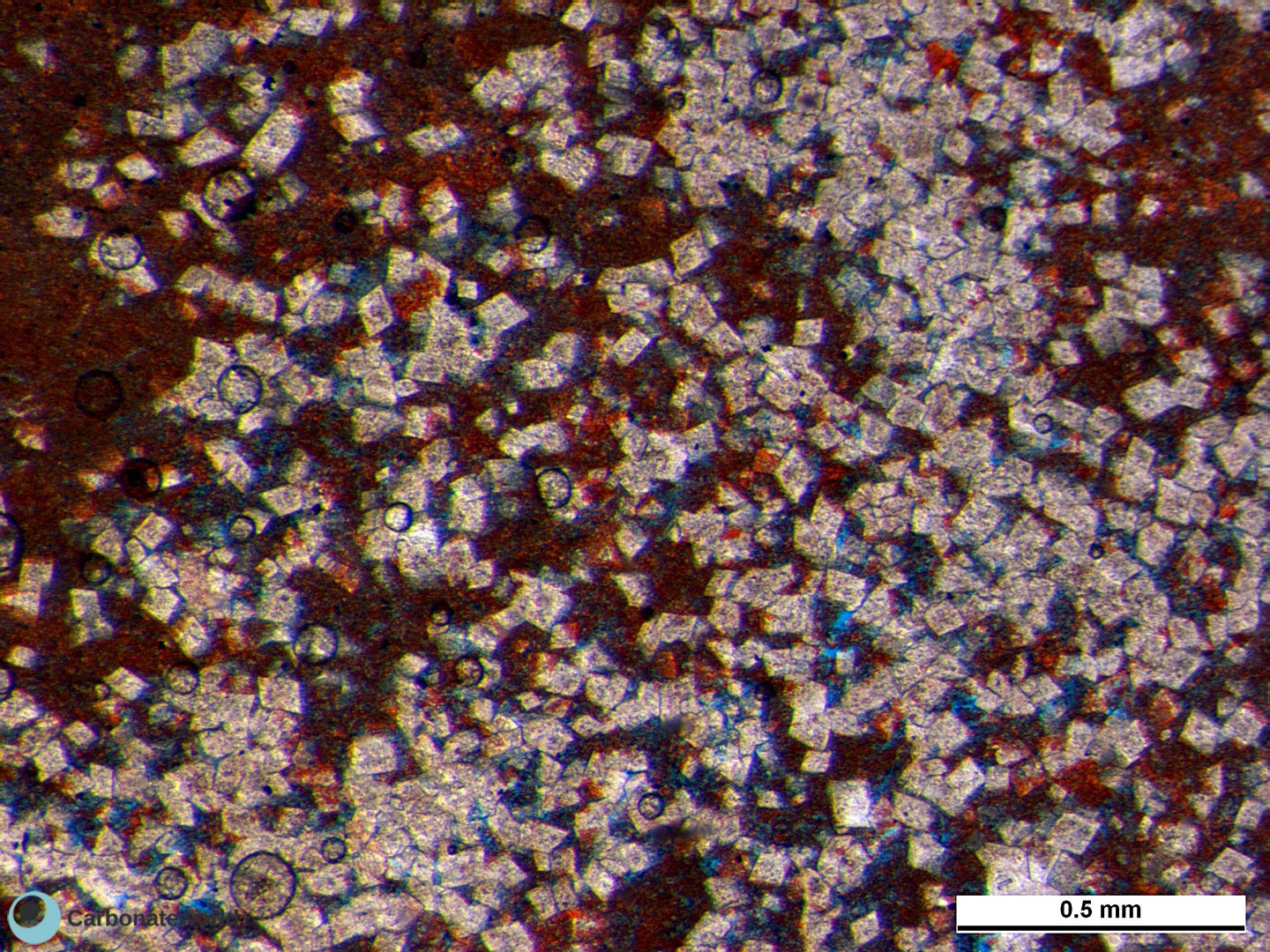
Hypidiotopic mosaic (planar-s subhedral) of fabric replacive dolomite. The dolomite rhombs display zoned crystals with darker subparallel growth lines due to changes in composition of the dolomitizing fluid during crystal growth.
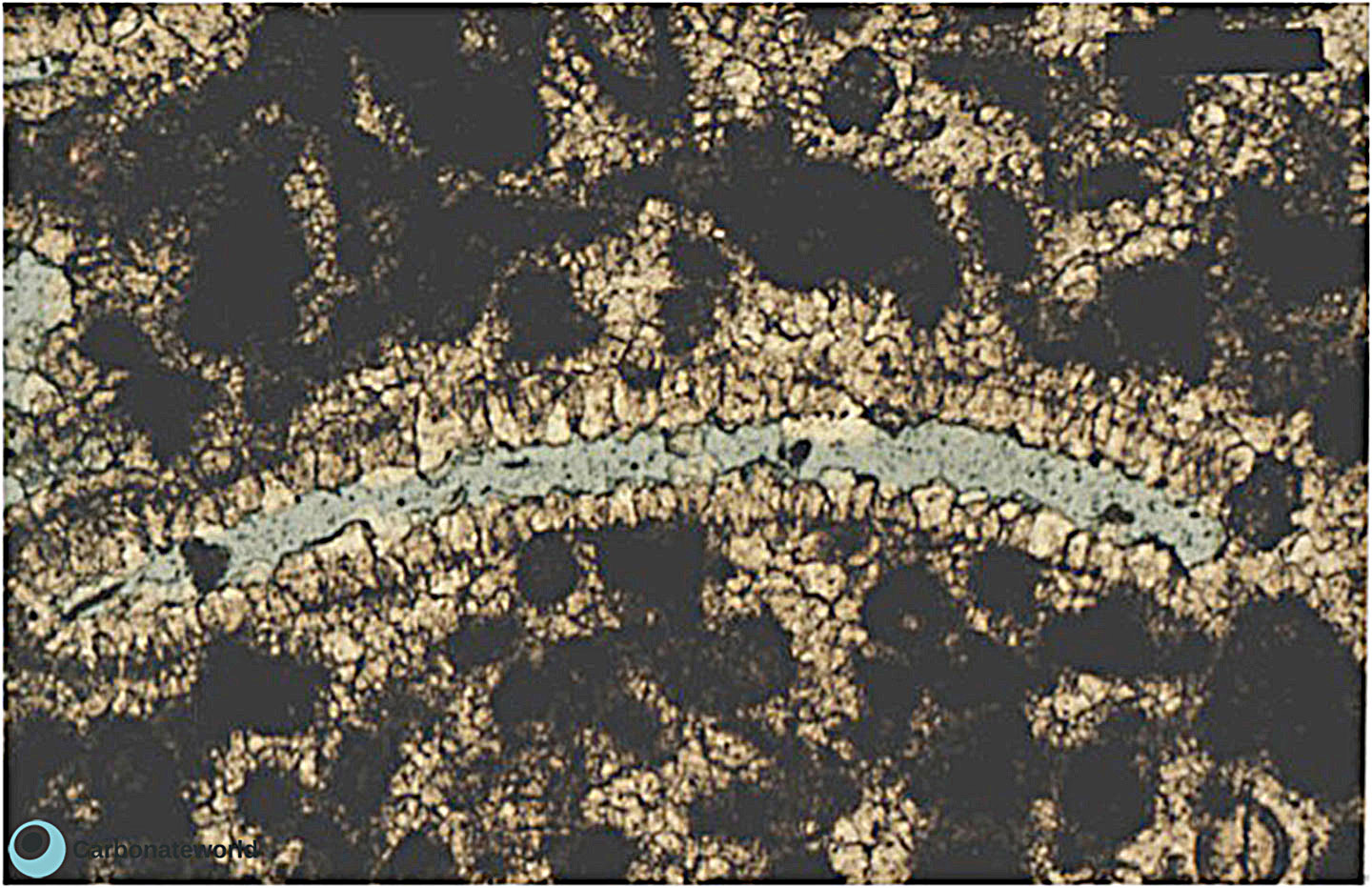
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
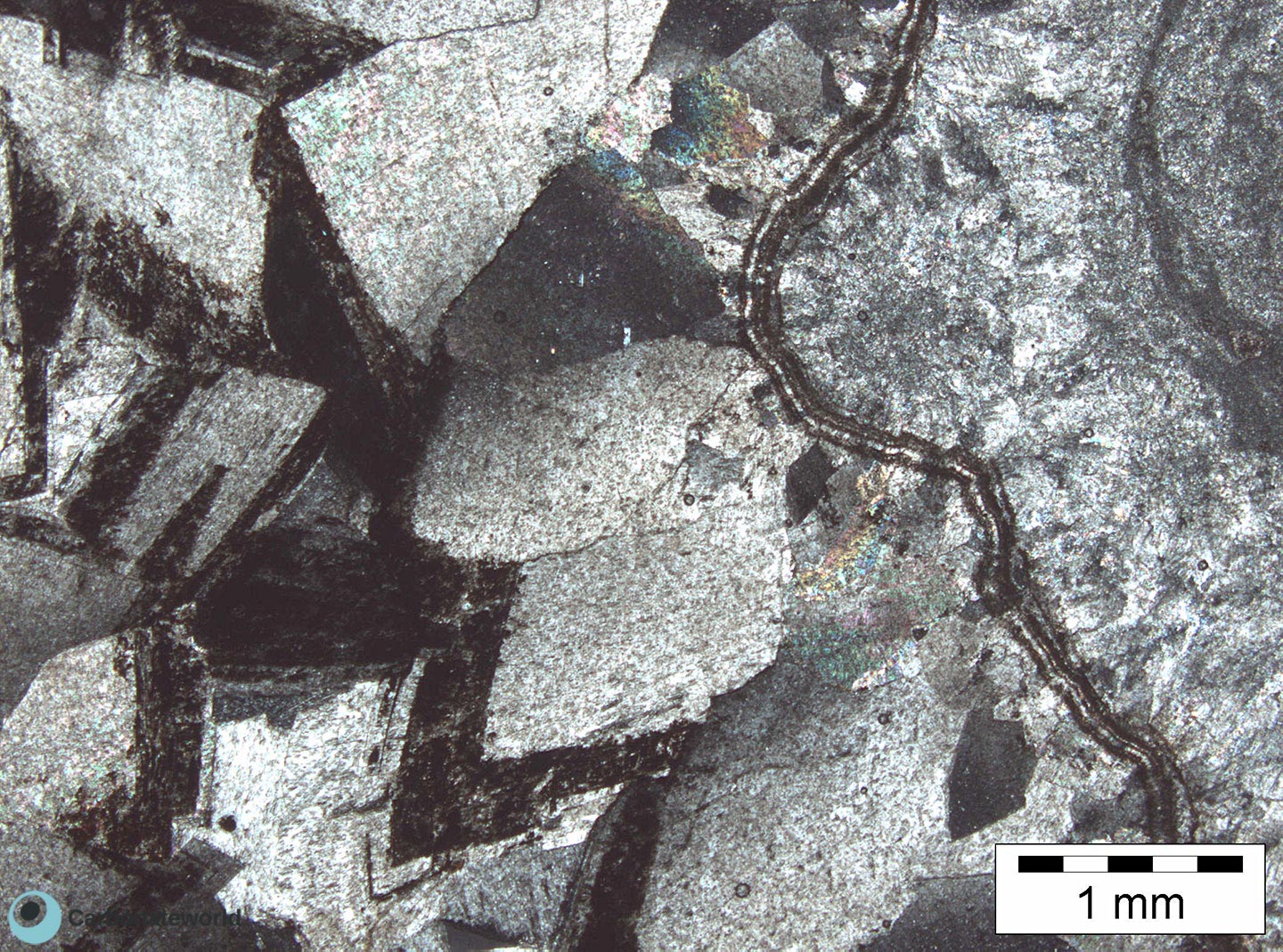
8. Zoned Dolomite
Previous image viewed in crossed polarisers. Hypidiotopic mosaic (planar-s subhedral) of fabric replacive dolomite. The zoned dolomite crystals display darker subparallel areas due to changes in composition of the dolomitizing fluid during crystal growth.
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
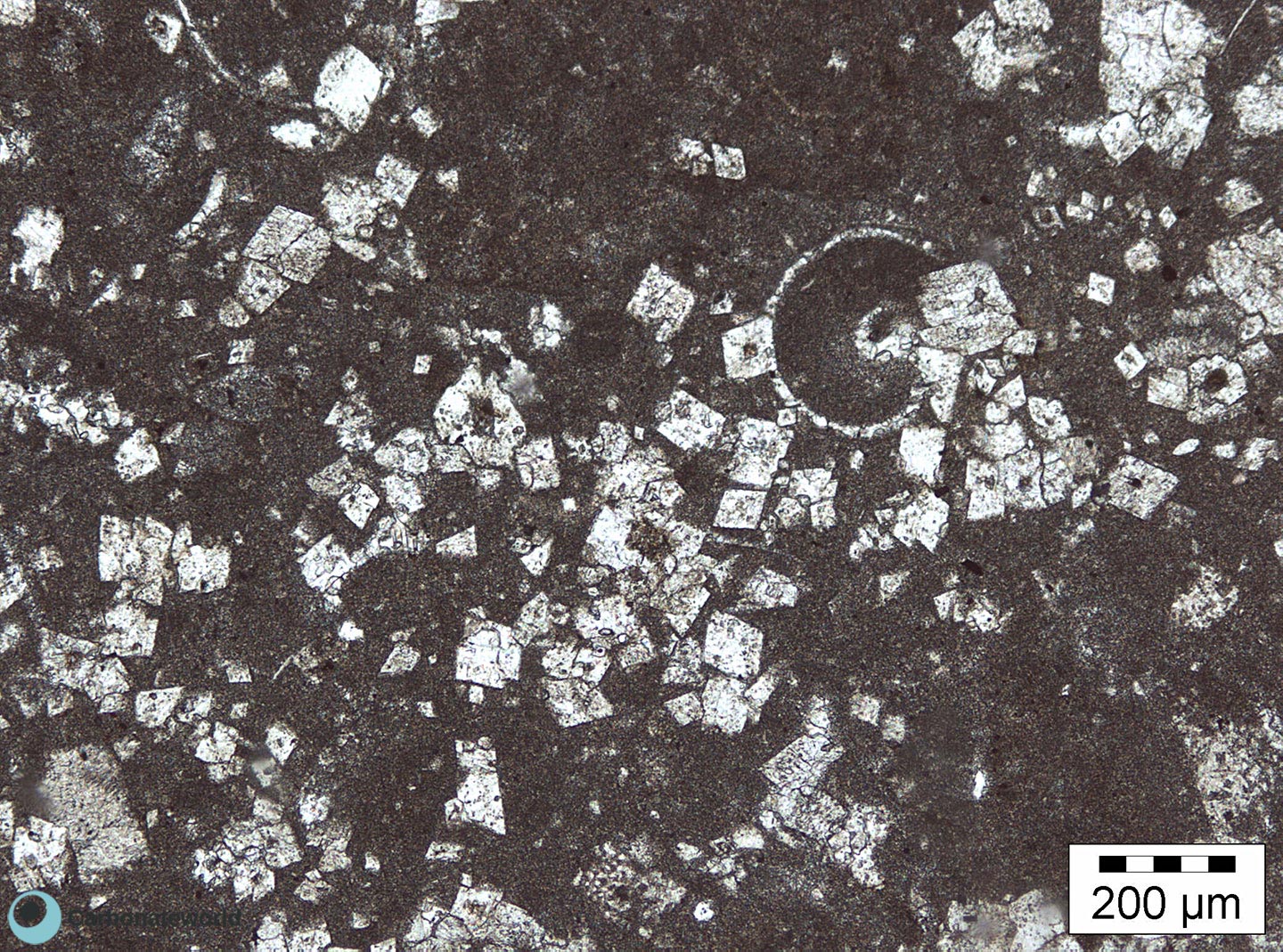
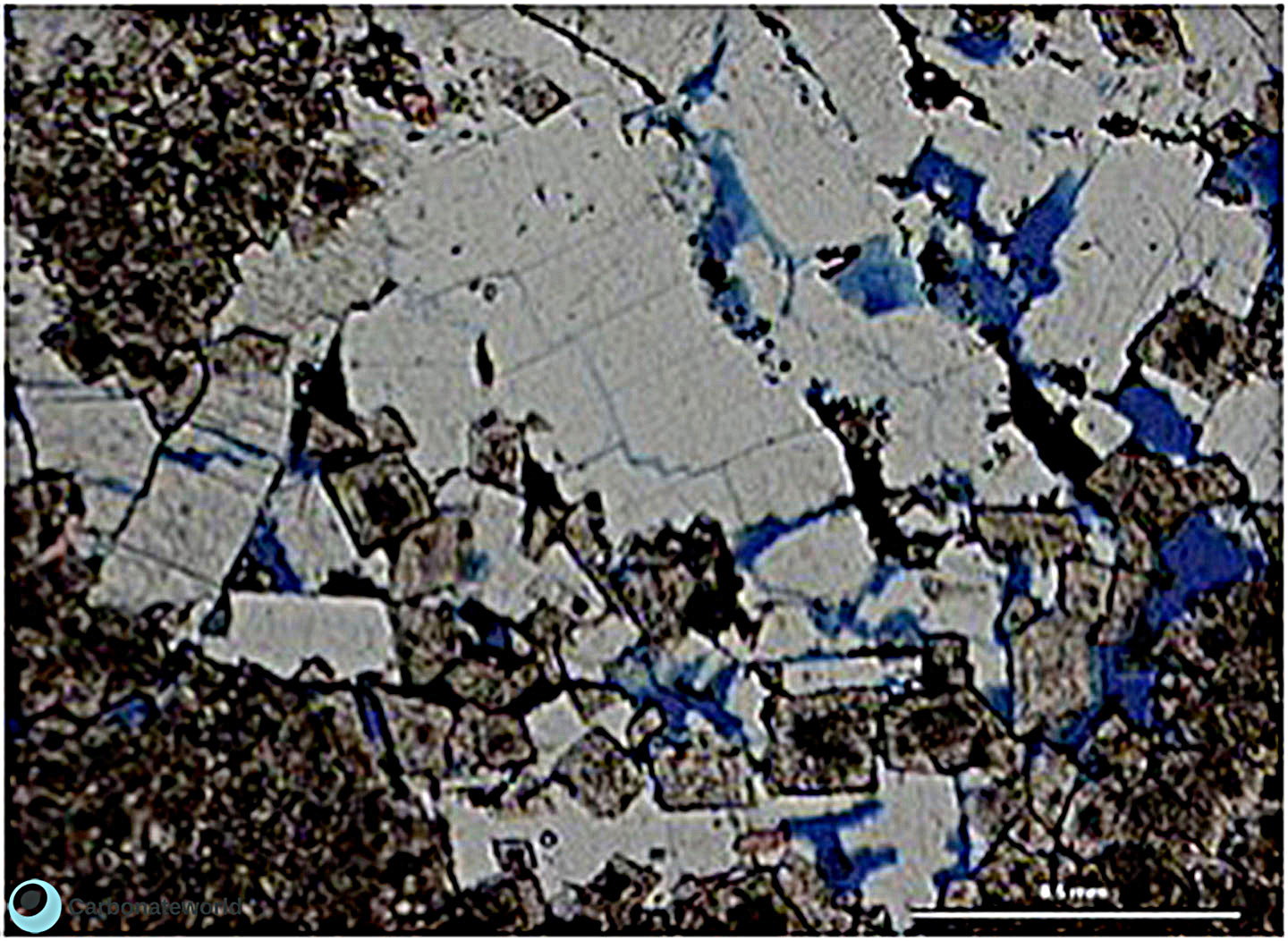
9. Anhedral Dolomite
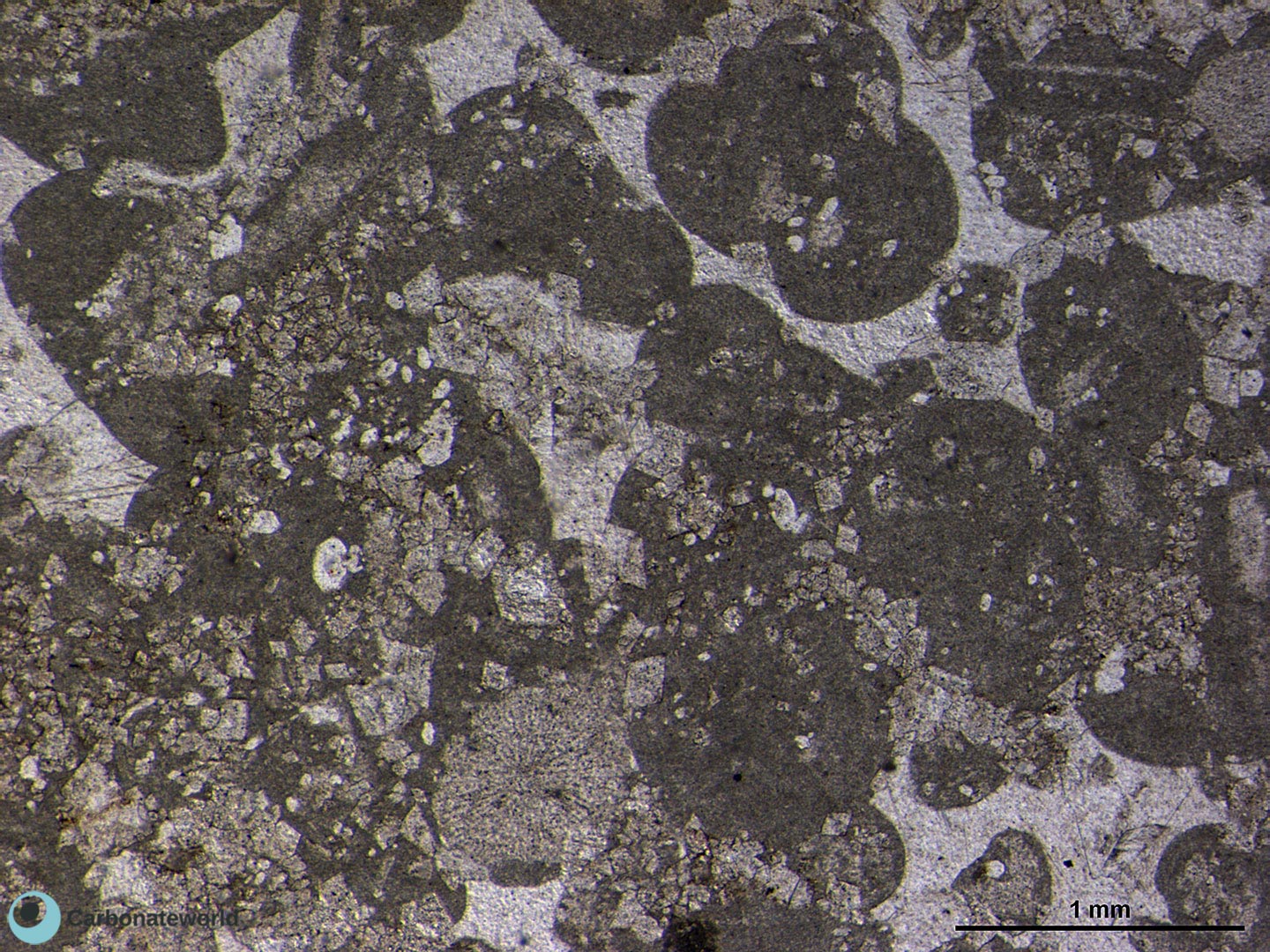
Xenotopic mosaic (non planar anhedral) of fabric replacive dolomite. The host rock must have been a skeletal packstone/wackestone with echinoderms. The micrite matrix and possible bioclasts were completely replaced. The high Mg calcite echinoderm fragments and the associated syntaxial calcite cement have partly resisted to the replacive dolomitizing process.
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
10. Anhedral Dolomite
Xenotopic (non planar anhedral) to hypidiotopic (planar-s subhedral) mosaic of fabric replacive dolomite with sparse euhedral rhombs.
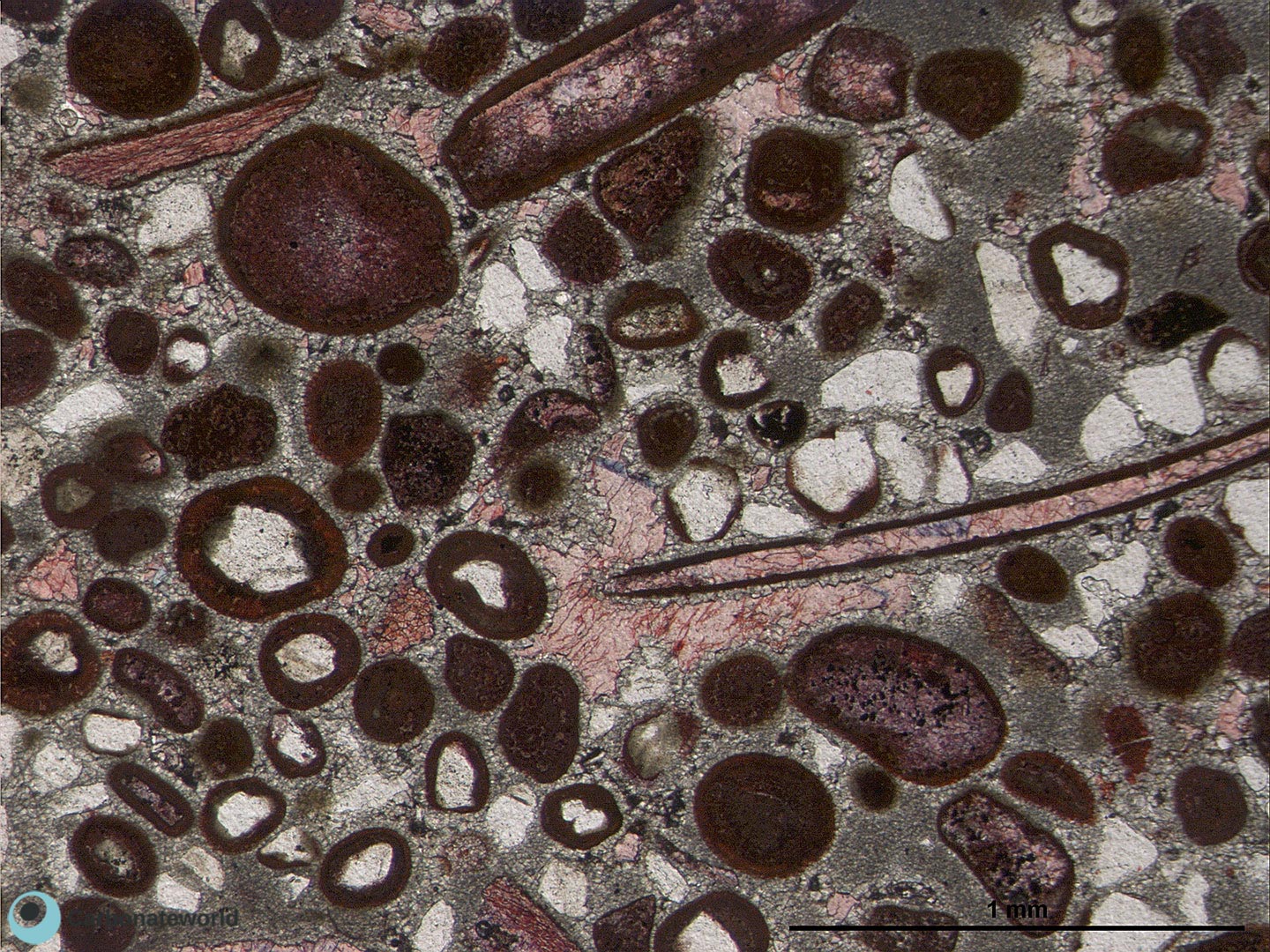
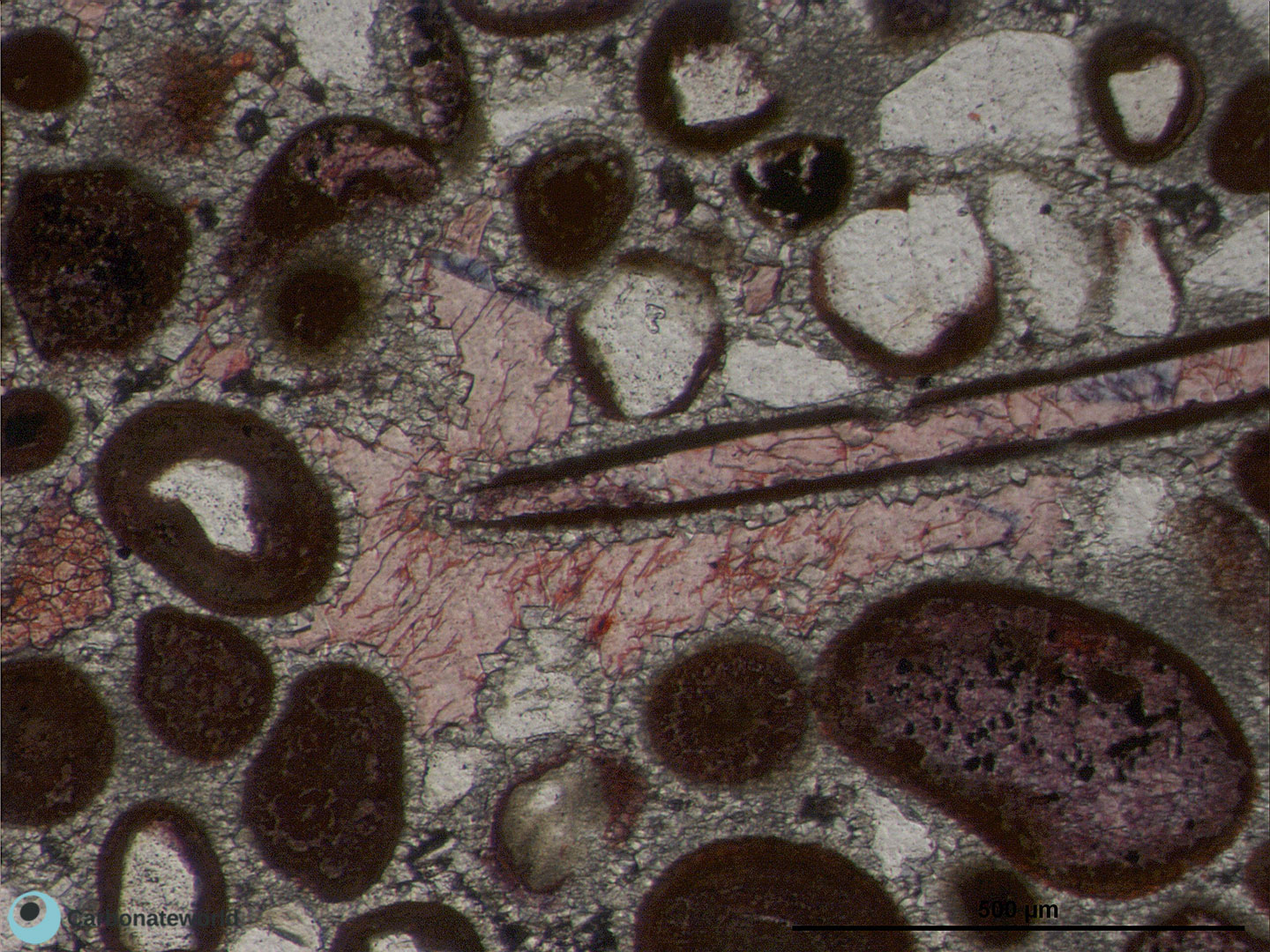
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
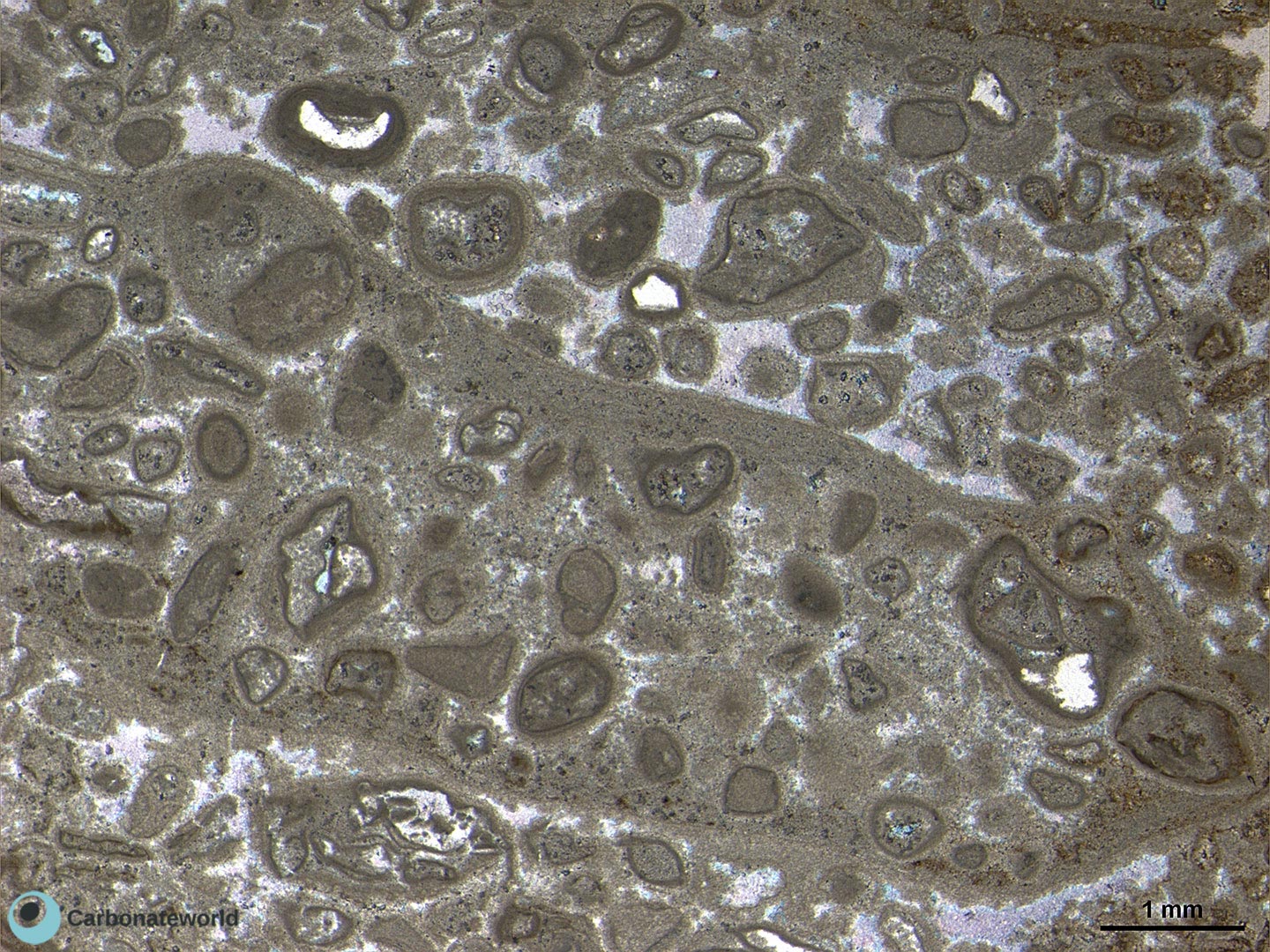
11. Anhedral Dolomite
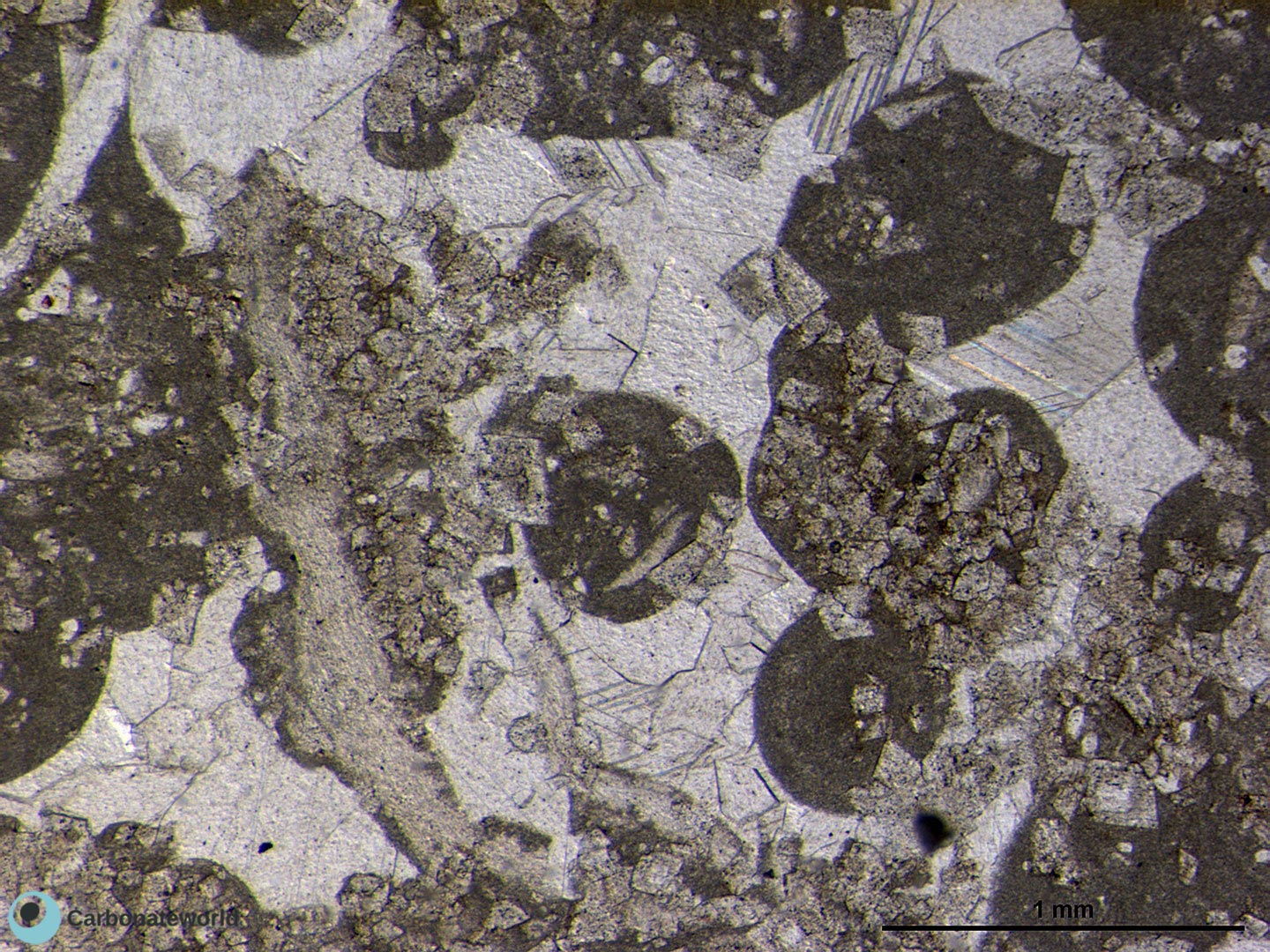
Xenotopic mosaic (non planar anhedral) of fabric replacive dolomite. The host rock must have been a skeletal packstone/wackestone. The micrite matrix and bioclasts have been completely replaced. Echinoderms and the central undetermined grain have partly resisted to the replacive process and contain euhedral dolomite rhombs.
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
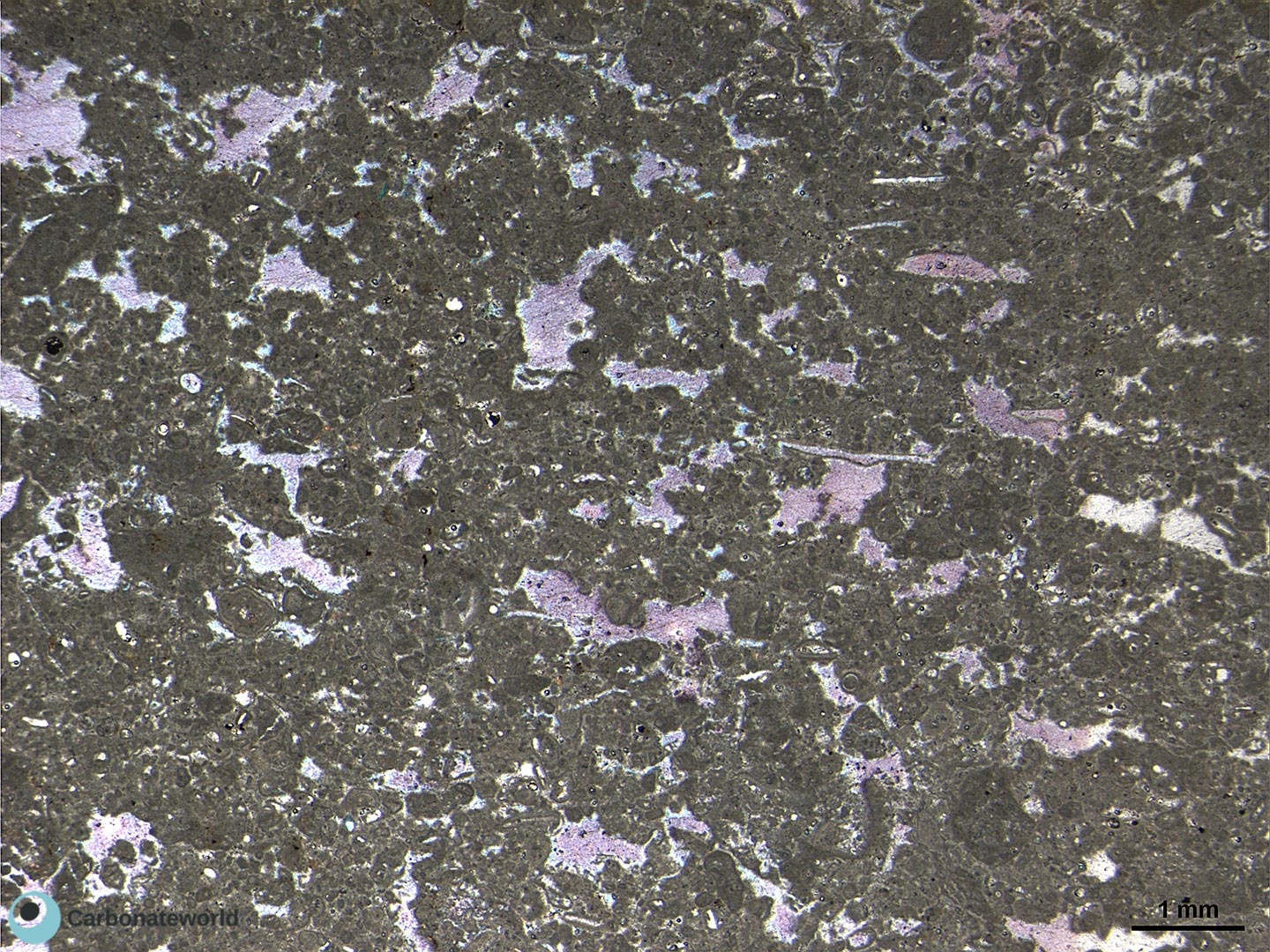
12. Anhedral Dolomite
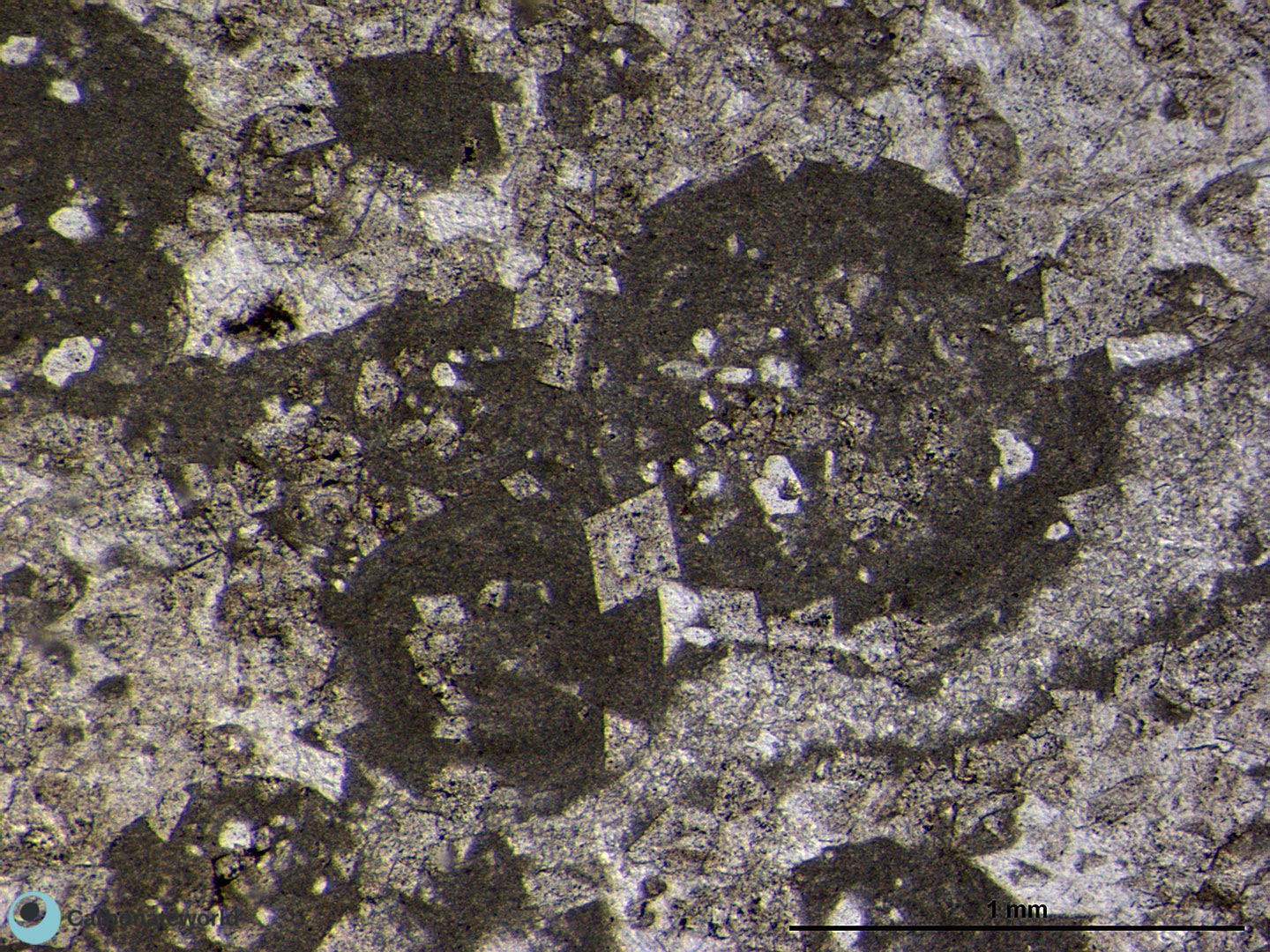
Xenotopic mosaic (non planar anhedral) of fabric replacive dolomite. The host rock must have been a skeletal packstone/wackestone with echinoderms. Echinoderm (High Mg calcite) in the centre and the associated syntaxial calcite cement were not affected by the replacive dolomitization.
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
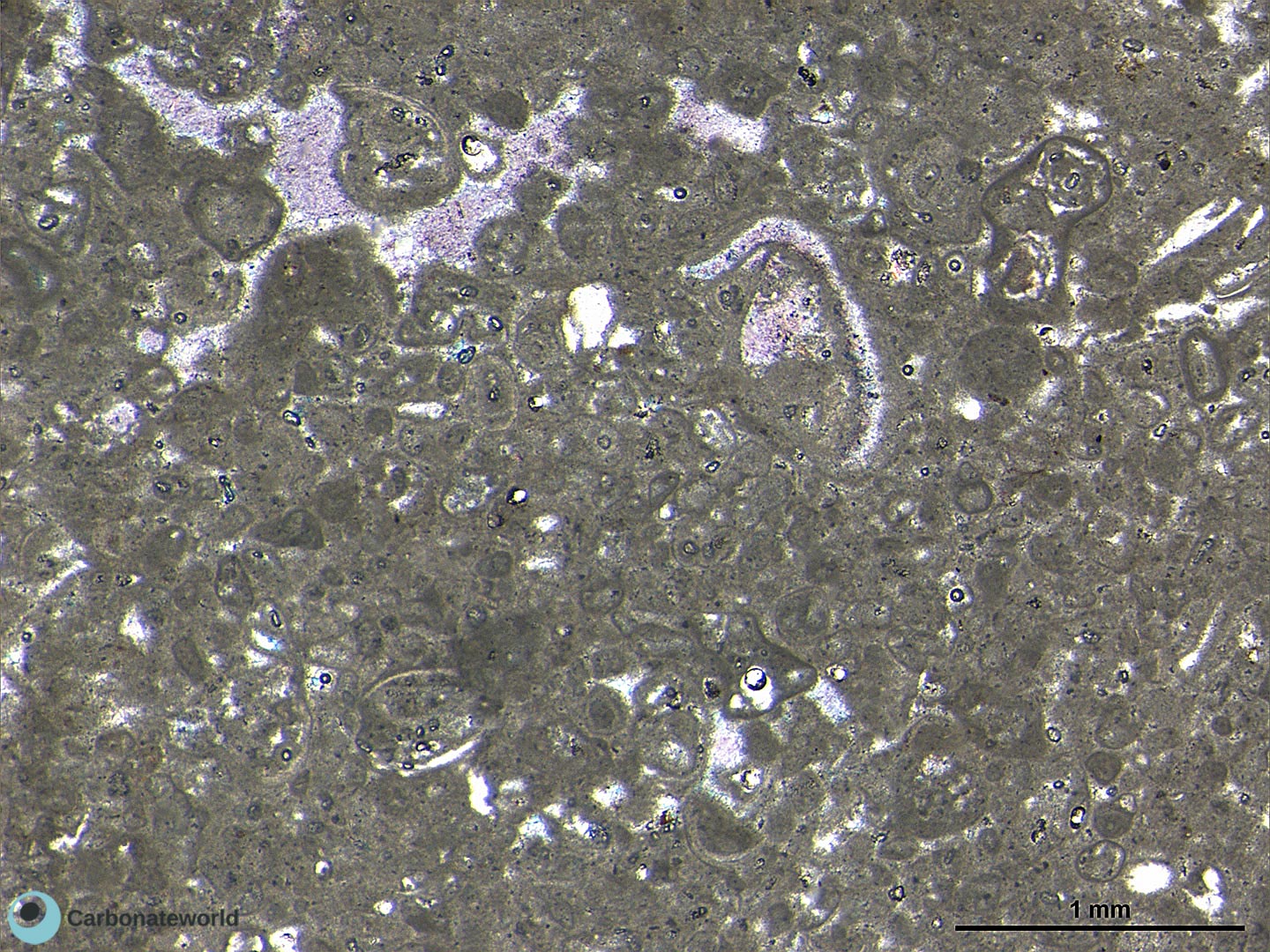
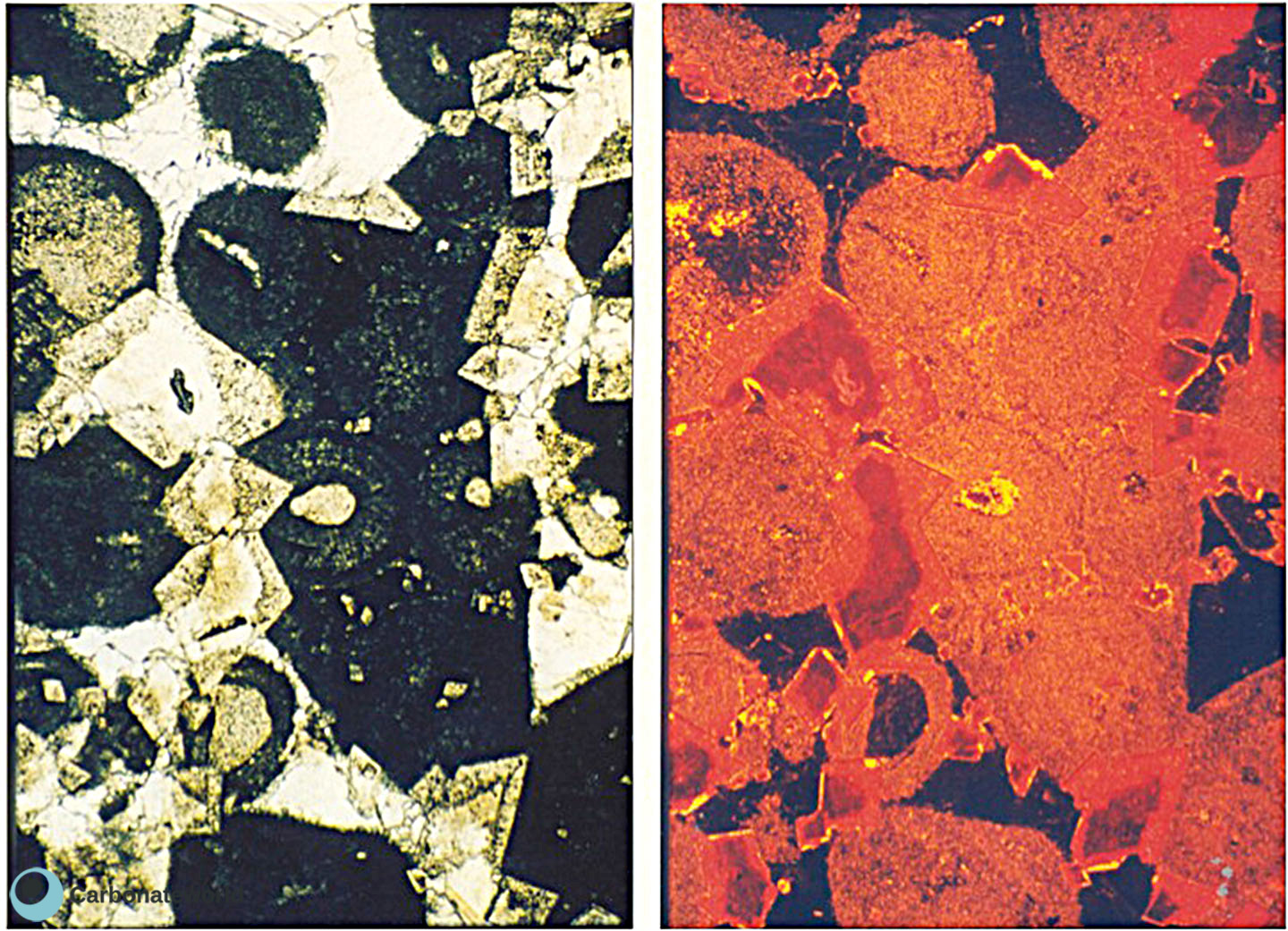
13. Anhedral Dolomite
Xenotopic mosaic (non planar anhedral) of fabric replacive dolomite. The host rock must have been a skeletal packstone/wackestone with echinoderms. The echinoderms (High Mg calcite) and the associated syntaxial calcite cement were not affected by the replacive dolomitization.
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
14. Euhedral Dolomite
Peloidal skeletal wackestone partly replaced by euhedral (planar e, idiotopic mosaic) dolomite.
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

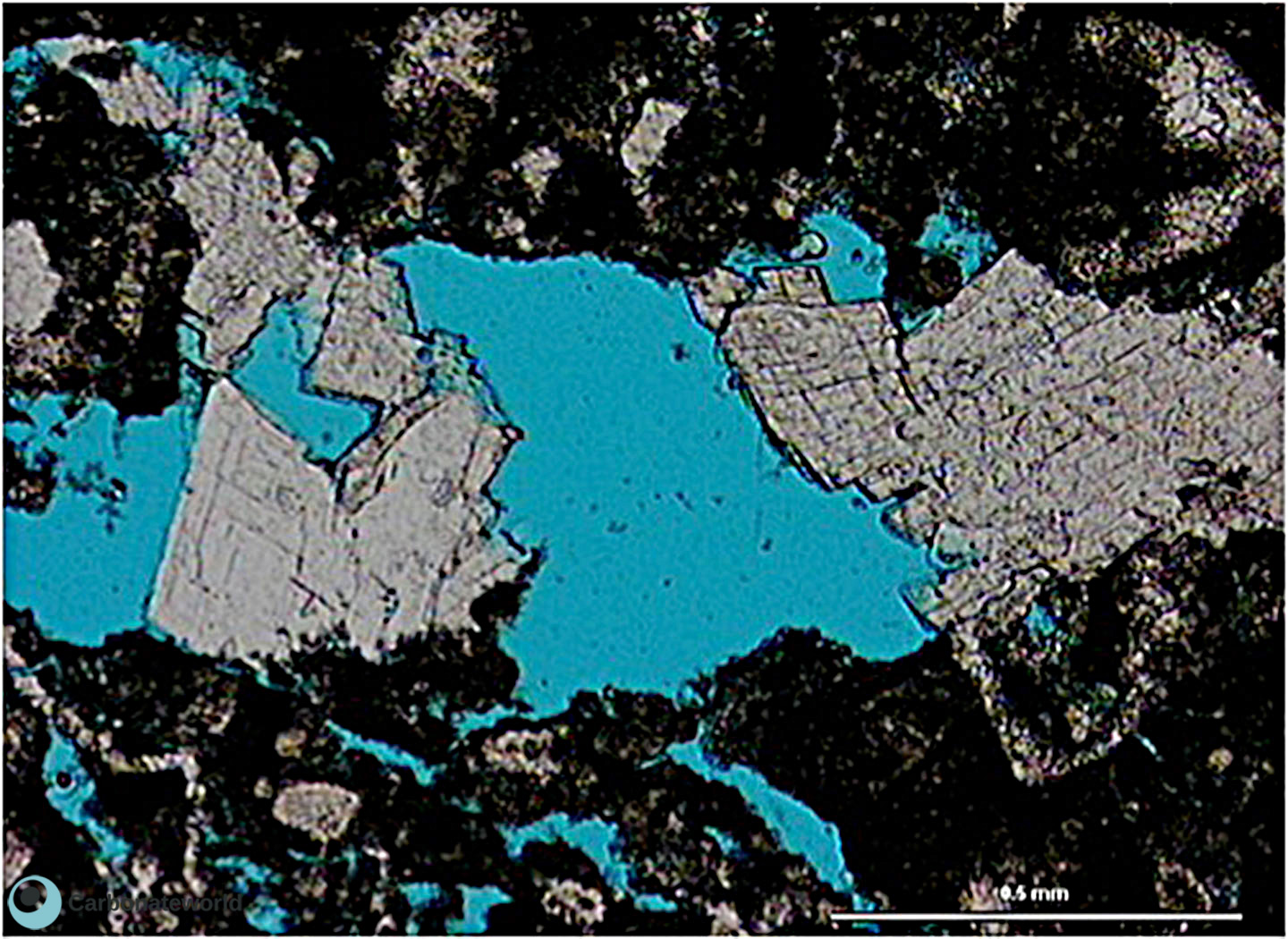
SHOW INFO
15. Euhedral Dolomite
Previous image viewed in crossed polarised light. Peloidal skeletal wackestone partly replaced by euhedral (planar e, idiotopic mosaic) dolomite.
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

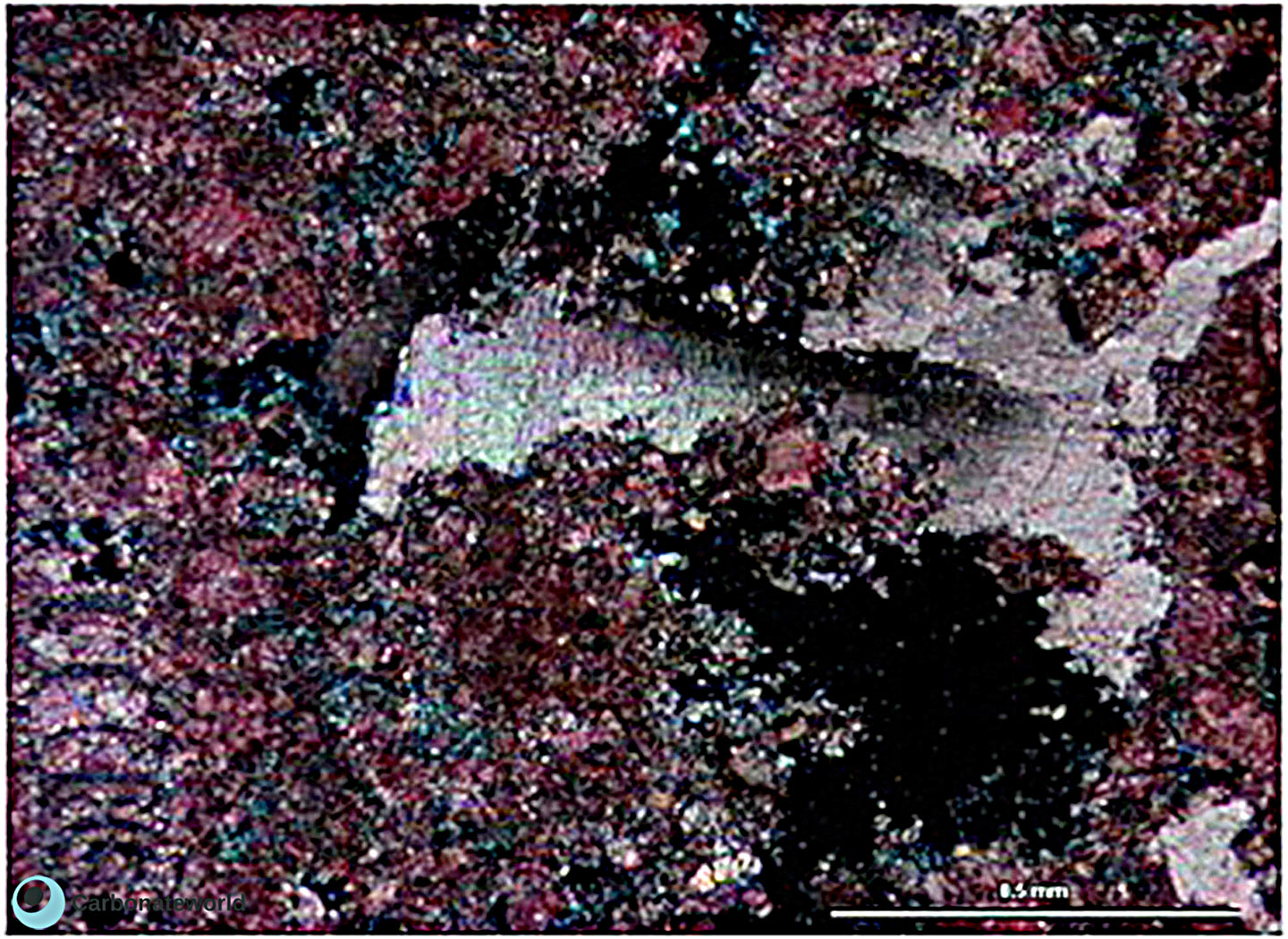
HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
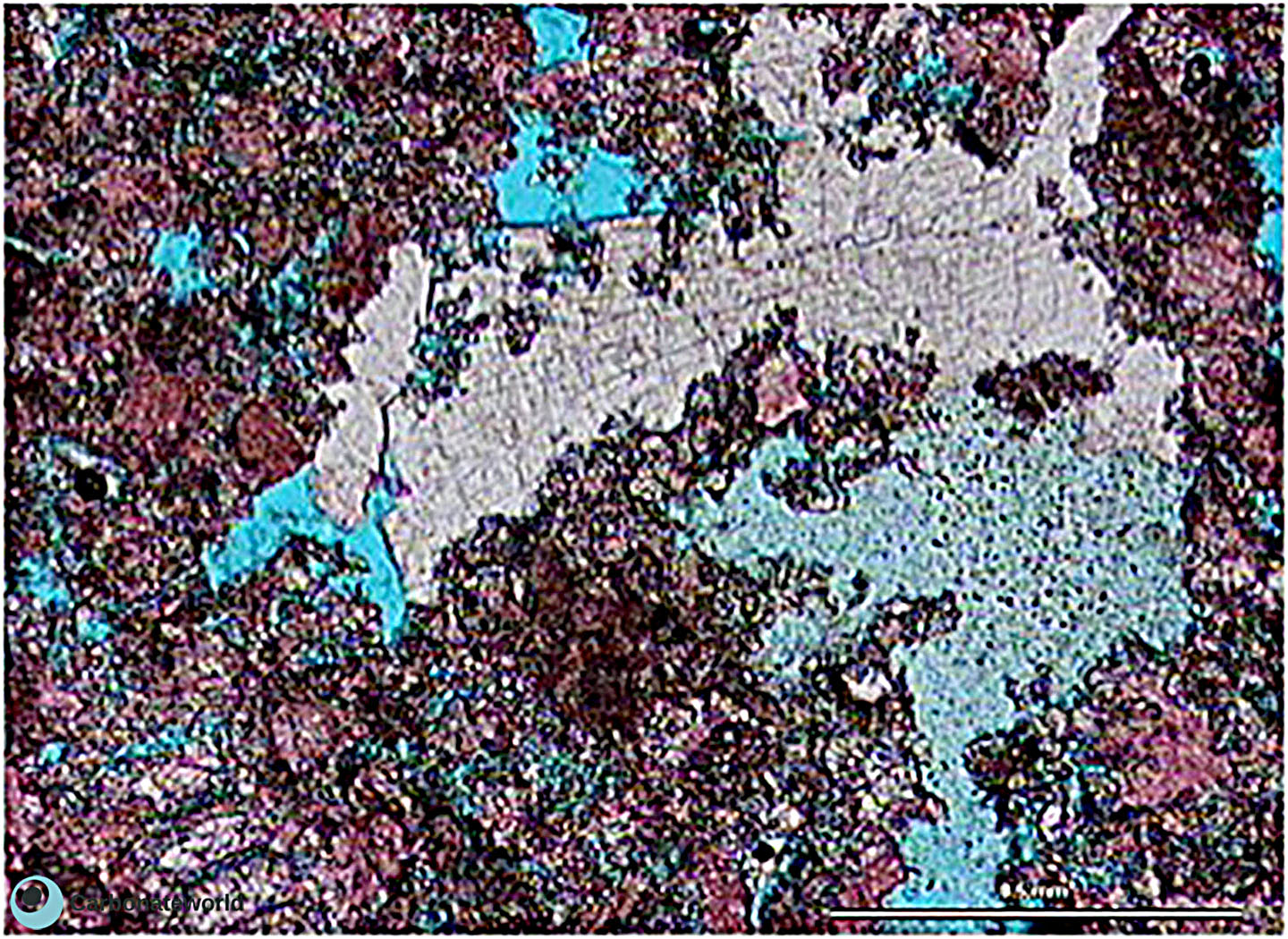
16. Subhedral Dolomite
Peloidal skeletal wackestone partly replaced by subhedral to euhedral (planar s and planar e, hypidiotopic and idiotopic mosaics, respectively) dolomite.
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
17. Euhedral Dolomite
Oncoidal peloidal wackestone (calcite in pink because of alizarin red staining) possibly of intertidal environment (voids can be interpreted as fenestrae and are infilled by dolomite crystals) with sparse euhedral dolomite rhombs (grey). Dolomite replacement occurred as < 100 microns size crystals on the micrite matrix and as 0.5 mm size crystals within the voids where most likely a coarser crystal calcite spar had been replaced.

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
18. Euhedral Dolomite
Detail of previous image (thin section stained with alizarin red) with possibly intertidal fenestrae filled by euhedral/subhedral dolomite crystals of 0.5 mm in size and sparse euhedral dolomite rhombs < 100 microns within the micrite matrix.

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
19. Euhedral Dolomite
As previous image (thin section stained with alizarin red), this is a detail of possibly intertidal fenestrae filled by euhedral/subhedral dolomite crystals replacing calcite blocky spar associated with sparse euhedral dolomite rhombs < 100 microns within the micrite matrix.

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
20. Euhedral Dolomite
Oncoidal peloidal wackestone (calcite in pink because of alizarin red) with sparse euhedral dolomite rhombs (grey). Dolomite replacement occurred on the micrite matrix as < 100 microns size crystals.

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
21. Dolomite Cement
Coated grain-ooidal (dolo)grainstone with an isopachous layer of dolomite rhombic crystal (grey) cement lining grains and interparticle pore space. In some cases, the interparticle space is occluded by a hypidiotopic mosaic of dolomite crystals; in other interparticle pore spaces calcite spar (pink) is present.

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
22. Dolomite Cement
Detail of previous image showing coated grain-ooidal (dolo)grainstone with an isopachous rim of dolomite cement (grey) lining grains and interparticle pore space. Calcite spar (pink) fills the remaining pore space.

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
23. Dolomite Cement
Detail of previous image showing coated grain-ooidal (dolo)grainstone with an isopachous rim of dolomite cement (grey, alizarin red unstained) lining grains and interparticle pore space. Calcite spar (pink) fills the remaining pore space.

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
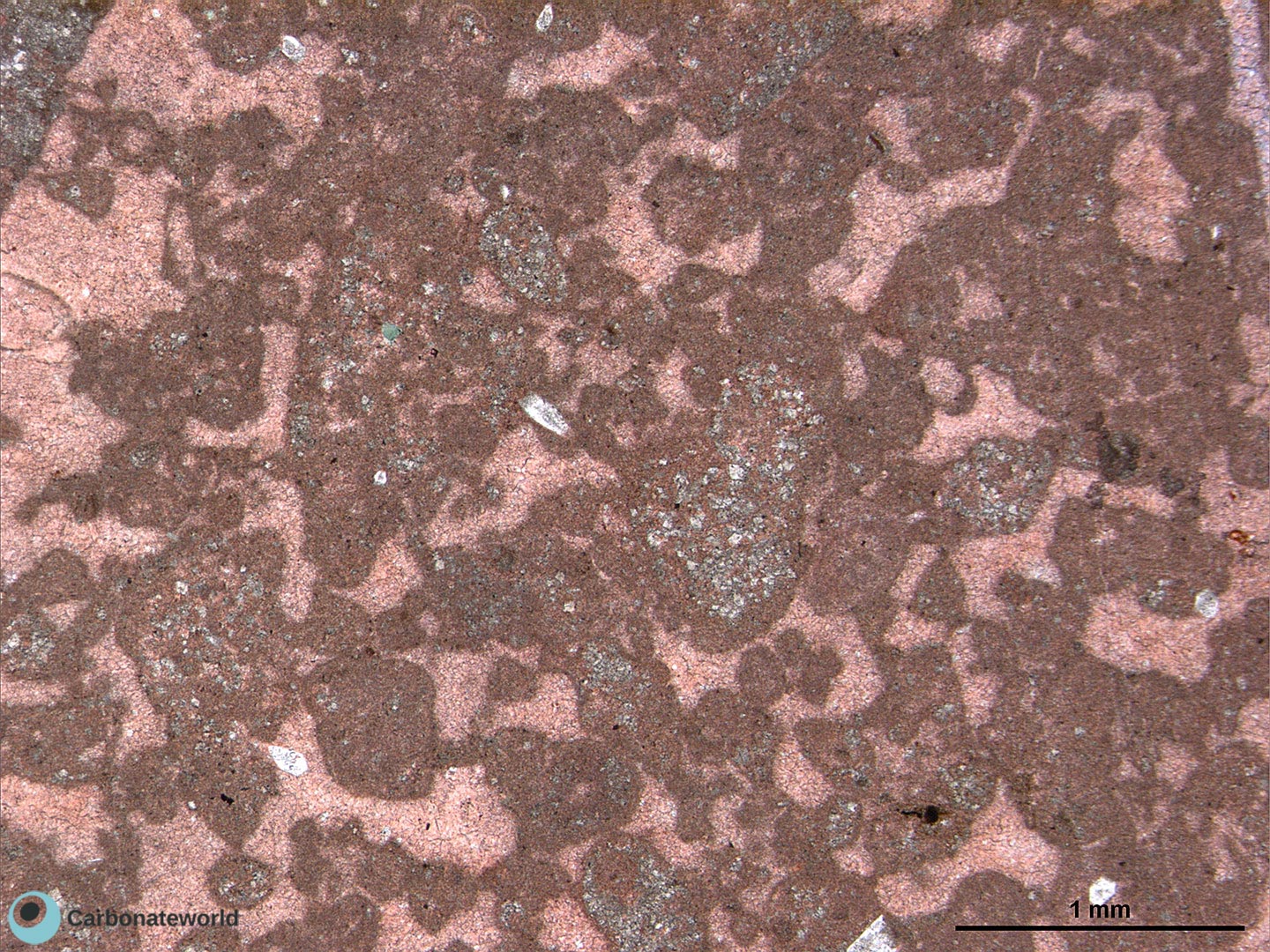
24. Dedolomite
Ooidal grainstone (pink, alizarin red staining) with fabric replacive, dolomite crystals 1-2 mm in size. Dolomite crystals appear affected by corrosion, calcite replacement in pink (dedolomitization) and oxide inclusions because of their instability in a meteoric superficial setting (outcrops).
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
25. Dedolomite
As previous photo, ooidal grainstone (pink, alizarin red staining) with fabric replacive dolomite crystals, 1-2 mm in size. Dolomite crystals appear affected by corrosion and oxide inclusions and show calcitic patches (pink) overlying the dolomitic (grey) crystalline structures.
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
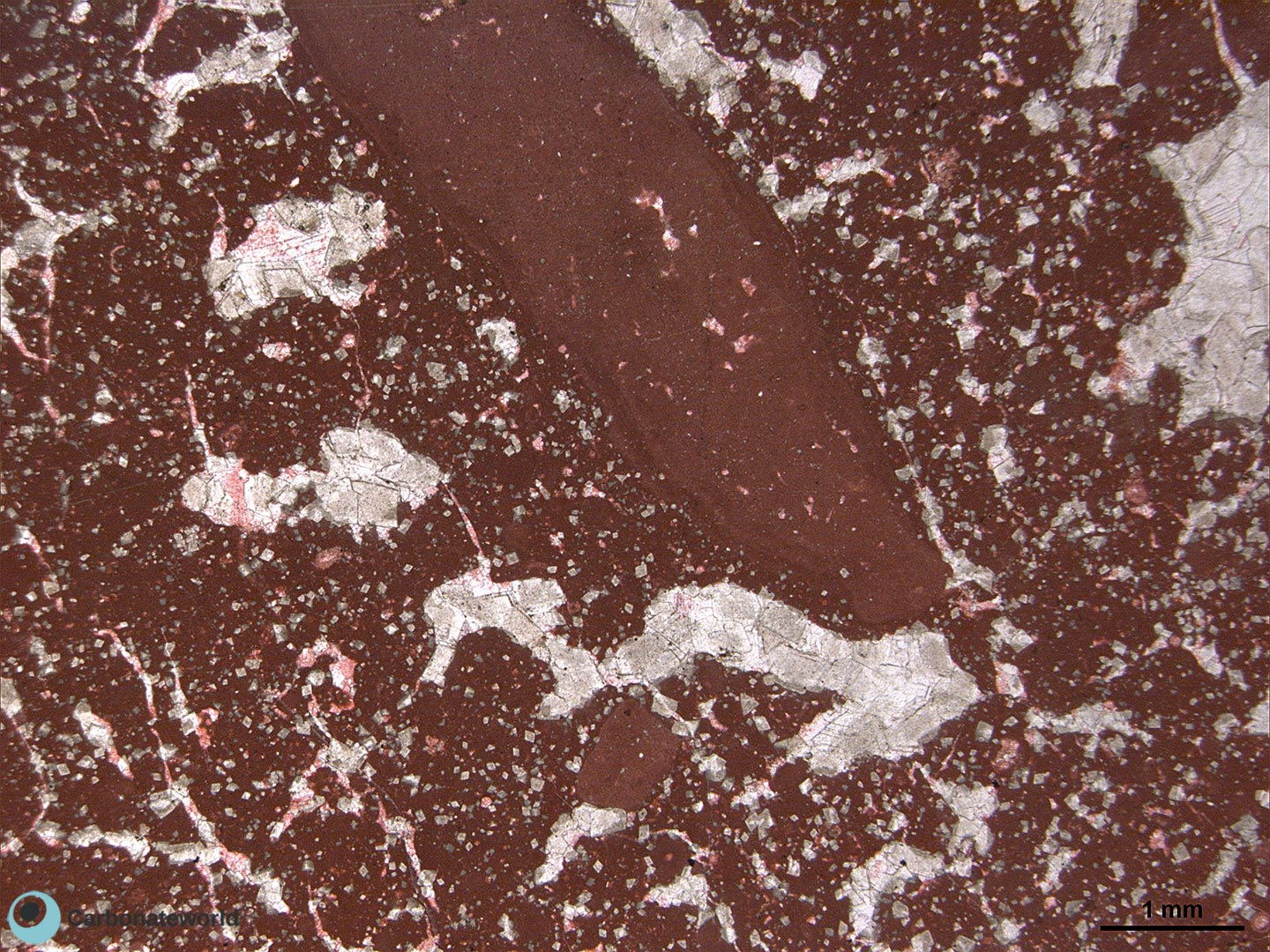
26. Dedolomite
Ooidal (dolo)grainstone (pink, alizarin red staining) with 1-2 mm in size, fabric replacive dolomite crystals. Dolomite crystals are clearly affected by a replacive process of transformation of dolomite into calcite with numerous calcitic patches (pink) overlying the dolomitic (grey) crystalline structures.
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
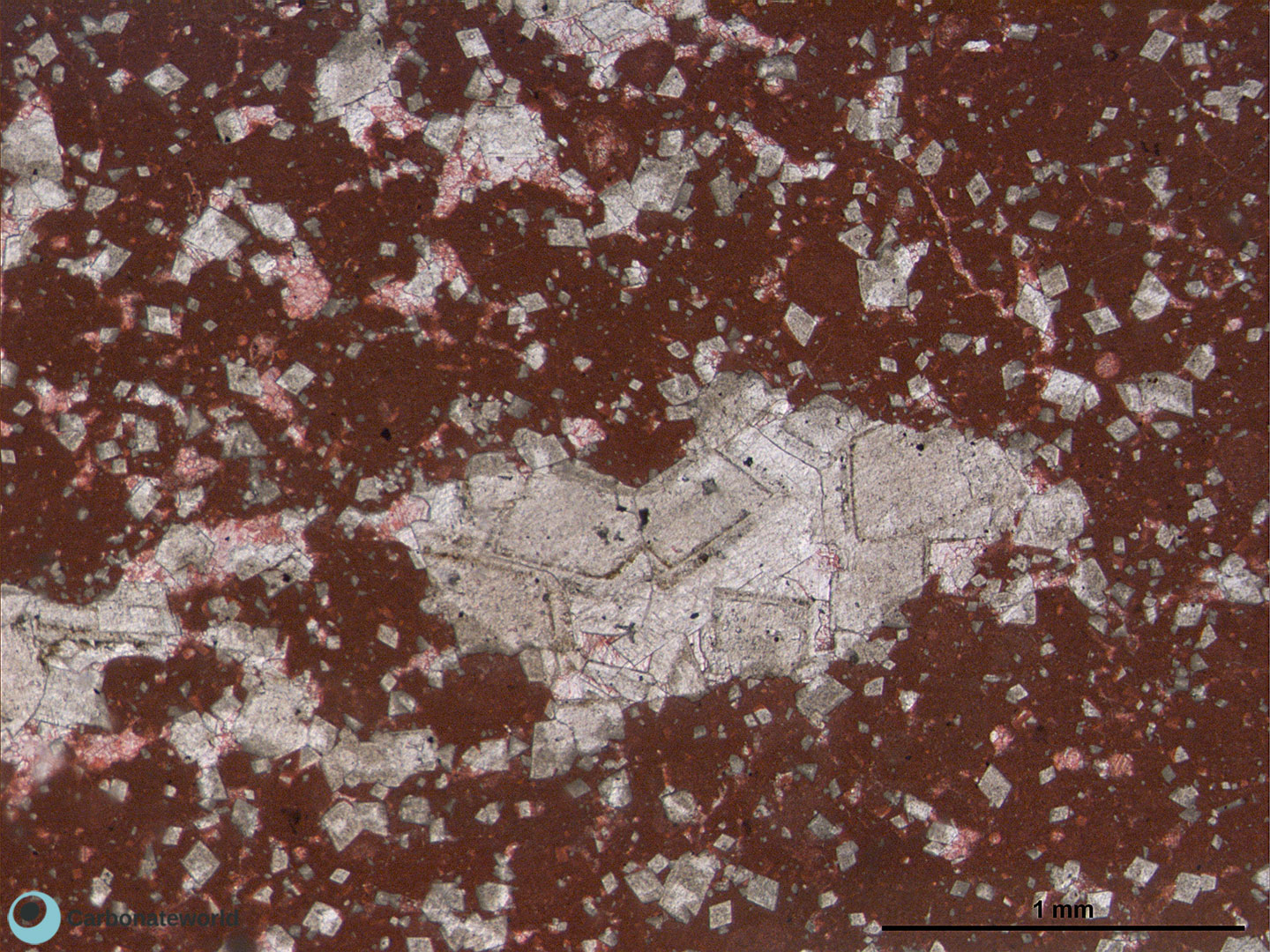
27. Dedolomite
As previous photo, ooidal (dolo)grainstone (pink, alizarin red staining) with 1-2 mm in size, fabric replacive dolomite crystals. Dolomite crystals are affected by a replacive process of transformation of dolomite into calcite with numerous calcitic patches (pink) overlying the dolomitic (grey) crystalline structures.
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

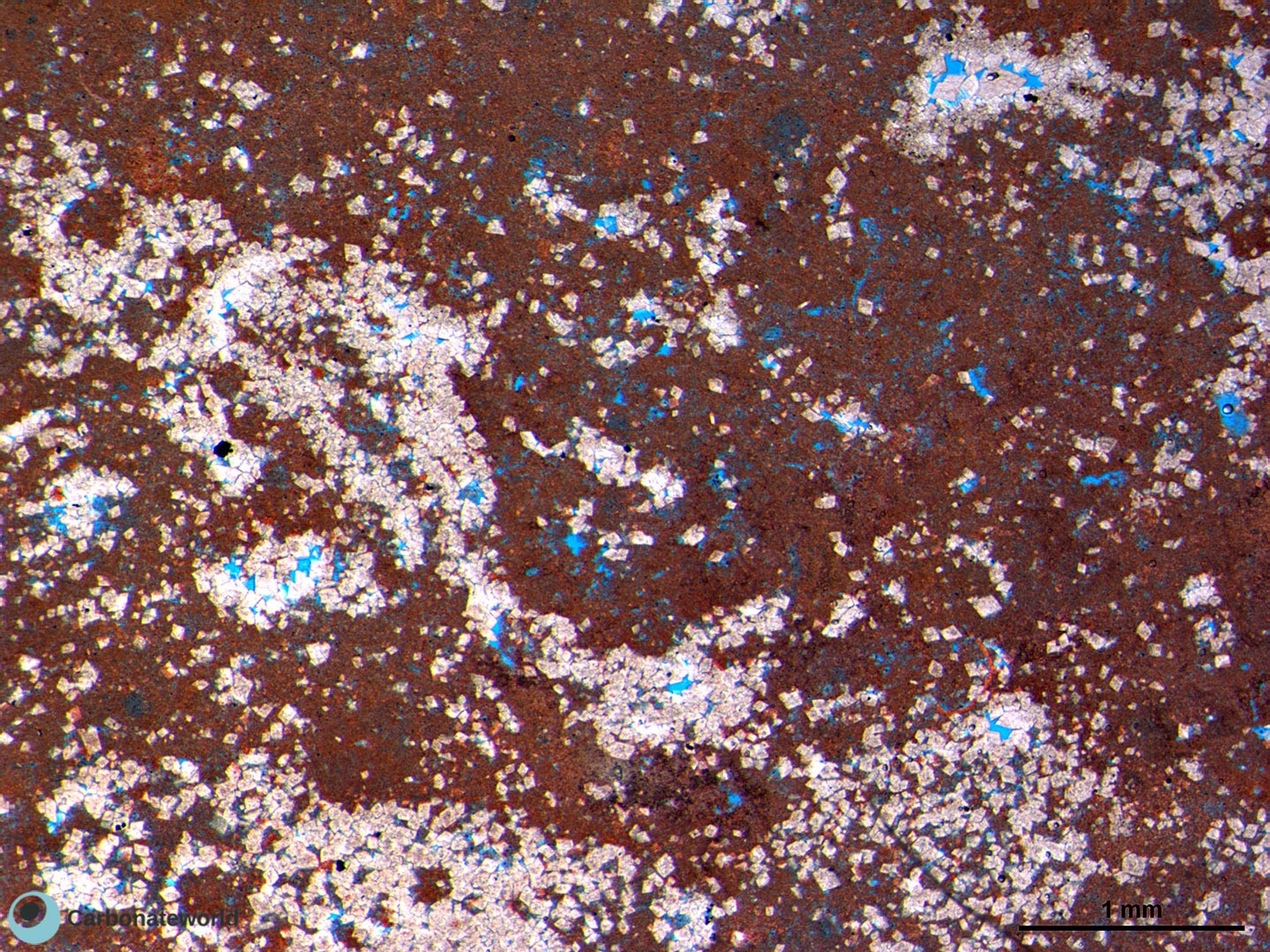
SHOW INFO
28. Subhedral Dolomite
Crystals of radiaxial fibrous calcite, 2-3 mm in height, are lining a clotted peloidal microbial boundstone facies (light pink). Subhedral hypidiotopic mosaics of dolomite (grey/light green) have replaced the radiaxial fibrous marine cement. Turquoise/green is a common colour of ferroan (burial) dolomite after staining with K ferricyanide (Dickson, 1965).
Pennsylvanian, Asturias, N Spain, cf. Bahamonde et al. (2015, 2017)

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
29. Anhedral Dolomite
Skeletal peloidal grainstone to packstone with 50 microns size dolomite crystals (grey/green) forming a xenotopic mosaic over ferroan calcite cement (light blue). Turquoise/green is a common colour of ferroan (burial) dolomite after staining with K ferricyanide (Dickson, 1965).

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
30. Anhedral Dolomite
Replacive dolomite forming < 50 microns crystals (green/grey) next to two fractures filled by burial ferroan calcite (blue with K ferricyanide staining).

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
31. Anhedral Dolomite
Xenotopic mosaic of dolomite (grey) replacive probably on the micrite matrix. In the centre a biomould filled by calcite sparite (dark pink).

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
32. Subhedral Dolomite
Micrite matrix with secondary porosity (blue epoxy) partly replaced by a hypidiotopic mosaic of dolomite (white).

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
33. Euhedral Dolomite
Idiotopic planar-e mosaic of dolomite rhomb crystals (white) replacing micrite. The blue areas are secondary porosity due to micrite dissolution.

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
34. Subhedral Dolomite
Hypydiotopic mosaic of dolomite rhomb crystals (white) replacing a skeletal packstone. The blue areas are secondary porosity due to micrite dissolution. A stylolite is filled by bitumen.

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
35. Subhedral Dolomite
Coated grain (micritised ooids and cortoids) grainstone with sparse euhedral to subhedral dolomite. Dolomite rhombs at grain contacts seem to have been affected by compaction. This might suggest that dolomitization took place before mechanical compaction.
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
36. Subhedral Dolomite
Subhedral to euhedral crystals of dolomite preferentially replacing the micritised grains. The lack of dolomite on the calcite spar cement and the corroded aspect of dolomite at the contact with the calcite spar suggest that dolomite preceded the burial sparite precipitation.
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
37. Euhedral Dolomite
Euhedral dolomite at grain contacts that might have precipitated pre-compaction.
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
38. Subhedral Dolomite
Hypidiotopic mosaic of subhedral dolomite crystals.
Permian, Texas, USA

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
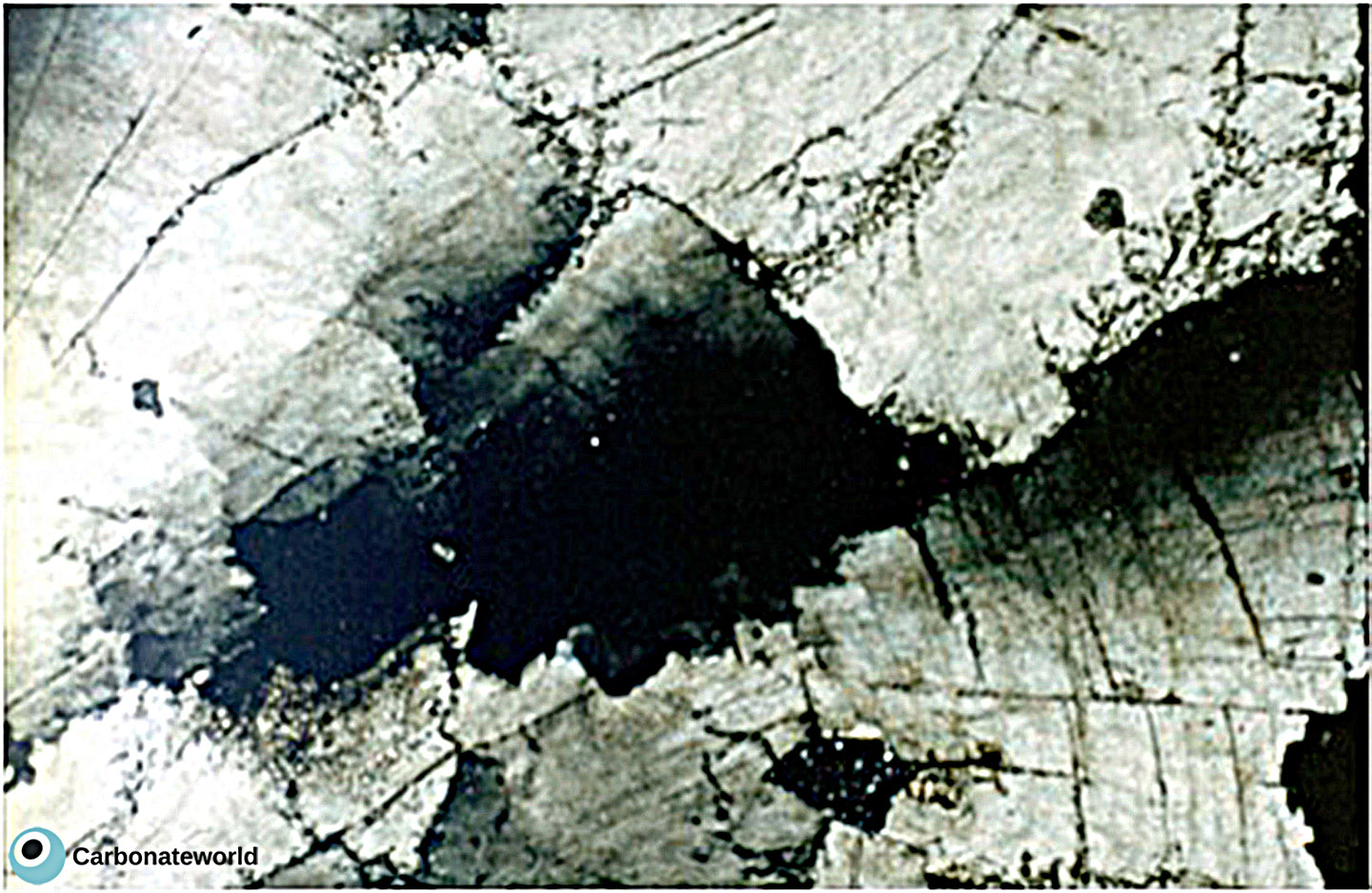
39. Saddle Dolomite
Saddle (or baroque) dolomite is characterised by curved crystals (due to warped crystal lattice), curved cleavage planes and undulose extinction. It is commonly Ca-rich and may have high Fe content and it forms at high (around 100ºC) temperatures (Tucker and Wright, 1990).
Permian, Texas, USA

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
40. Saddle Dolomite
Previous image of saddle dolomite viewed in crossed polarised light showing the undulose extinction.
Permian, Texas, USA

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
41. Saddle Dolomite
Saddle (or baroque) dolomite is characterised by curved crystals (due to warped crystal lattice), curved cleavage planes and undulose extinction. It is commonly Ca-rich and may have high Fe content and it forms at high (around 100ºC) temperatures (Tucker and Wright, 1990).
Permian, Texas, USA

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
42. Saddle Dolomite
Previous image viewed in crossed polarised light. Saddle dolomite is characterised by curved crystals and undulose extinction.
Permian, Texas, USA

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
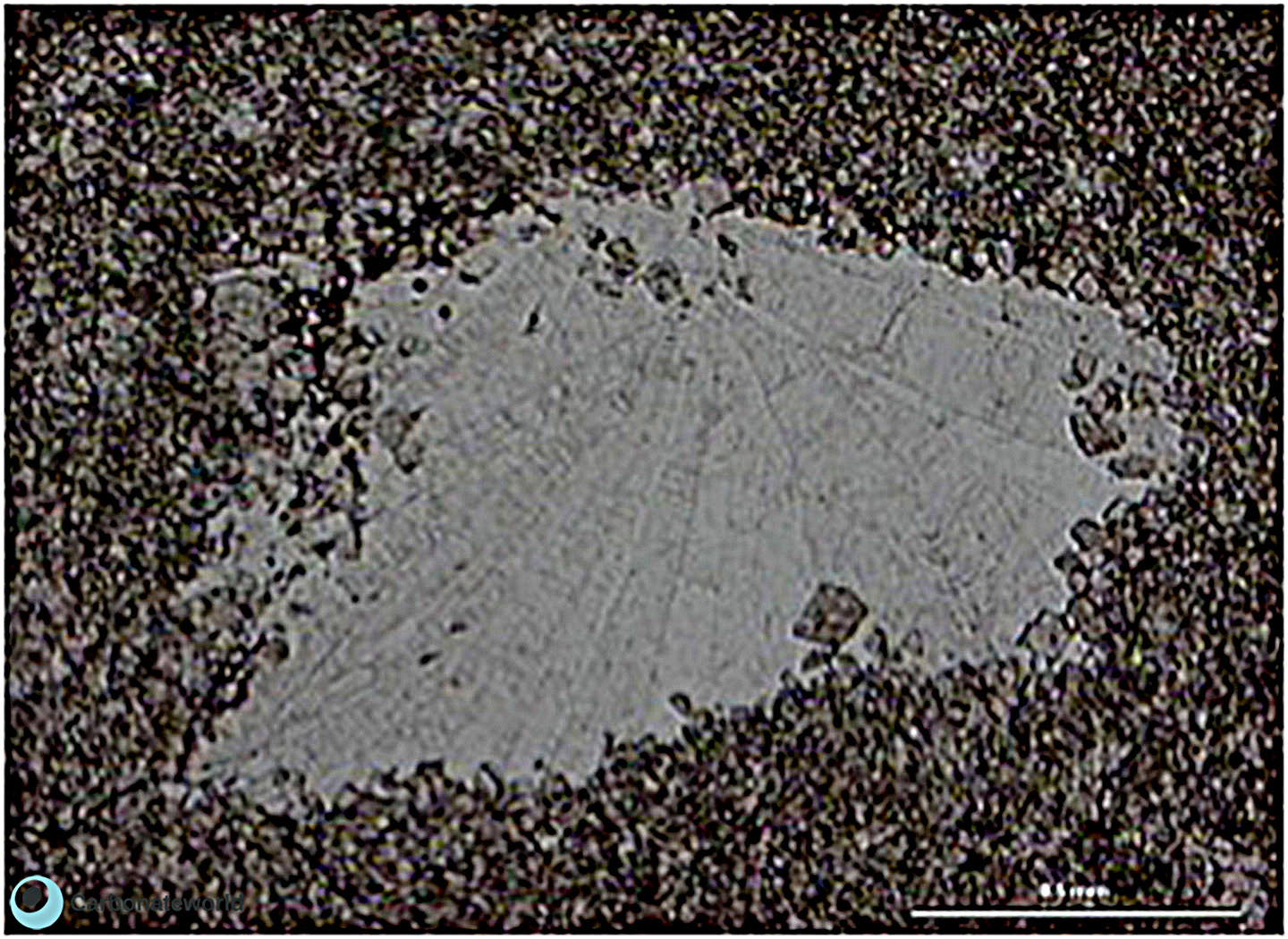
43. Subhedral Dolomite
Hypidiotopic mosaic of replacive euhedral to subhedral dolomite associated with silicification.
Permian, Texas, USA

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
44. Subhedral Dolomite
Previous image viewed in crossed polarised light. Hypidiotopic mosaic of replacive euhedral to subhedral dolomite associated with silicification.
Permian, Texas, USA

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
45. Subhedral Dolomite
View in crossed polarised light of a hypidiotopic mosaic of replacive dolomite. The host rock has been completely replaced.
Permian, Texas, USA

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
46. Subhedral Dolomite
Hypidiotopic mosaic of dolomite.
Permian, Texas, USA

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
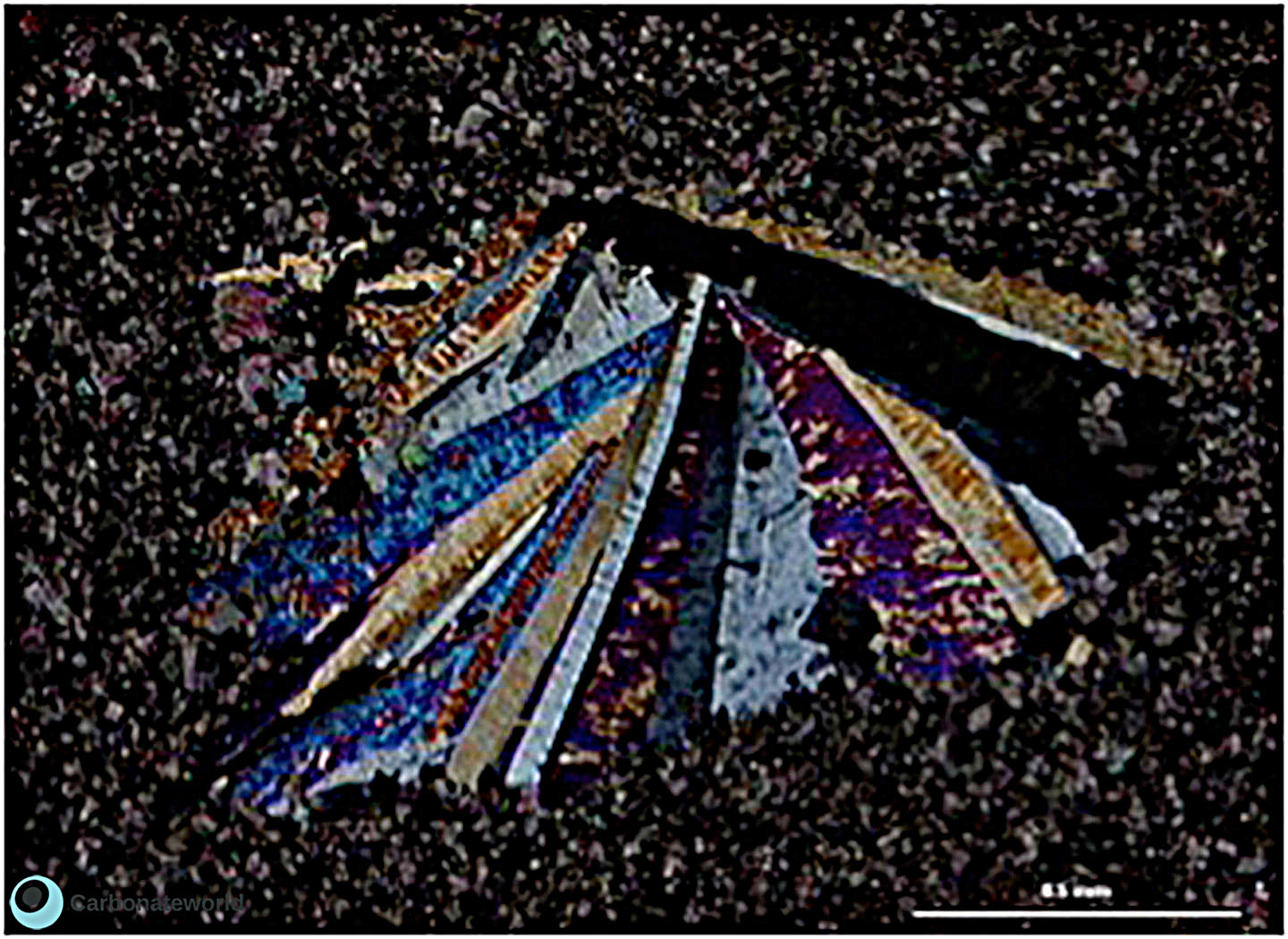
47. Saddle Dolomite
Saddle (baroque) dolomite showing curved cleavage planes.
Permian, Texas, USA

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
48. Anhedral Dolomicrospar
Peloidal pack-grainstone with meniscus micritic cement binding grains followed by fine (<100 microns) calcite spar (pink with Alizarin red). Dolomicrospar (<50 microns; gray) has formed within some of the micrite grains in an intertidal inner ramp.
Lower Jurassic, High Atlas, Morocco, cf. Merino-Tome' et al. (2012)

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
49. Anhedral Dolomicrospar
Peloidal grainstone with binding micritic crusts deposited in an intertidal inner ramp. Sparse dolomicrospar occurs locally on the micritic grains.
Lower Jurassic, High Atlas, Morocco, cf. Merino-Tome' et al. (2012)

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
50. Anhedral Dolomite
Peloidal grainstone with isopachous rims of marine cement (pink with alizarin red) and sparse xenotopic mosaic of dolomite (grey) replacive on the micrite grains.
Lower Jurassic, High Atlas, Morocco, cf. Merino-Tome' et al. (2012)

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
51. Mimetic Dolomicrite
Lower Jurassic intertidal inner ramp fenestral peloidal wackestone with mimetic dolomicrite. Dolomicrite might be of early syn-sedimentary origin in the intertidal setting. Voids (fenestrae) are infilled by calcite spar.
Lower Jurassic, High Atlas, Morocco, cf. Merino-Tome' et al. (2012)

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
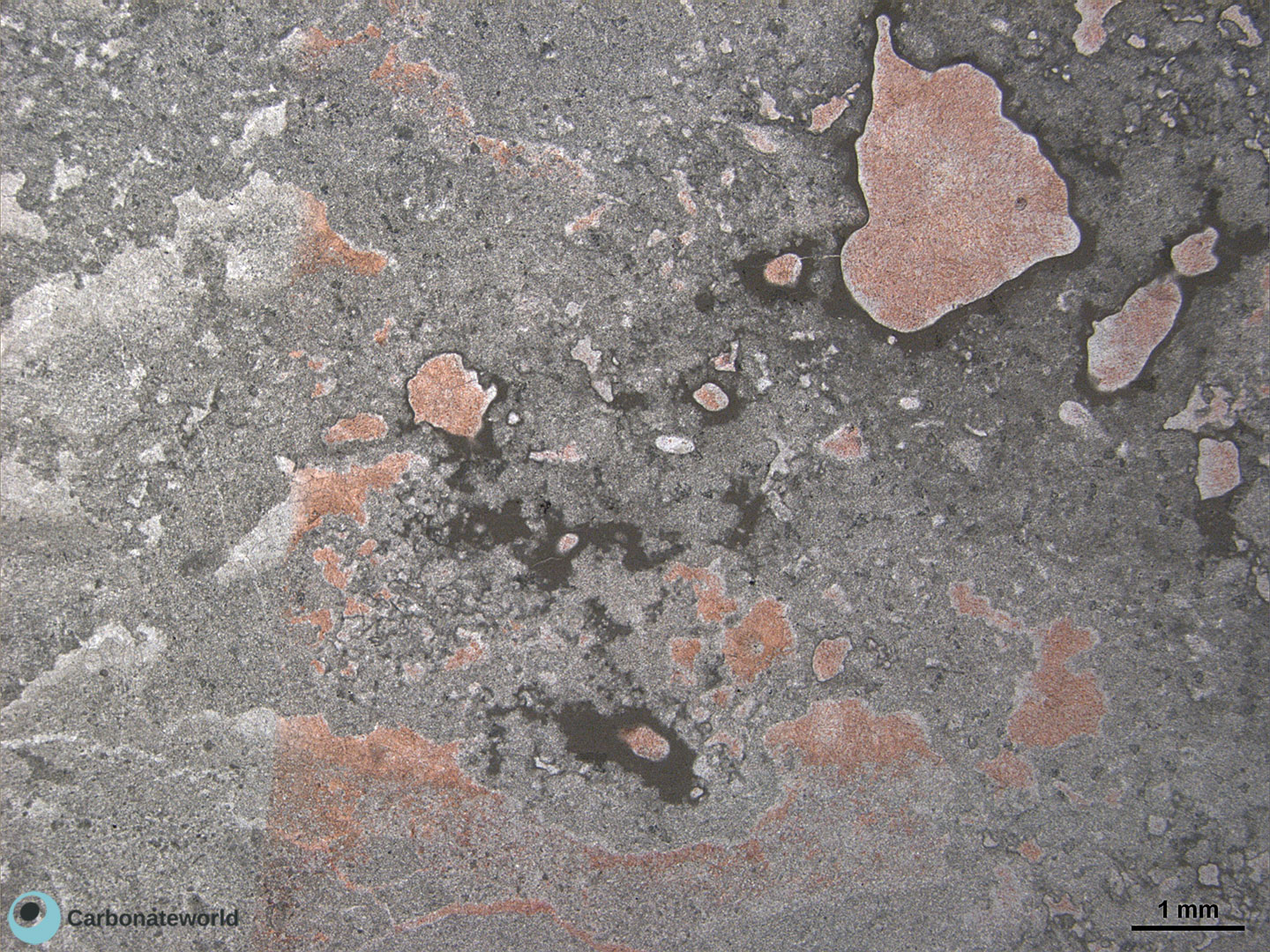
52. Mimetic Dolomicrite
Lower Jurassic intertidal inner ramp fenestral peloidal wackestone with mimetic dolomicrite (grey). Dolomicrite might be of early syn-sedimentary origin in the intertidal evaporative setting. Fenestrae are geopetally filled by a dolomite silt and calcite spar (pink).
Lower Jurassic, High Atlas, Morocco, cf. Merino-Tome' et al. (2012)

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
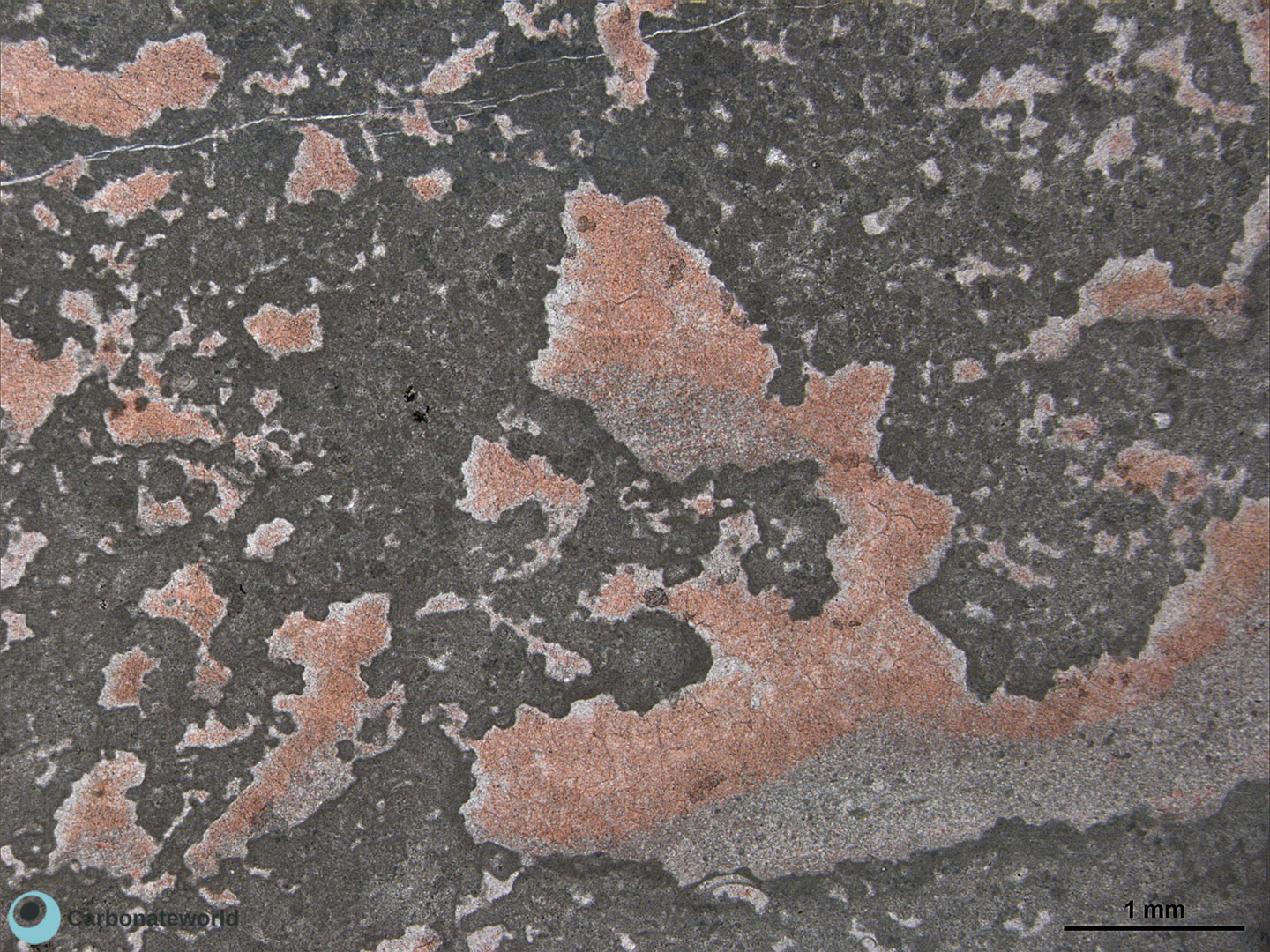
53. Mimetic Dolomicrite
Non obliterative dolomicrite (grey, thin section stained with both alizarin red and K ferricyanide) penecontemporaneous to the deposition of the peloidal packstone. Voids are filled by ferroan (burial) calcite spar (blue).
Lower Jurassic, High Atlas, Morocco, cf. Merino-Tome' et al. (2012)

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
54. Mimetic Dolomite
Non obliterative dolomicrite (grey, thin section stained with both alizarin red and K ferricyanide) penecontemporaneous to the deposition of the ooidal grainstone. Interparticle space includes euhedral dolomite rhombs (white).
Lower Jurassic, High Atlas, Morocco, cf. Merino-Tome' et al. (2012)

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
55. Mimetic Dolomite
Non obliterative dolomicrite (grey, thin section stained with both alizarin red and K ferricyanide) penecontemporaneous to the deposition of the peloidal packstone. Voids are filled by calcite spar (pink).
Lower Jurassic, High Atlas, Morocco, cf. Merino-Tome' et al. (2012)

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
56. Mimetic Dolomite
Pisoidal grainstone from the supratidal zone of the inner ramp with mimetic dolomicrite (grey, thin section stained with both alizarin red and K ferricyanide). Calcite spar cement has a slight blue tone and might be of burial origin (ferroan calcite).
Lower Jurassic, High Atlas, Morocco, cf. Merino-Tome' et al. (2012)

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
57. Mimetic Dolomite
Non obliterative dolomicrite (grey, thin section stained with both alizarin red and K ferricyanide) penecontemporaneous to the deposition of the fenestral peloidal packstone in the intertidal zone. Fenestrae are occluded by calcite spar (pink).
Lower Jurassic, High Atlas, Morocco, cf. Merino-Tome' et al. (2012)

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
58. Mimetic Dolomite
Non obliterative dolomicrite (grey, thin section stained with both Alizarin red and K ferricyanide) on a skeletal peloidal packstone. Interparticle space is occluded by calcite spar (pink).
Lower Jurassic, High Atlas, Morocco, cf. Merino-Tome' et al. (2012)

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
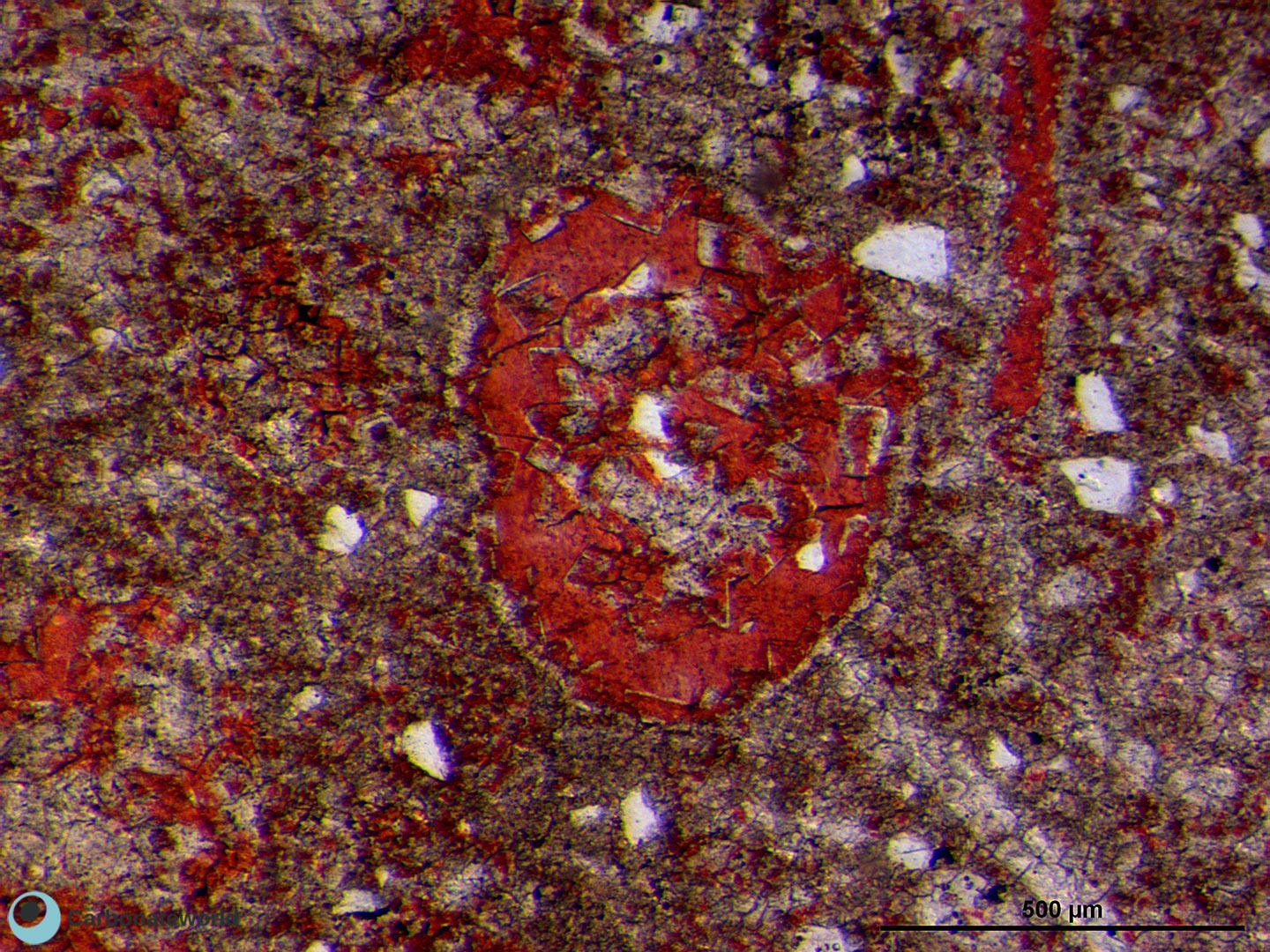
59. Dedolomitization
Stained thin section (alizarin red) showing an euhedral crystal of dolomite (rhombic shape and unstained) replacing an ooidal grainstone. The dolomite is affected by dedolomitization due to exposure to meteoric conditions (telogenesis) as evidenced by the calcitic (pink) irregular patches forming on the dolomite crystal. Field of view approximately 1.5 mm wide.
Mississippian (Chadian), South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
60. Dolomite cement
Skeletal grainstone with bioclast moulds surrounded by micrite envelope. The thin section is stained with alizarin red and it is possible to distinguish the calcite grains and cement from the rhombic dolomite crystal. This dolomite is late diagenetic cement in the intergranular pore space (blue epoxy). Minor mouldic porosity is also present.
Upper Cretaceous (Turonian), Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
61. Mimetic dolomite
This dolo-packstone to grainstone consists of peloids that have been subjected to early micro-crystalline dolomitization that has not obliterated the fabric (mimetic). Limpid dolomite cement lines the fenestral pore, surrounded by mimetic dolomite. The calcite spar occludes the pore space following dolomite cement precipitation. Field of view approximately 1.6 mm wide.
Late Precambrian, Oman

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
62. Etched dolomite
On the right, the ooidal grainstone was partly replaced by euhedral dolomite. The dolomite seals the grain contacts and must have formed after compaction. Dolomite crystals appear to have been corroded before the precipitation of calcite poikilotopic cement. On the left, image in cathodoluminescence shows carbonate grains (ooids and grapestones) micritized and luminescent, dolomite crystals display bright luminescence in the corroded edges and the late diagenetic poikilotopic spar is not luminescent. Field of view approximately 1.5 mm wide.
Mississippian, Gully Oolite, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
63. Etched dolomite
Euhedral dolomite crystals replacing a coated grain grainstone (pink with alizarin red staining). Dolomite crystals show etched edges in the portion grown in the former interparticle pore spaces where poikilotopic cement precipitated following dolomitization.
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
64. Etched dolomite
Dolomite crystals replacing coated grain grainstone (pink with alizarin red staining). Dolomite crystals show etched edges in the portion grown in the former interparticle pore spaces where poikilotopic cement precipitated following dolomitization.
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
65. Dolomization phases
Euhedral dolomite (idiotopic mosaic planar-e) overprinting anhedral (xenotopic) dolomite along a microstylolite.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
66. Euhedral dolomite
Mostly euhedral dolomite crystals forming an idiotopic planar-e mosaic. To notice the intercrystalline porosity evidenced by the blue epoxy.
Upper Cretaceous (Turonian), Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
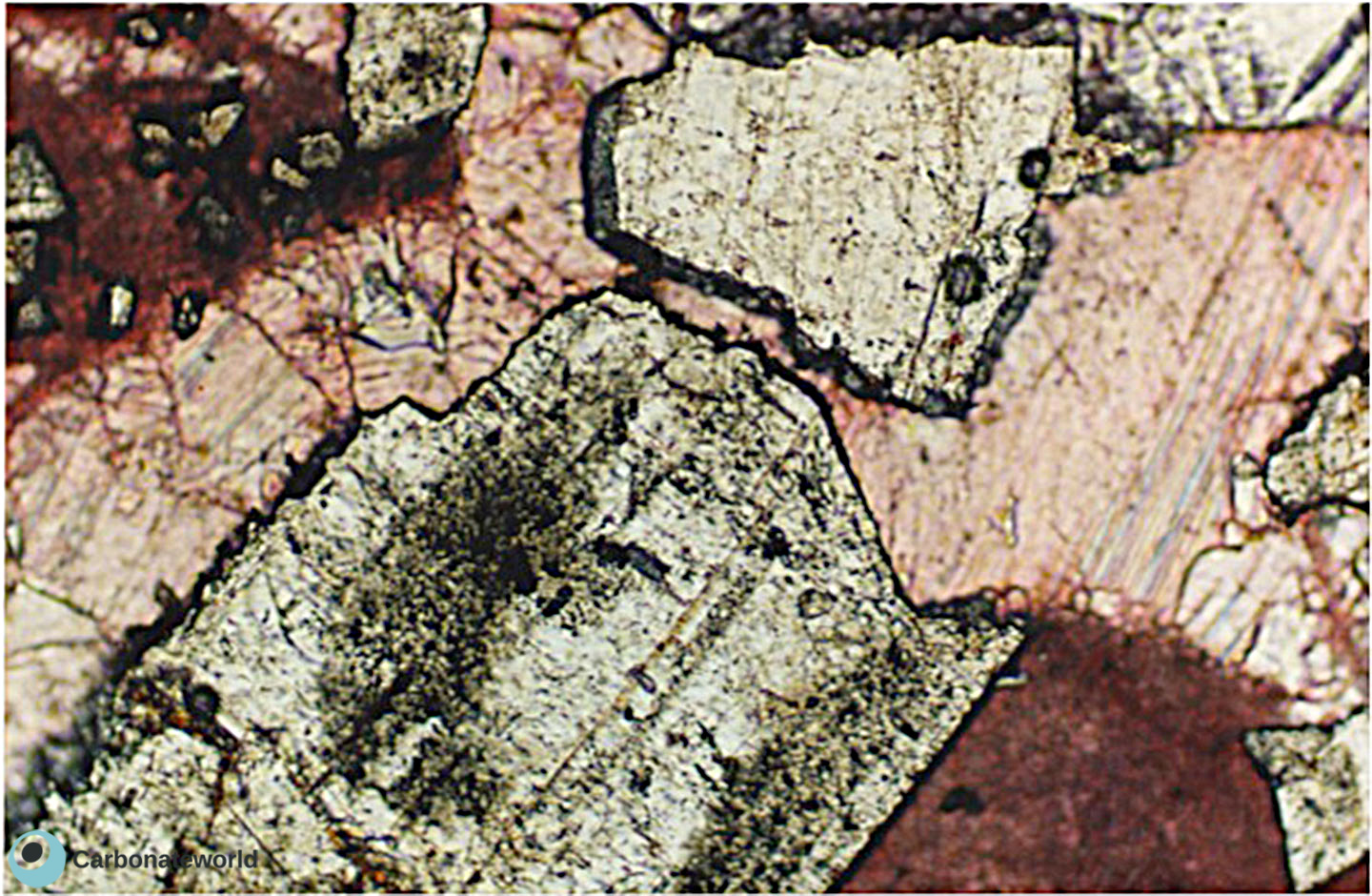
67. Euhedral dolomite
Mostly euhedral dolomite crystals forming an idiotopic planar-e mosaic. To notice the intercrystalline porosity evidenced by the blue epoxy.
Upper Cretaceous (Turonian), Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
68. Euhedral dolomite
Idiotopic planar-e mosaic of dolomite leaving open intercrystalline porosity. Field of view approximately 1.6 mm wide.
Carboniferous, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
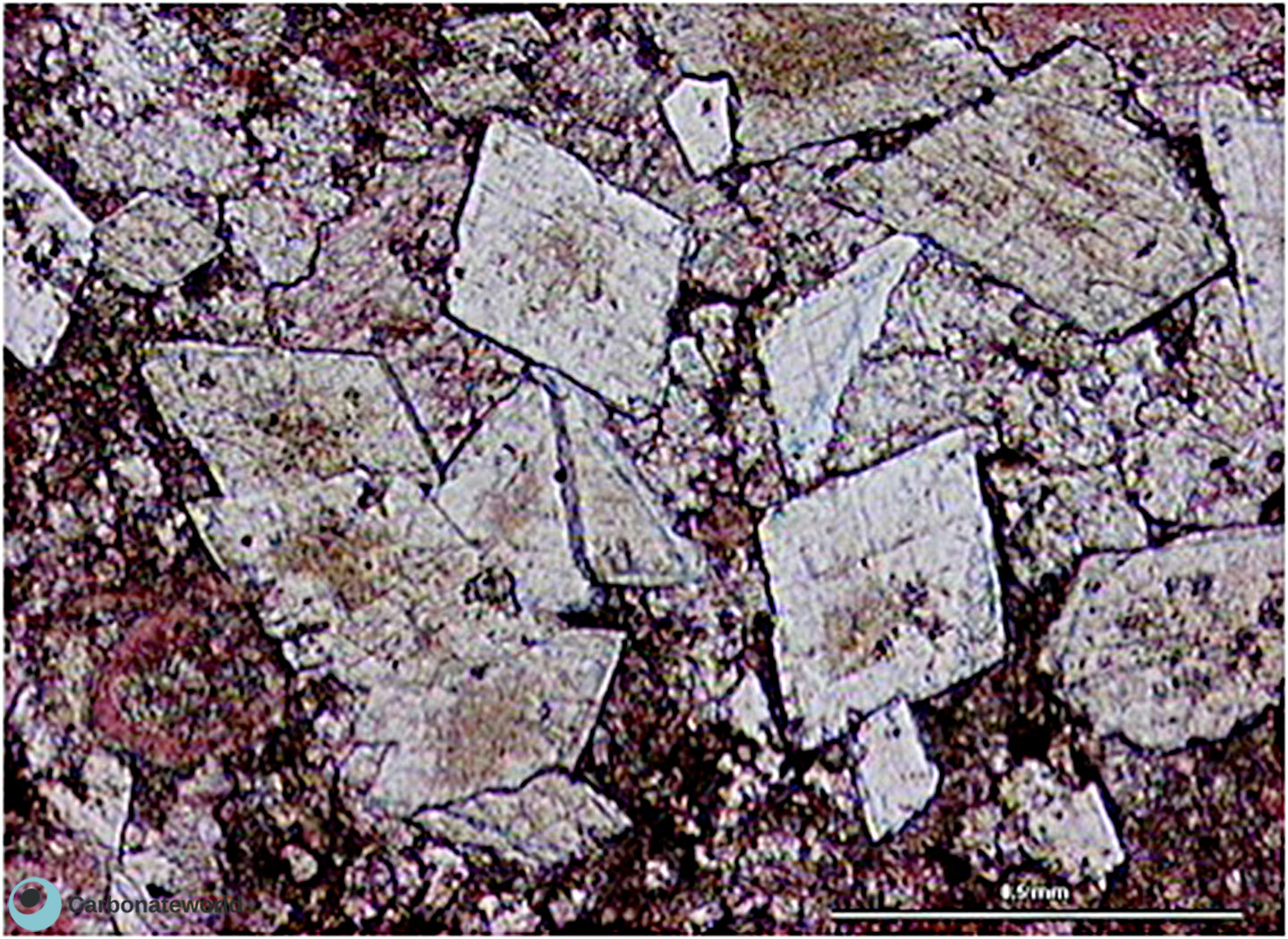
69. Mimetic dolomite
Mimetic dolomite replacing a peloidal fenestral grainstone and dolomite cement lining pore space. Field of view approximately 1.6 mm wide.
Zechstein Limestone, Permian, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
70. Dolomite and anhydrite
Anhydrite and euhedral dolomite formed during burial diagenesis viewed in plane polarized light. Field of view approximately 1.6 mm wide.
Upper Cretaceous (Turonian), Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
71. Dolomite and anhydrite
Anhydrite and dolomite formed during burial diagenesis in plane polarized light. Field of view approximately 1.6 mm wide.
Upper Cretaceous (Turonian), Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
72. Dolomite and anhydrite
Anhydrite and dolomite formed during burial diagenesis in cross-polarized light. Field of view approximately 1.6 mm wide.
Upper Cretaceous (Turonian), Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
73. Dolomite and anhydrite
Anhydrite and dolomite formed during burial diagenesis in cross polarized light.
Upper Cretaceous (Turonian), Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
74. Saddle dolomite
Saddle (baroque) dolomite that formed in burial diagenetic environment viewed in cross polarized light showing undulose extinction. Field of view approximately 1 mm wide.
Jurassic, N Spain

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
75. Saddle dolomite
Saddle (baroque) dolomite that formed in burial diagenetic environment viewed in plane polarized light showing curved cleavage surfaces. Field of view approximately 1 mm wide.
Jurassic, N Spain

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
76. Saddle dolomite
Saddle dolomite (unstained) enveloping bladed calcite (stained pink with alizarine red) in a fracture in a skeletal (rotalid foraminifera) packstone.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
77. Saddle dolomite
Saddle dolomite in a vein in a skeletal packstone. Both have been leached and the clay mineral dickite has filled the late corrosion pore space. Image in cross polarisers show saddle dolomite undulose/sweeping extinction.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
78. Saddle dolomite
Previous image in plane polarisers. Saddle dolomite in a vein in a skeletal packstone. Both have been leached and the clay mineral dickite has filled the late corrosion pore space.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
79. Saddle dolomite
Image in cross polarisers of corroded saddle dolomite in a fracture showing undulose/sweeping extinction.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
80. Saddle dolomite
Saddle dolomite in plane polarizers.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
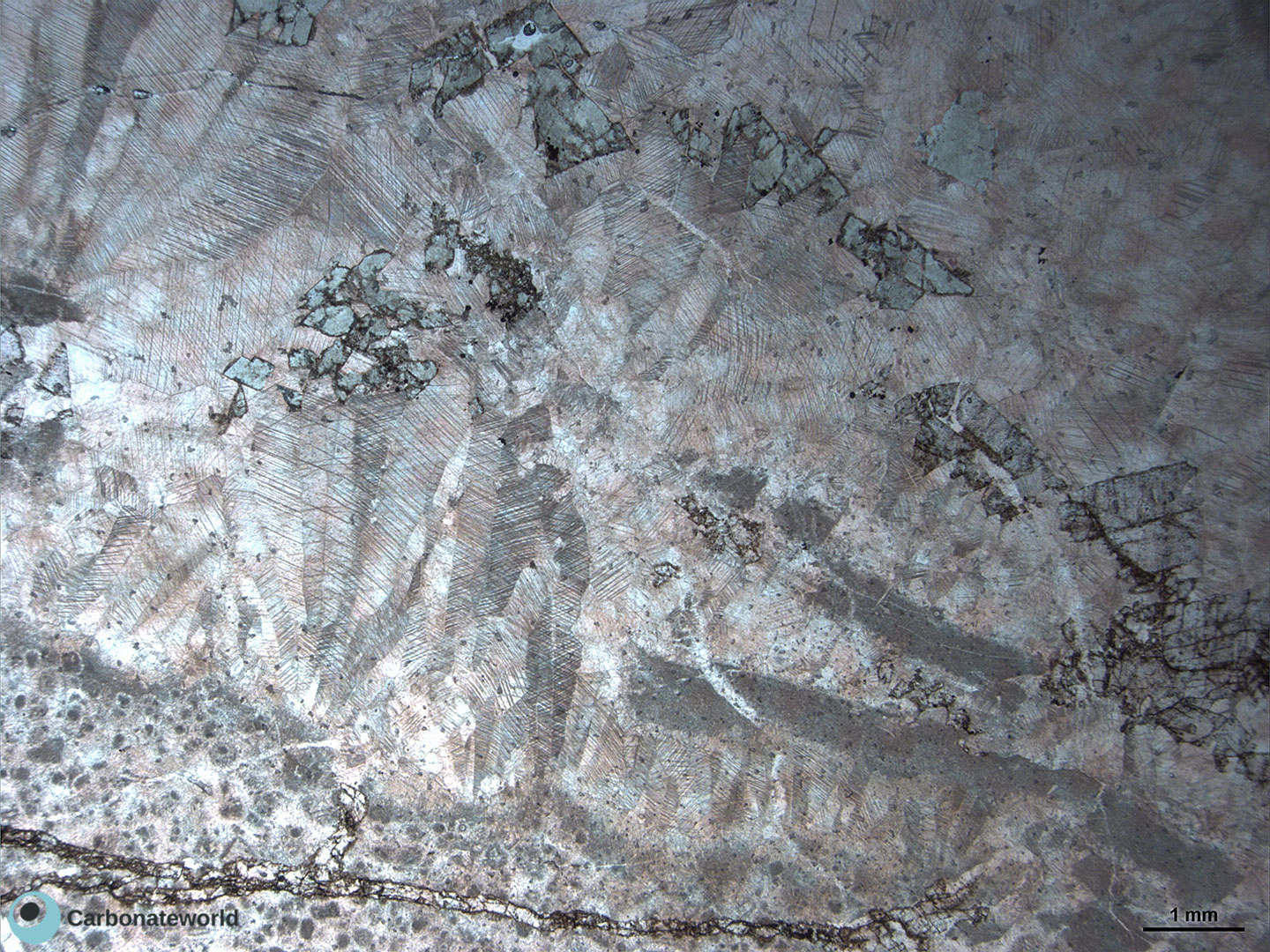
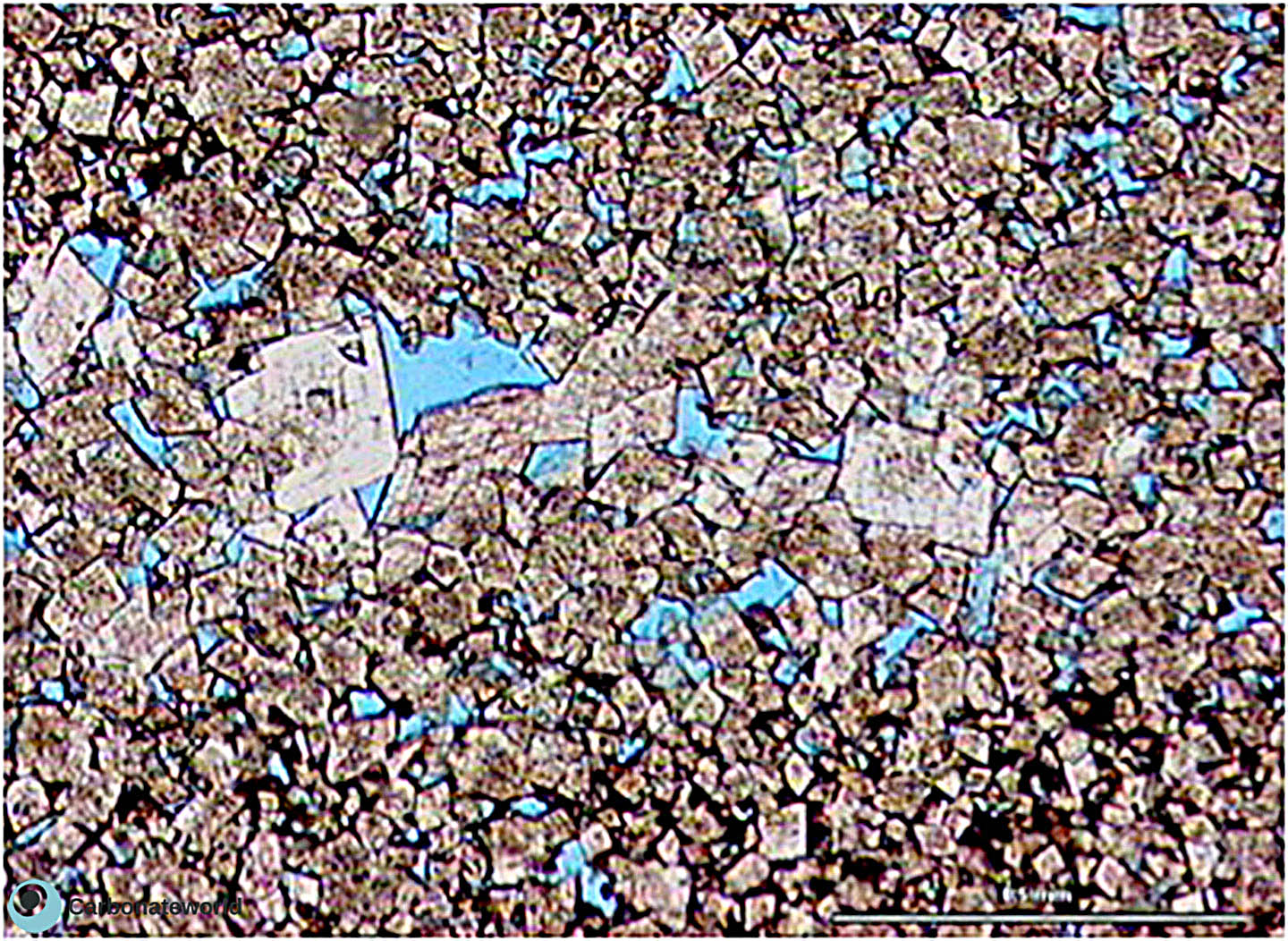
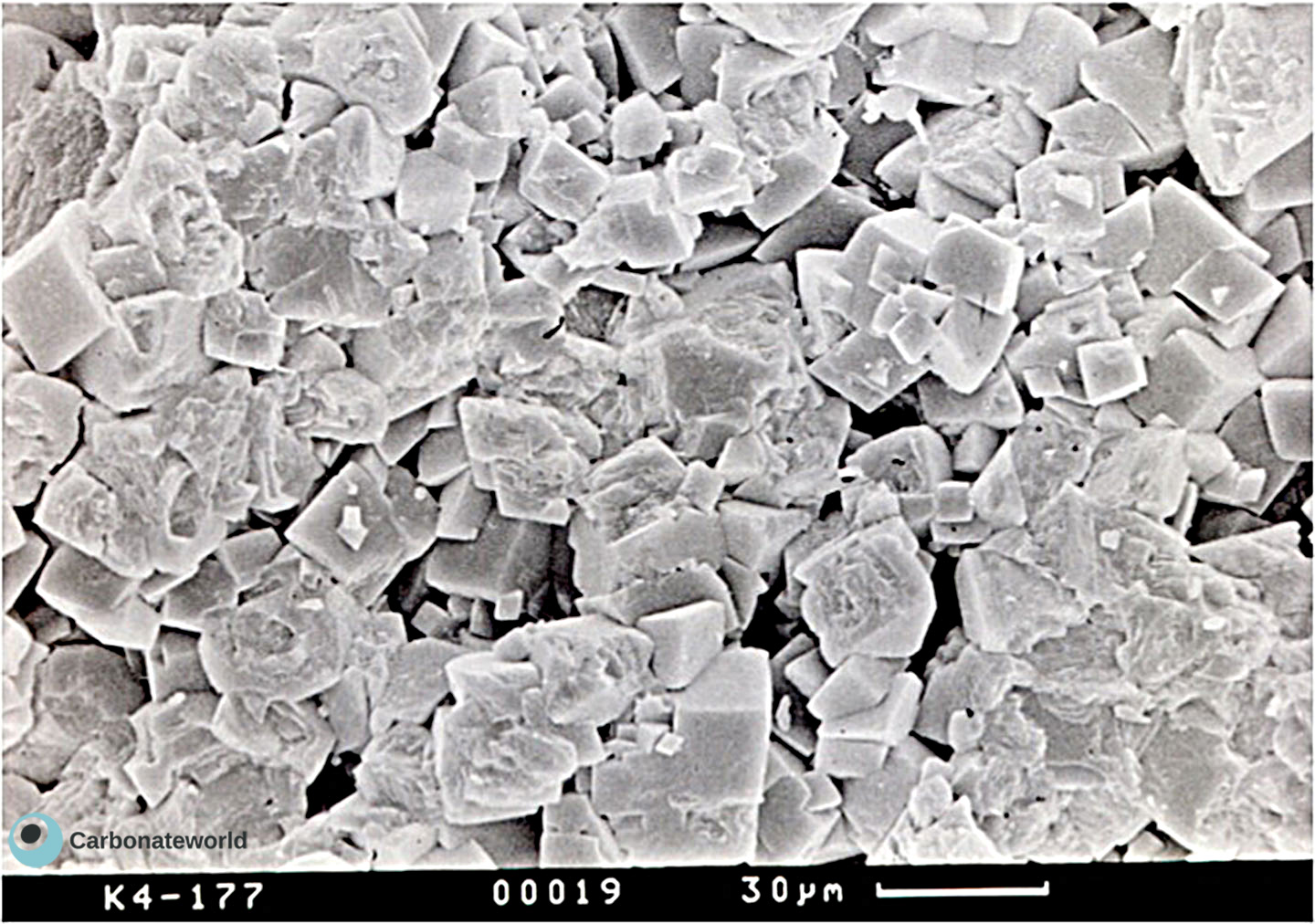
81. SEM dolomite
SEM image of dolomite crystals forming an idiotopic to hypidiotopic (dolomite planar-e and –s type) mosaic.
Carboniferous, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
IMAGE INDEX
1. Euhedral Dolomite
2. Dolomitization Timing
3. Zoned Dolomite
4. Euhedral/Subhedral Dolomite
5. Subhedral Dolomite
6. Euhedral Dolomite
7. Zoned Dolomite
8. Zoned Dolomite
9. Anhedral Dolomite
10. Anhedral Dolomite
11. Anhedral Dolomite
12. Anhedral Dolomite
13. Anhedral Dolomite
14. Euhedral Dolomite
15. Euhedral Dolomite
16. Subhedral Dolomite
17. Euhedral Dolomite
18. Euhedral Dolomite
19. Euhedral Dolomite
20. Euhedral Dolomite
21. Dolomite Cement
22. Dolomite Cement
23. Dolomite Cement
24. Dedolomite
25. Dedolomite
26. Dedolomite
27. Dedolomite
28. Subhedral Dolomite
29. Anhedral Dolomite
30. Anhedral Dolomite
31. Anhedral Dolomite
32. Subhedral Dolomite
33. Euhedral Dolomite
34. Subhedral Dolomite
35. Subhedral Dolomite
36. Subhedral Dolomite
37. Euhedral Dolomite
38. Subhedral Dolomite
39. Saddle Dolomite
40. Saddle Dolomite
41. Saddle Dolomite
42. Saddle Dolomite
43. Subhedral Dolomite
44. Subhedral Dolomite
45. Subhedral Dolomite
46. Subhedral Dolomite
47. Saddle Dolomite
48. Anhedral Dolomicrospar
49. Anhedral Dolomicrospar
50. Anhedral Dolomite
51. Mimetic Dolomicrite
52. Mimetic Dolomicrite
53. Mimetic Dolomicrite
54. Mimetic Dolomite
55. Mimetic Dolomite
56. Mimetic Dolomite
57. Mimetic Dolomite
58. Mimetic Dolomite
59. Dedolomitization
60. Dolomite cement
61. Mimetic dolomite
62. Etched dolomite
63. Etched dolomite
64. Etched dolomite
65. Dolomization phases
66. Euhedral dolomite
67. Euhedral dolomite
68. Euhedral dolomite
69. Mimetic dolomite
70. Dolomite and anhydrite
71. Dolomite and anhydrite
72. Dolomite and anhydrite
73. Dolomite and anhydrite
74. Saddle dolomite
75. Saddle dolomite
76. Saddle dolomite
77. Saddle dolomite
78. Saddle dolomite
79. Saddle dolomite
80. Saddle dolomite
81. SEM dolomite

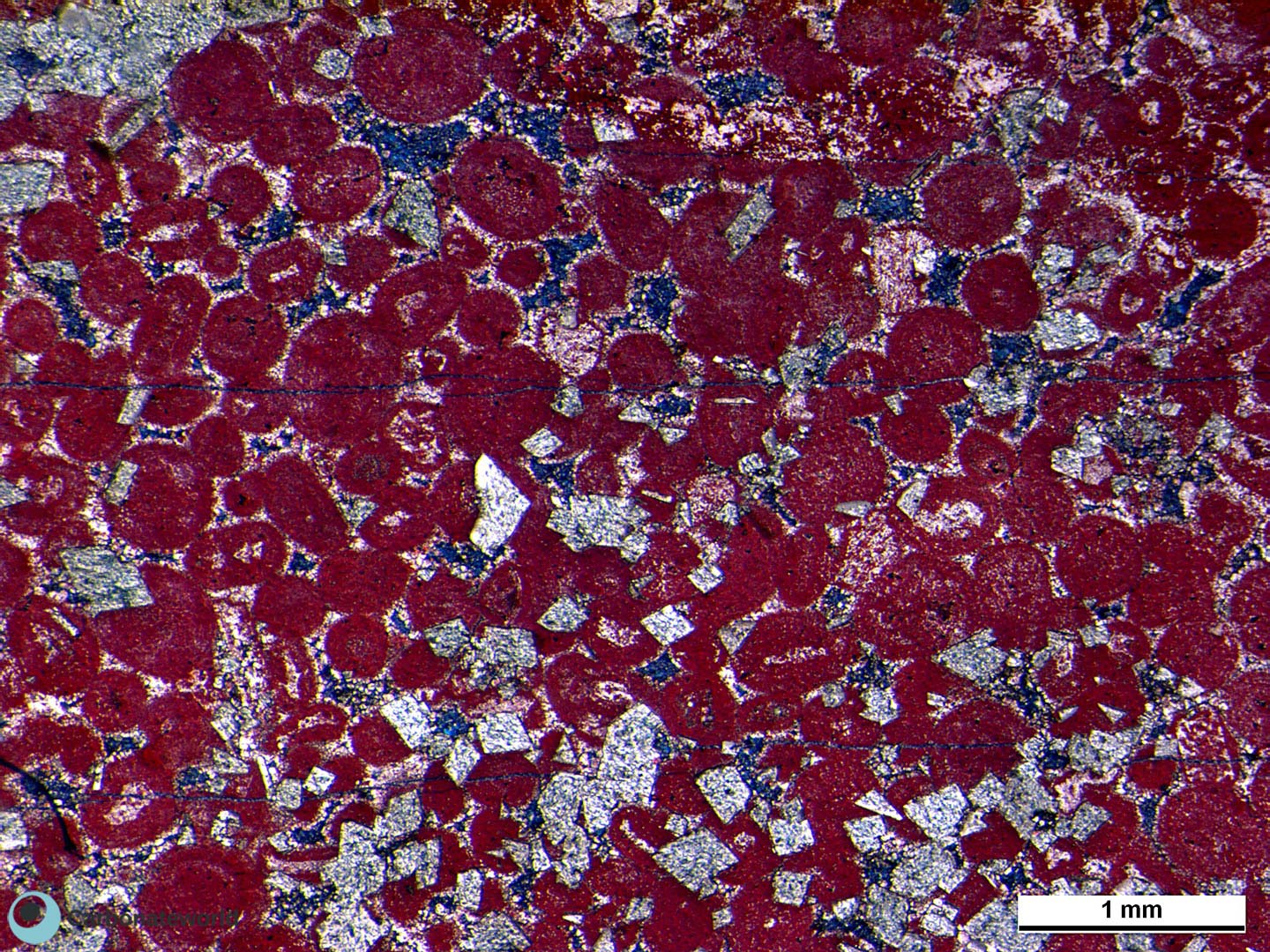

Dolomite

Ferroan calcite cement
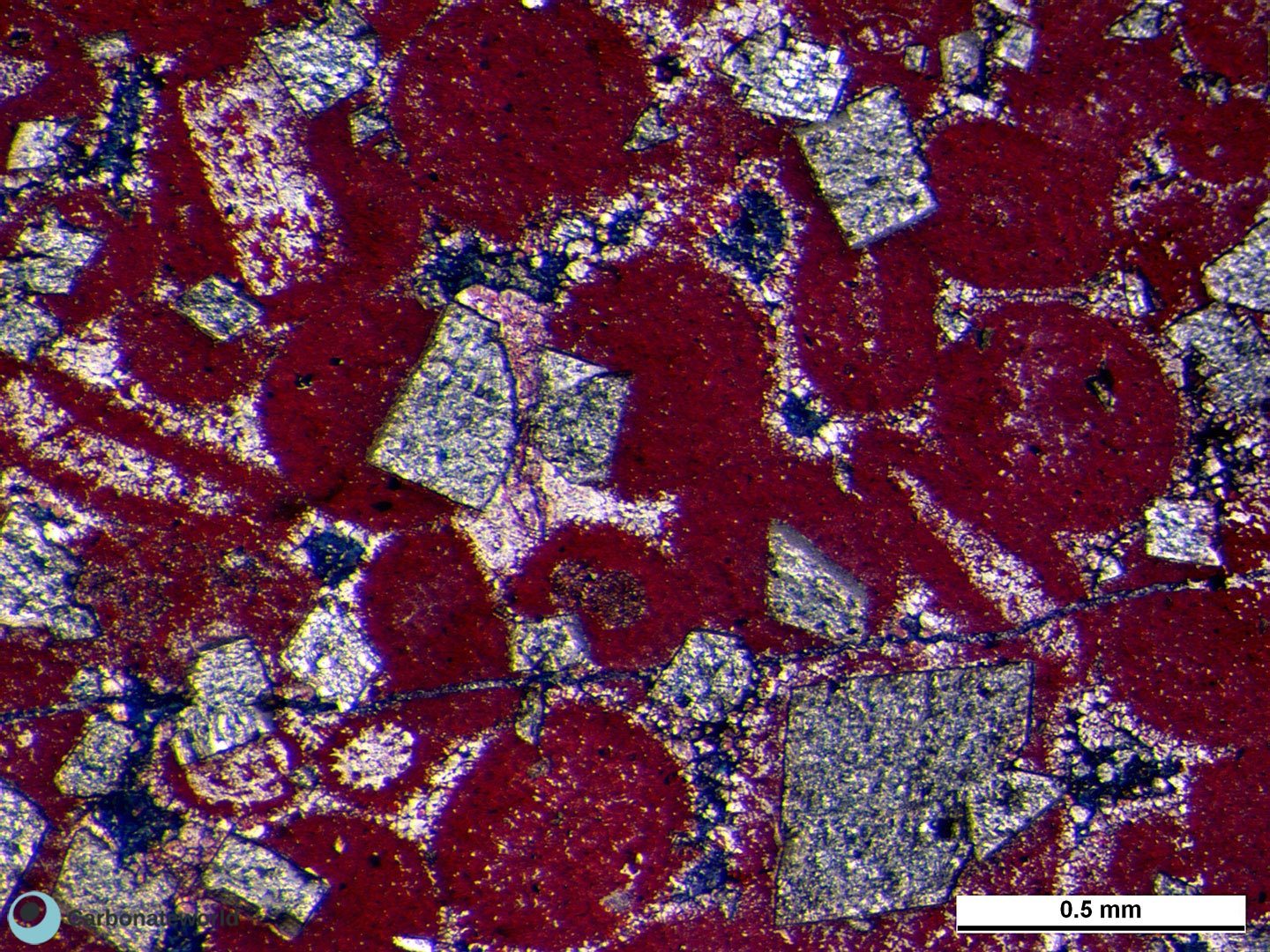

Dolomite
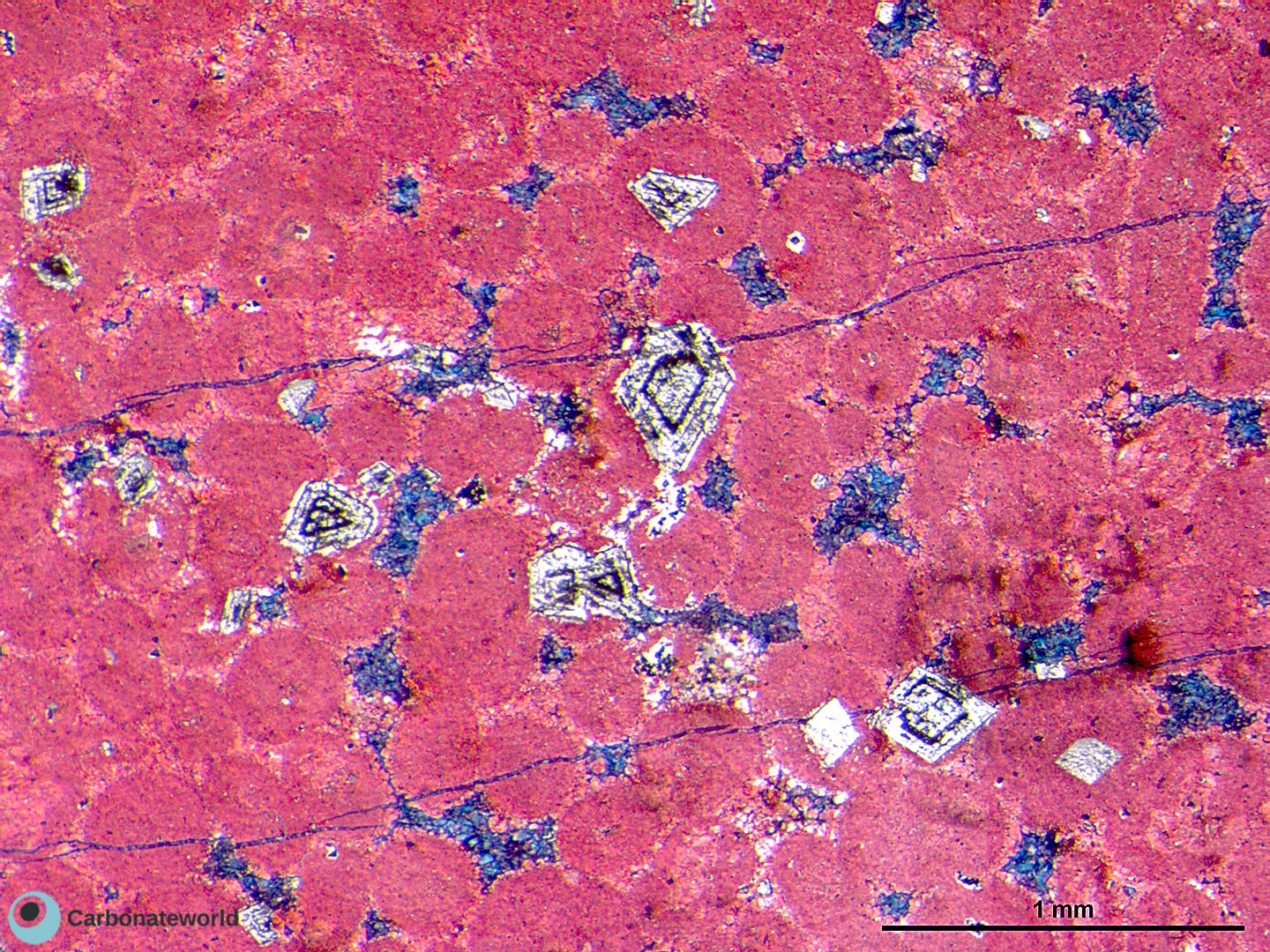

Dolomite

Ferroan calcite cement


Ooidal grainstone

Dolomite
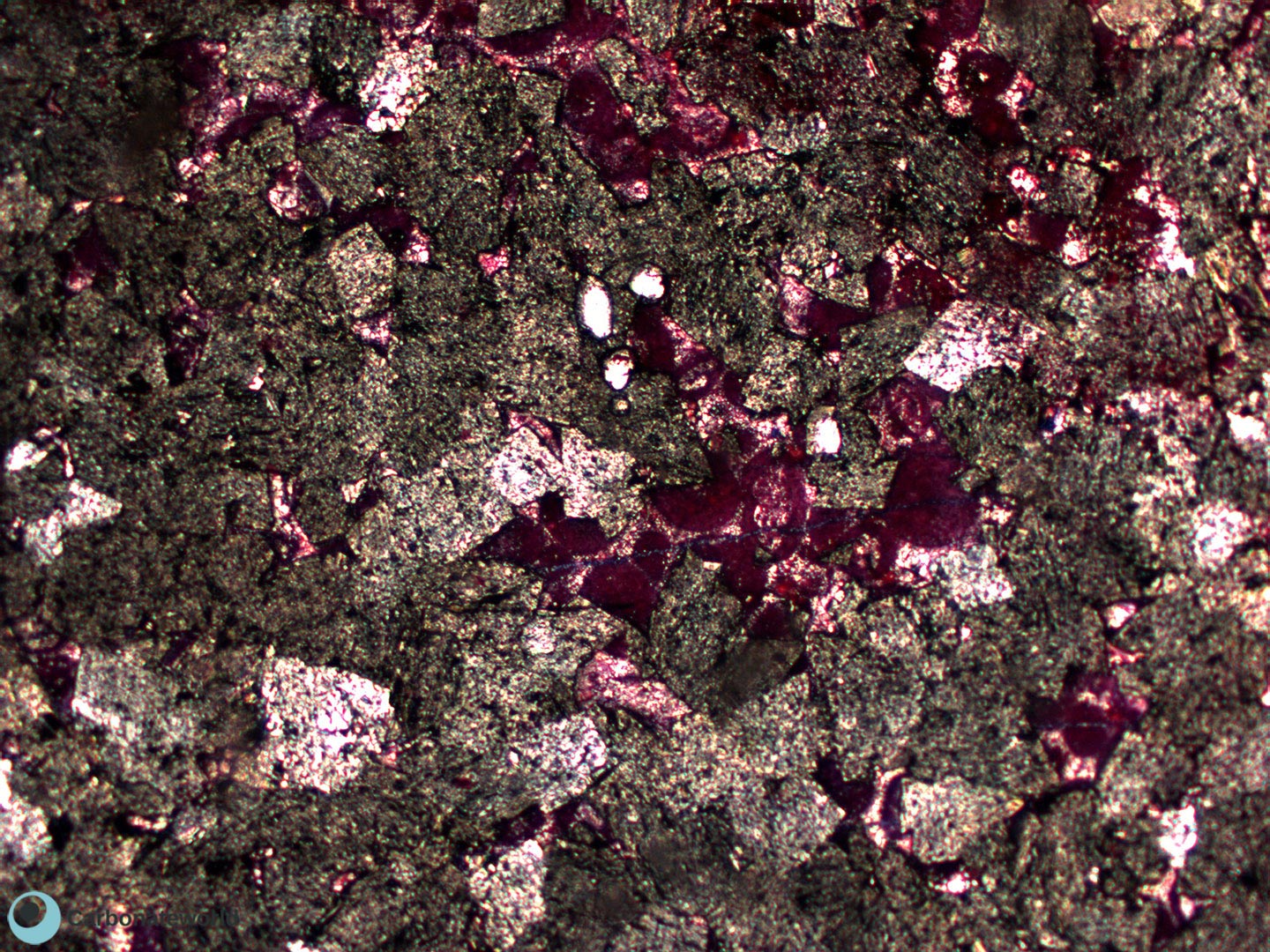

Subhedral dolomite


Dolomite

Microborings

Dolomite

Dolomite

Dolomite

Echinoderm

Dolomite

Dolomite

Dolomite

echinoderm

Dolomite

Dolomite

Dolomite

Dolomite

Dolomite

Fenestrae

Dolomite

Fenestrae

Dolomite

Calcite spar in fenestrae

Dolomite

Dolomite cement

Calcite spar cement

Dolomite cement

Calcite spar cement
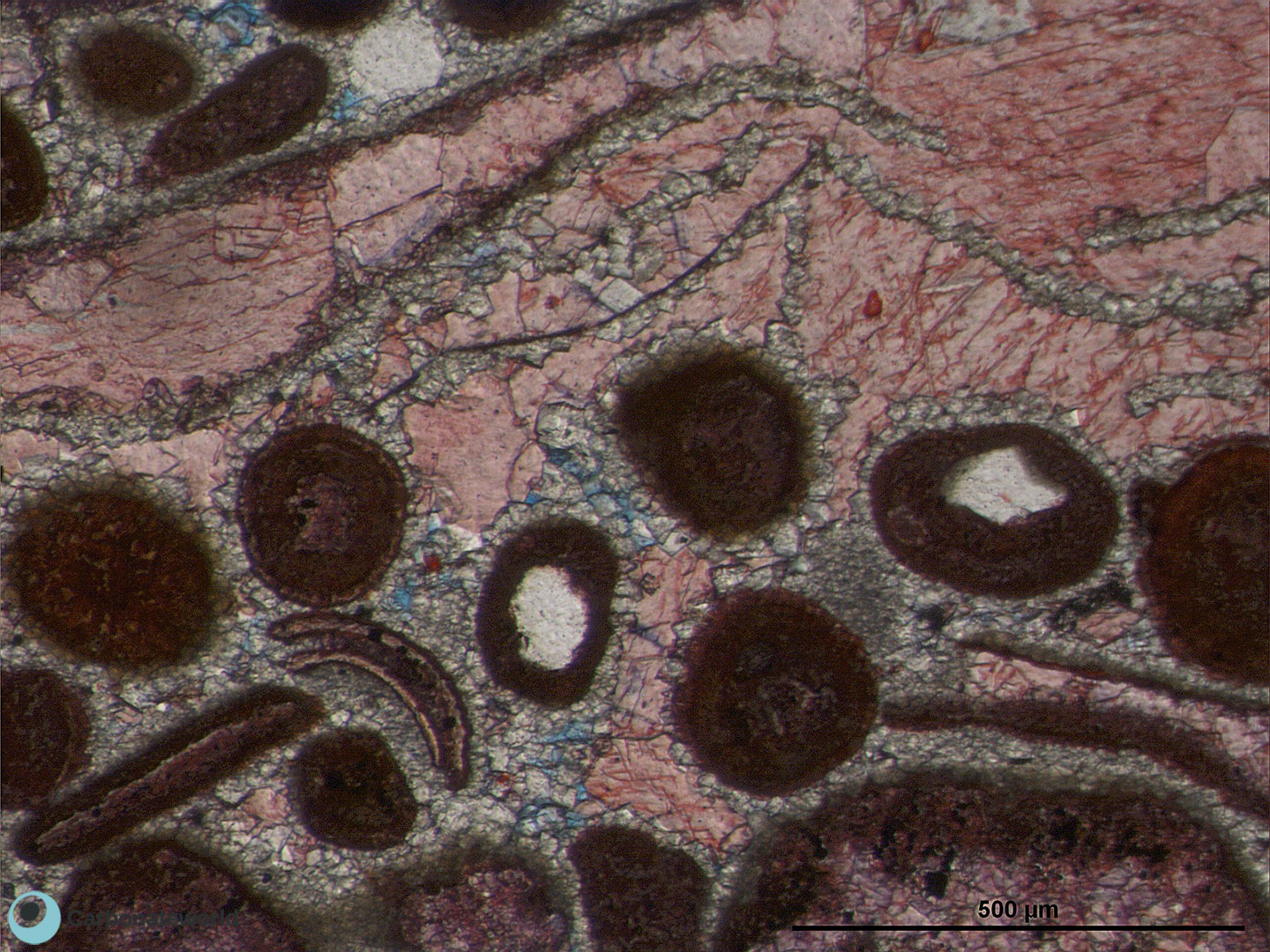

Dolomite cement

Calcite spar cement
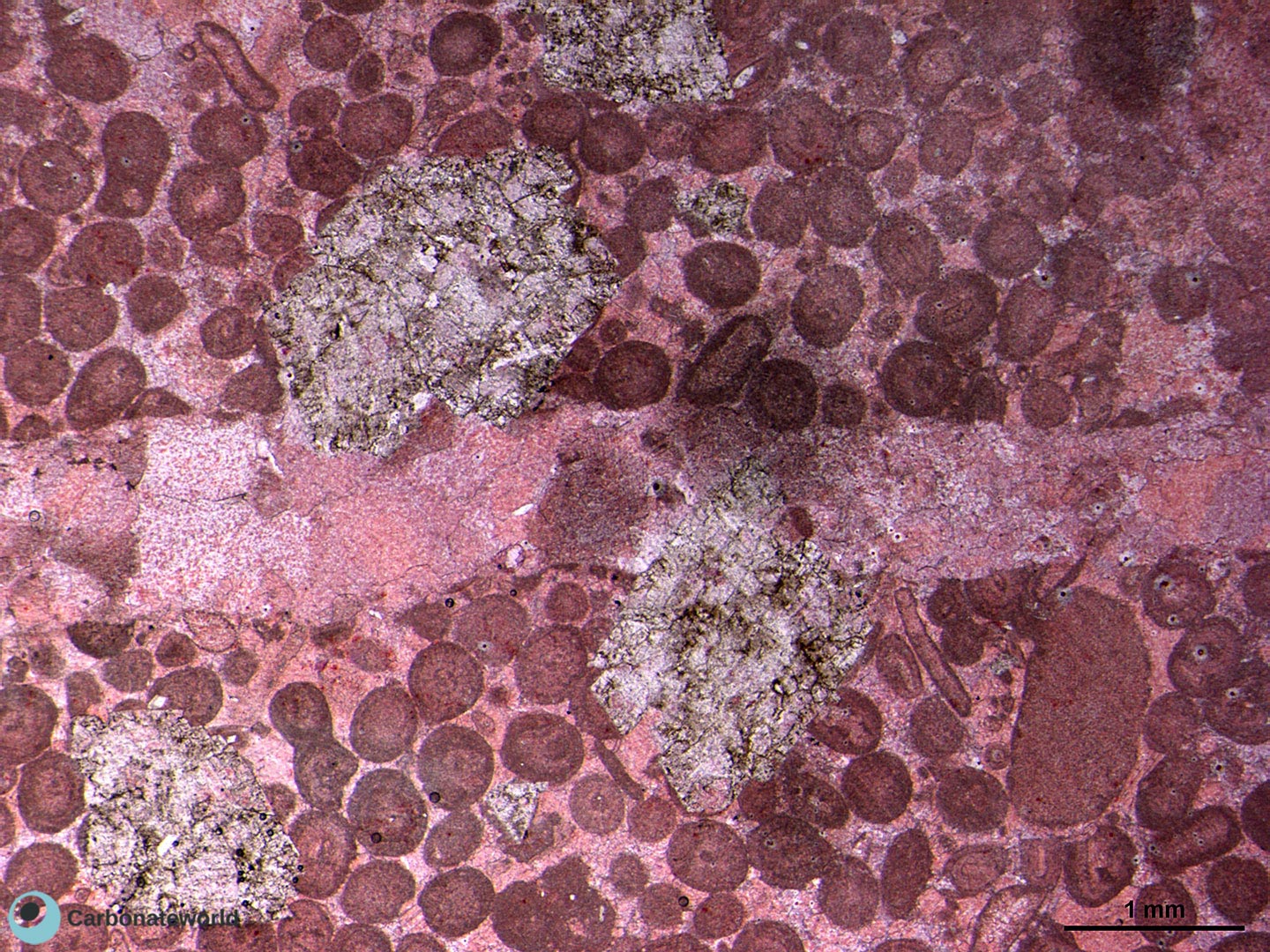

Dedolomitization on dolomite
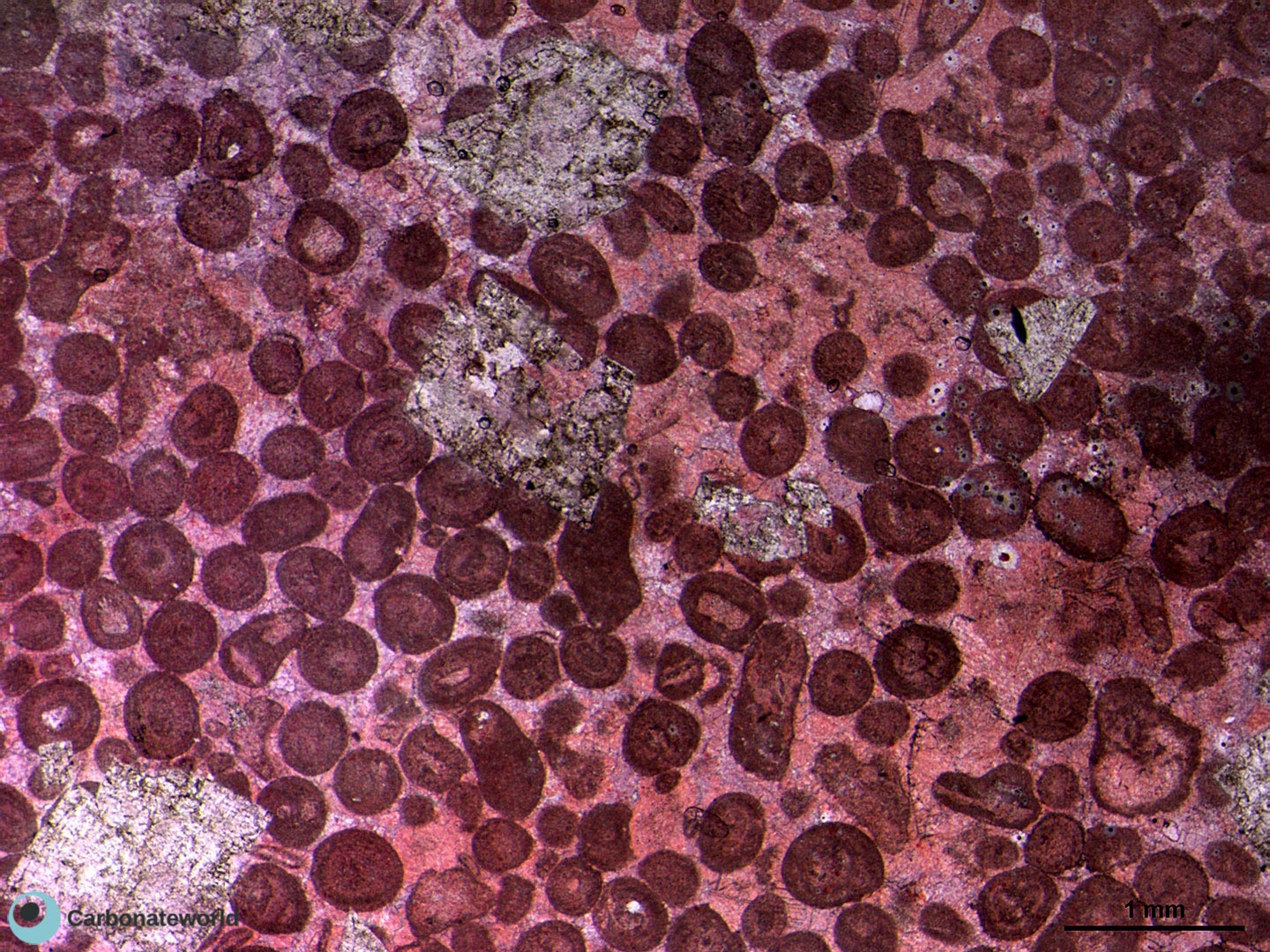

Dedolomitization on dolomite
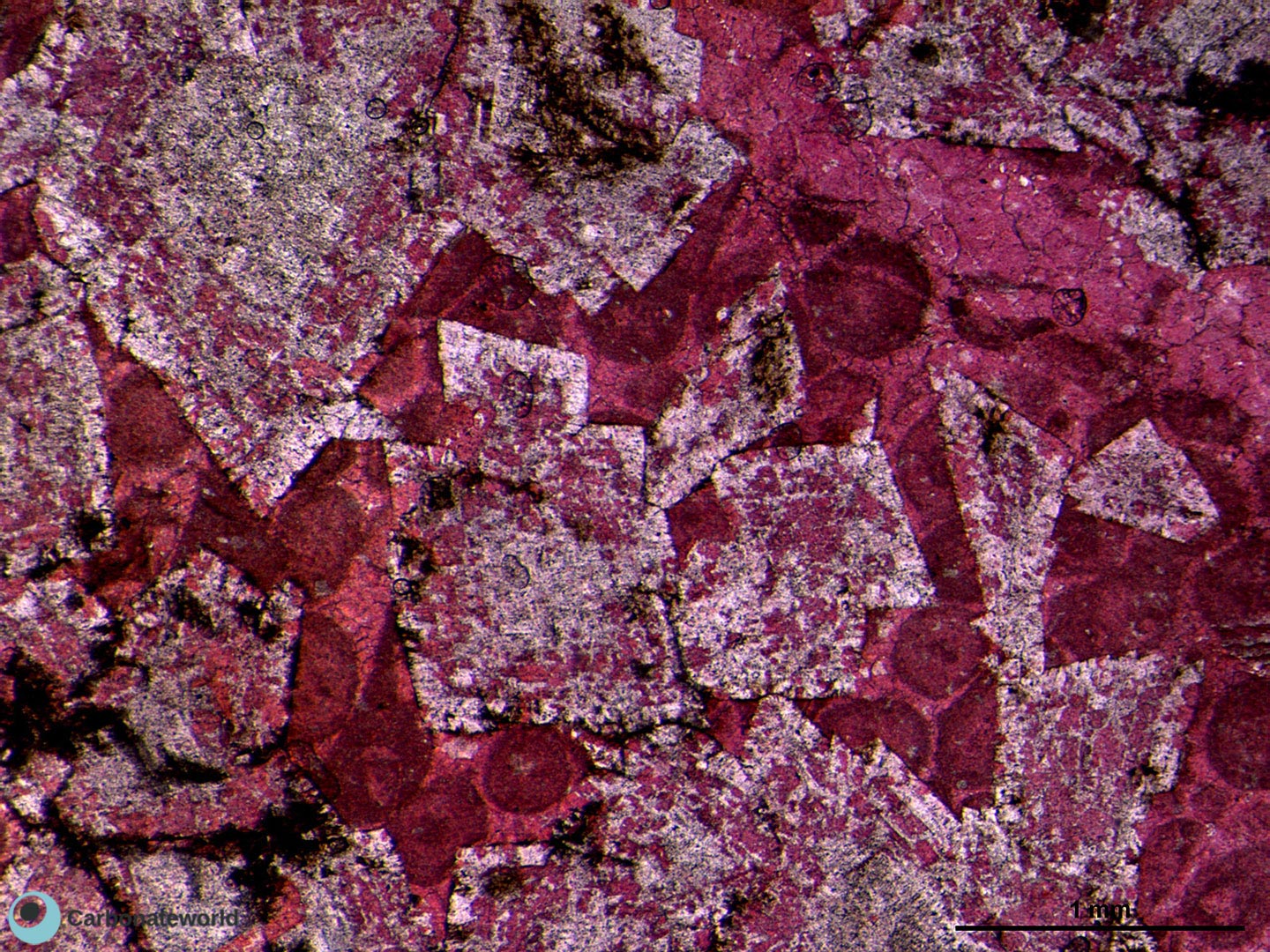

Dedolomitization on dolomite

Dedolomitization on dolomite


Dolomite

Radiaxial fibrous calcite


Dolomite

Dolomite

Ferroan calcite

Dolomite

Dolomite

Dolomite and porosity


Dolomite

Stylolite

Dolomite at grain contacts

Dolomite

Dolomite








Dolomite

Dolomite

Dolomite


Dolomicrite

Calcite spar


Mimetic dolomicrite

Fenestrae

Dolomicrite

ferroan calcite

Dolomicrite

Dolomicrite

Calcite spar

Dolomicrite

Fenestrae with calcite spar
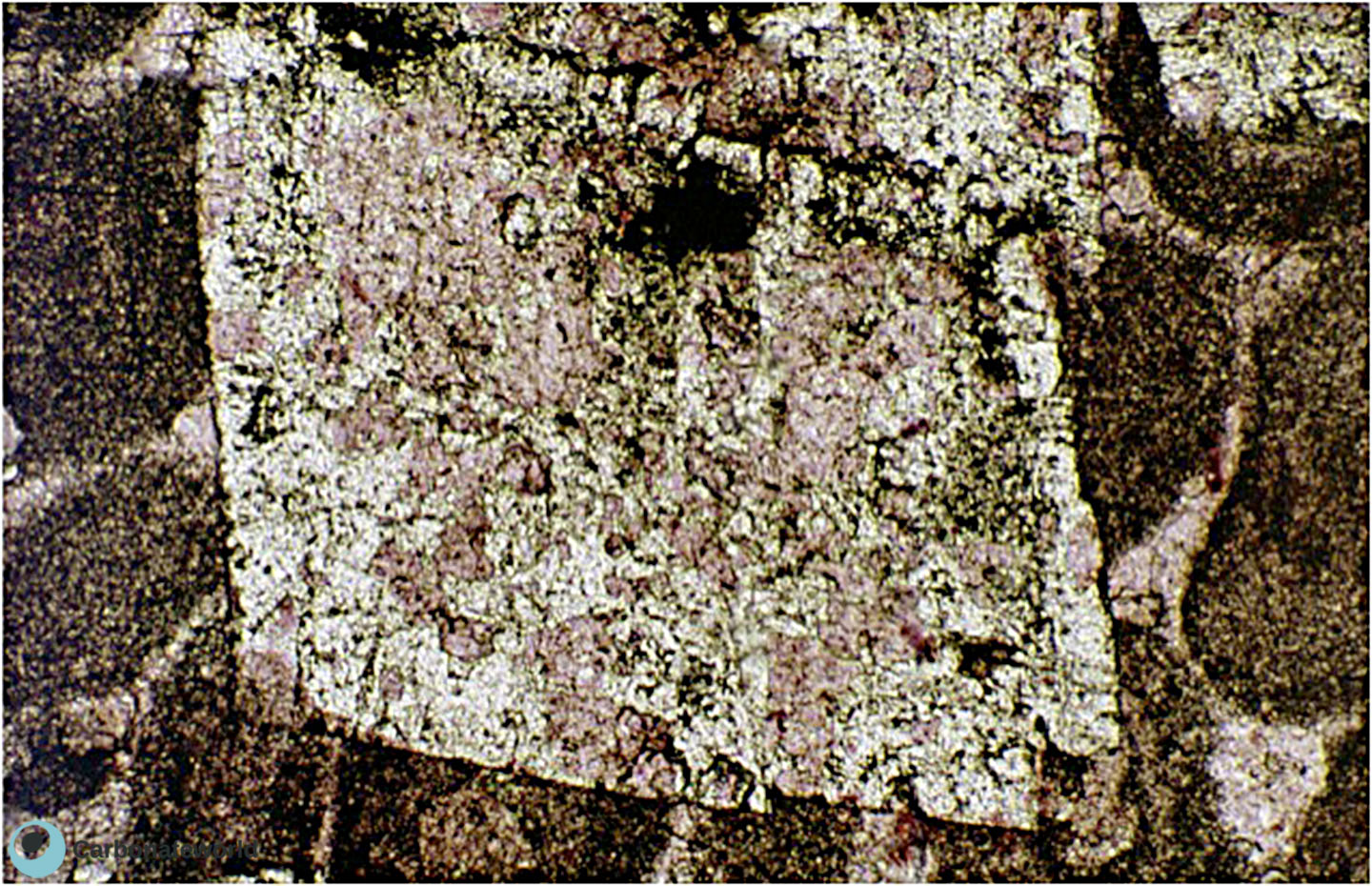


Dolomite crystal

Calcite due to dedolomitization
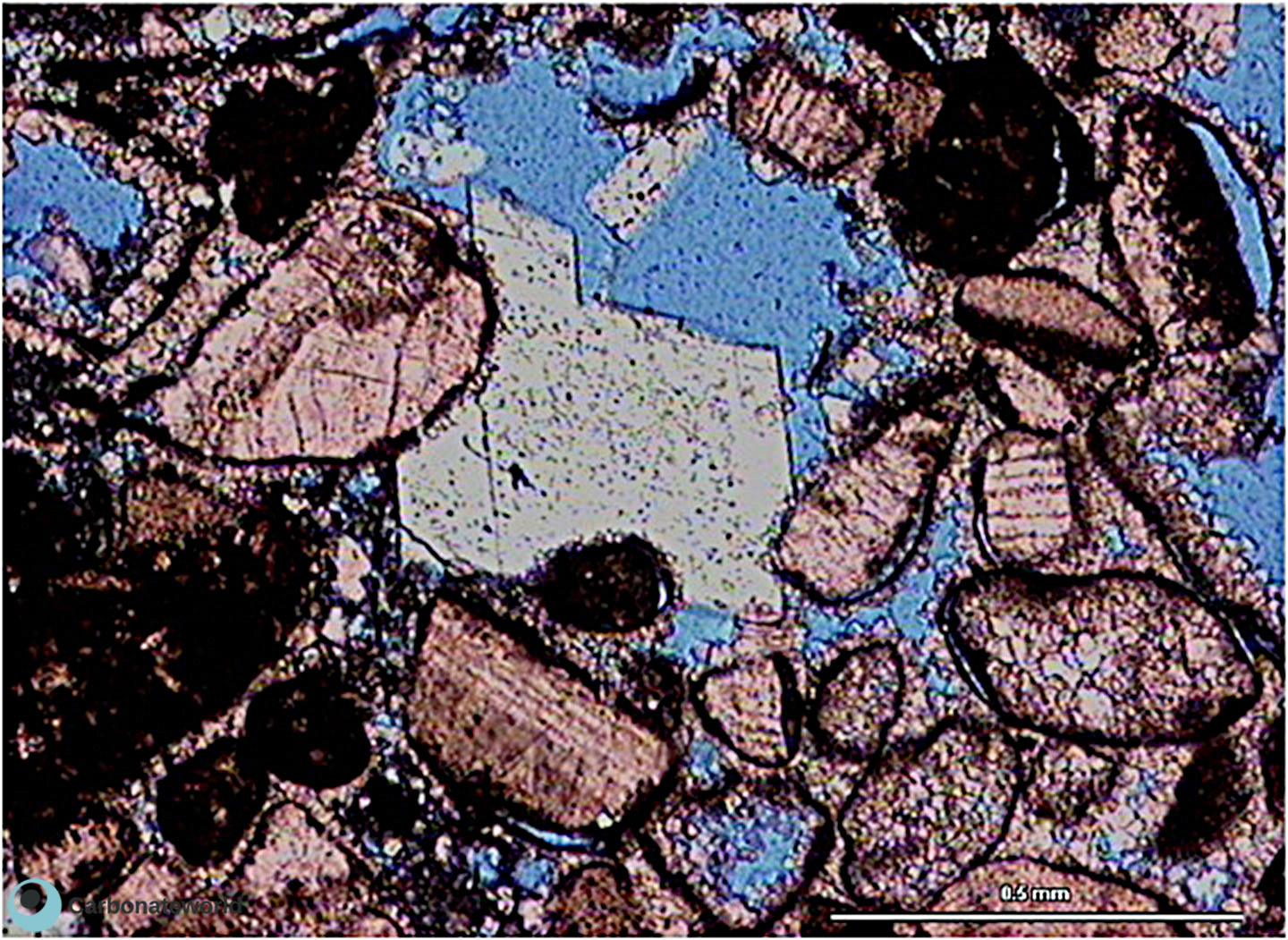


Dolomite cement

Mimetic dolomite

Dolomite cement

Calcite cement

Euhedral dolomite

Luminescent corroded edges

Non luminescent poikilotopic spar
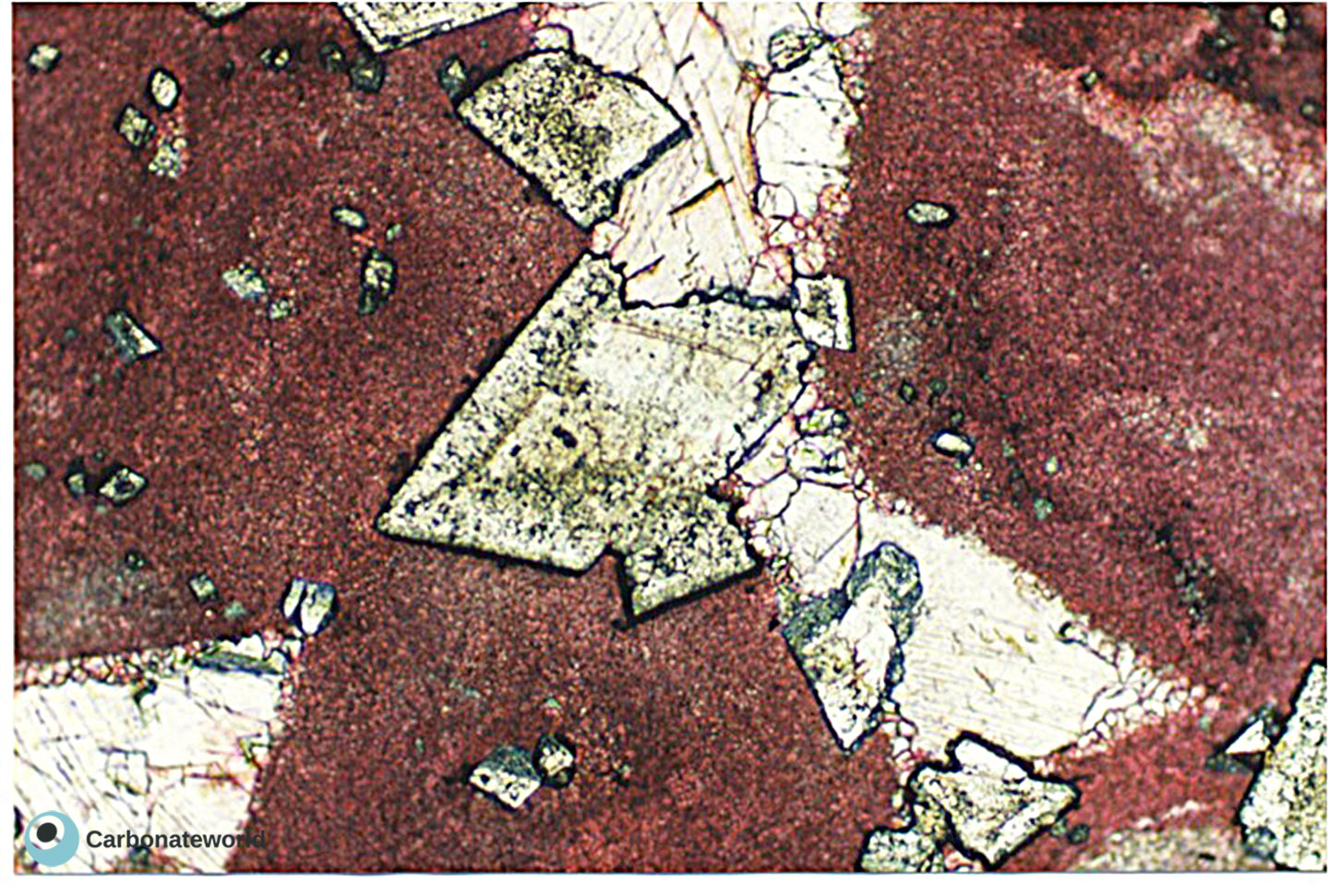


Etched dolomite edges

Poikilotopic cement


Etched dolomite edges

Calcite


Euhedral dolomite


Euhedral dolomite

Intercrystalline porosity


Intercrystalline porosity


Euhedral dolomite

Intercrystalline porosity

Mimetic dolomite

Dolomite cement

Euhedral dolomite

Anhydrite


Anhydrite

Dolomite


Anhydrite

Dolomite

Anhydrite

Dolomite


Undulose extinction in saddle dolomite

Saddle dolomite


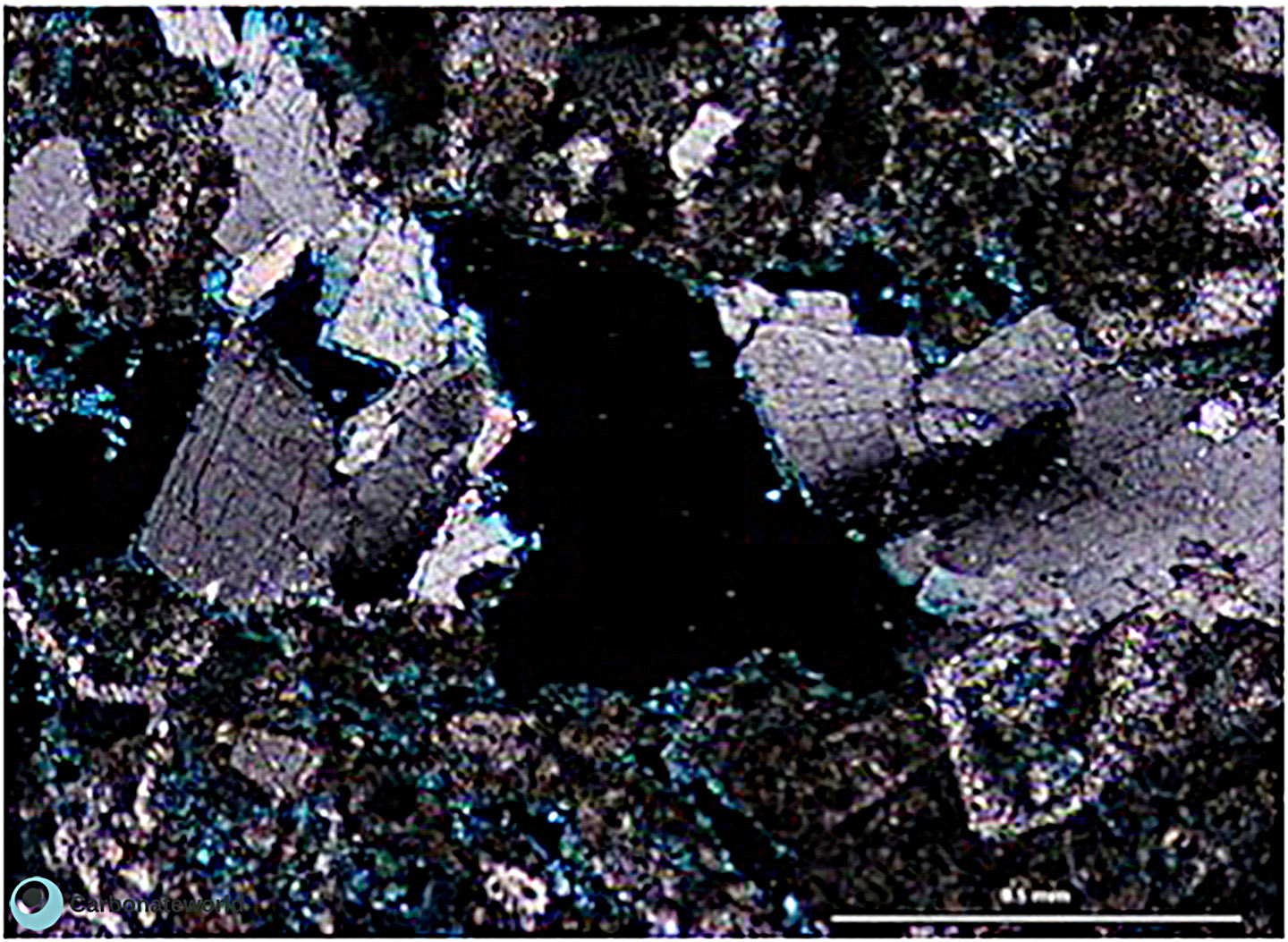
Saddle dolomite

Rotalid foraminifer

Saddle dolomite

Leached skeletal packstone

Saddle dolomite


Undulose sweeping extinction
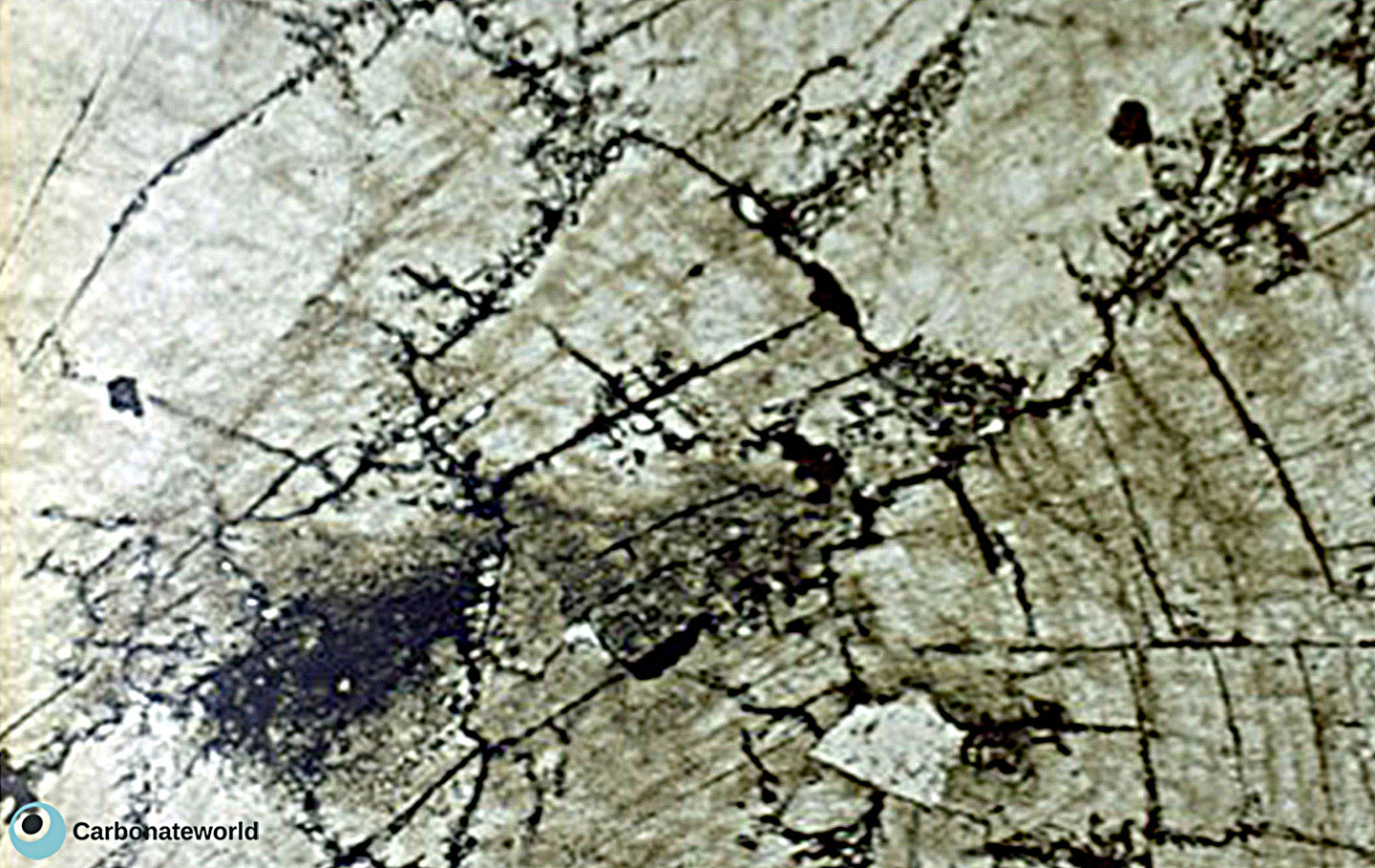



Dolomite