Porosity
1. Interparticle
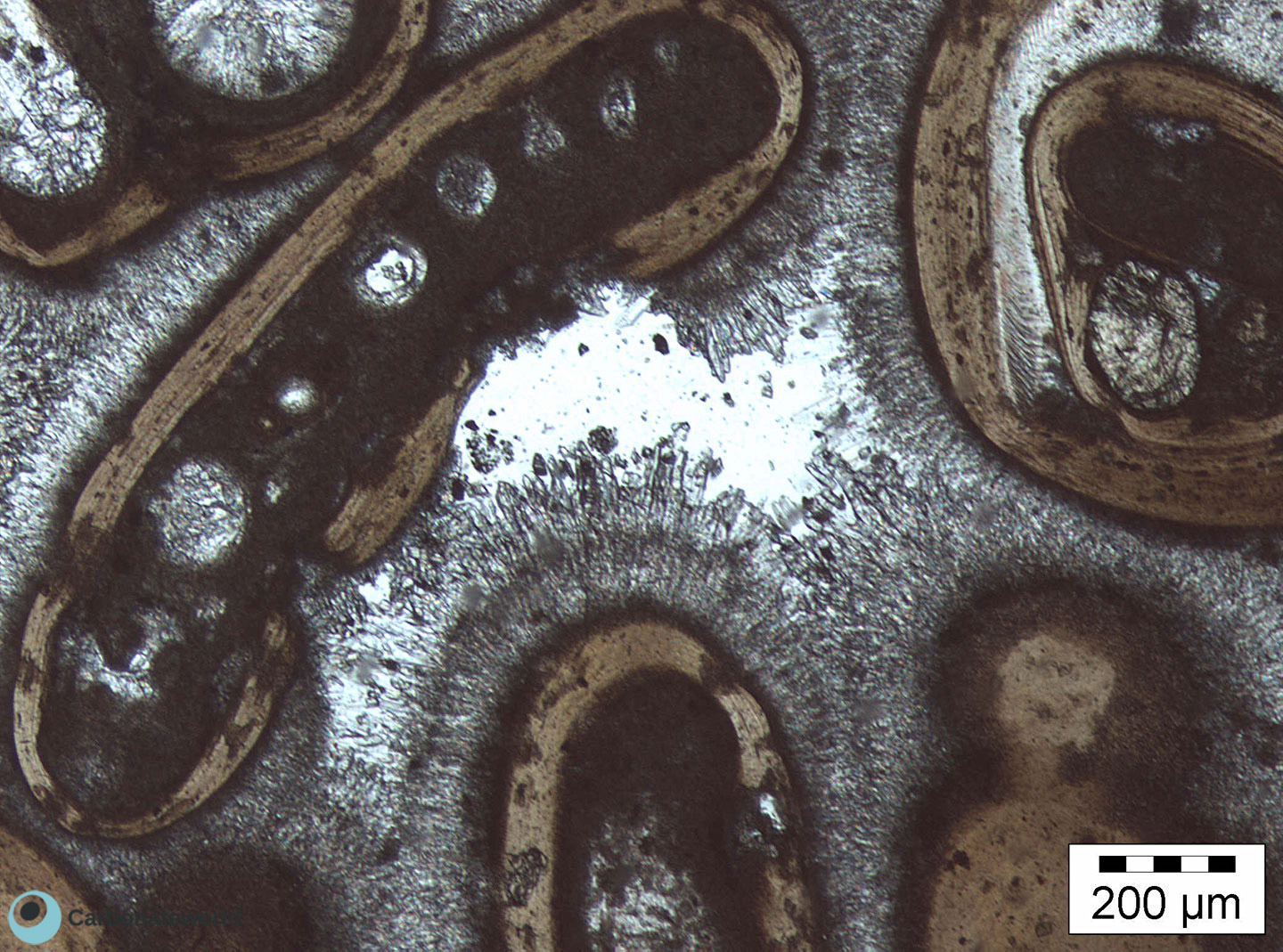
Ooidal grainstone with marine isopachous fibrous cement rims and interparticle (intergranular) porosity (white area in plane polarized light).
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
2. Interparticle
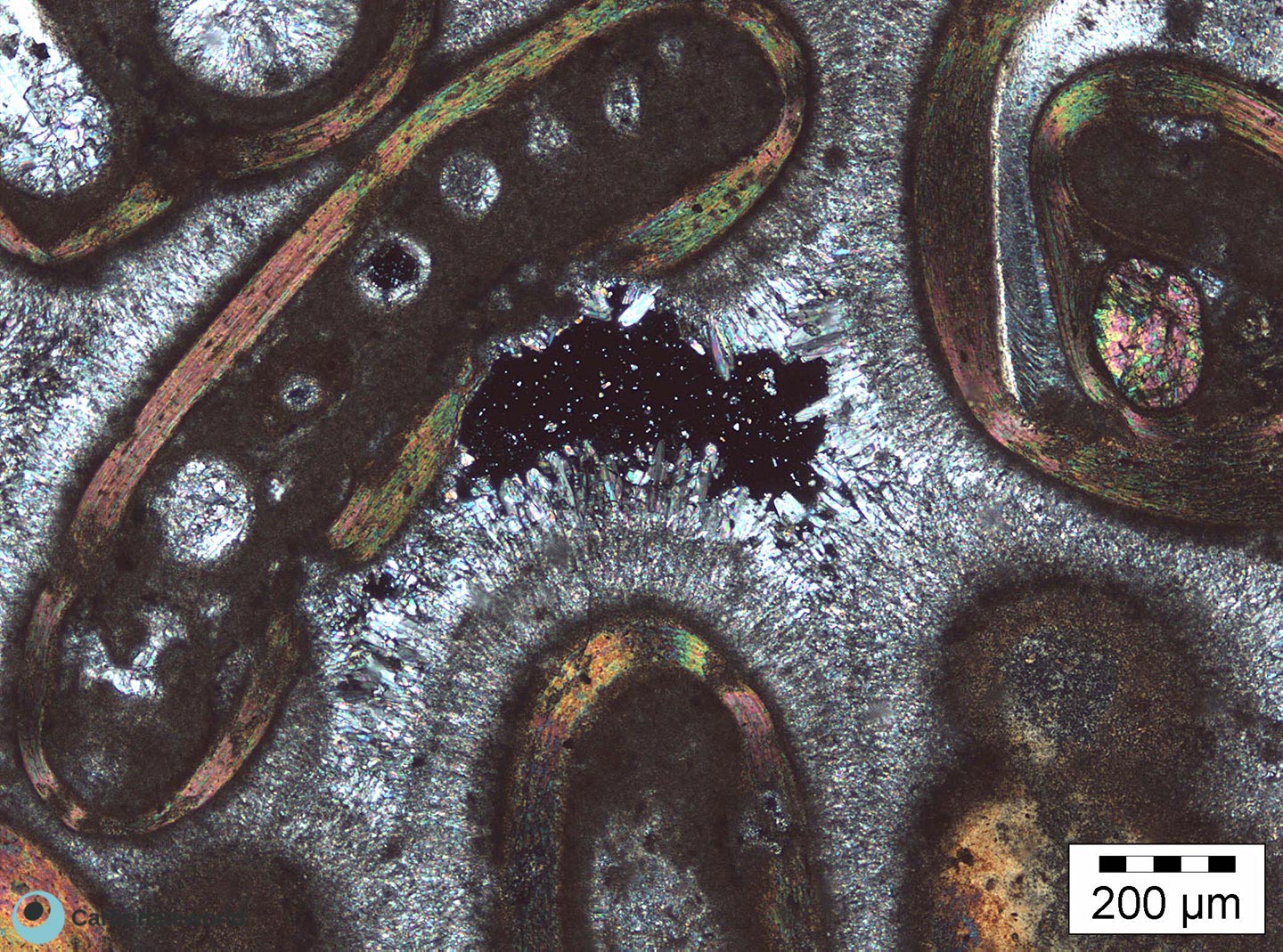
Previous image of an ooidal grainstone in cross-polarized light with the interparticle (intergranular) porosity (in extinction).
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
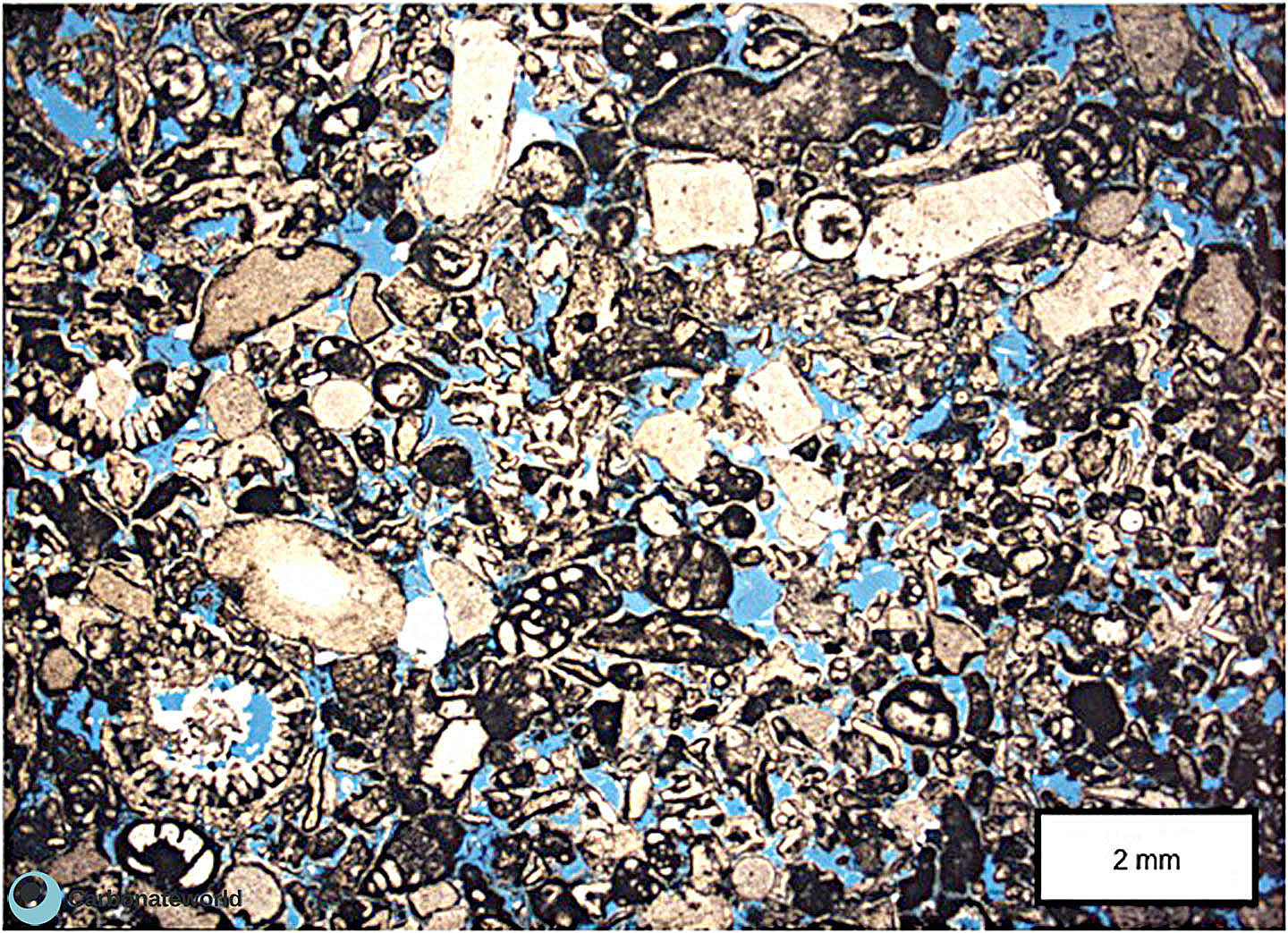
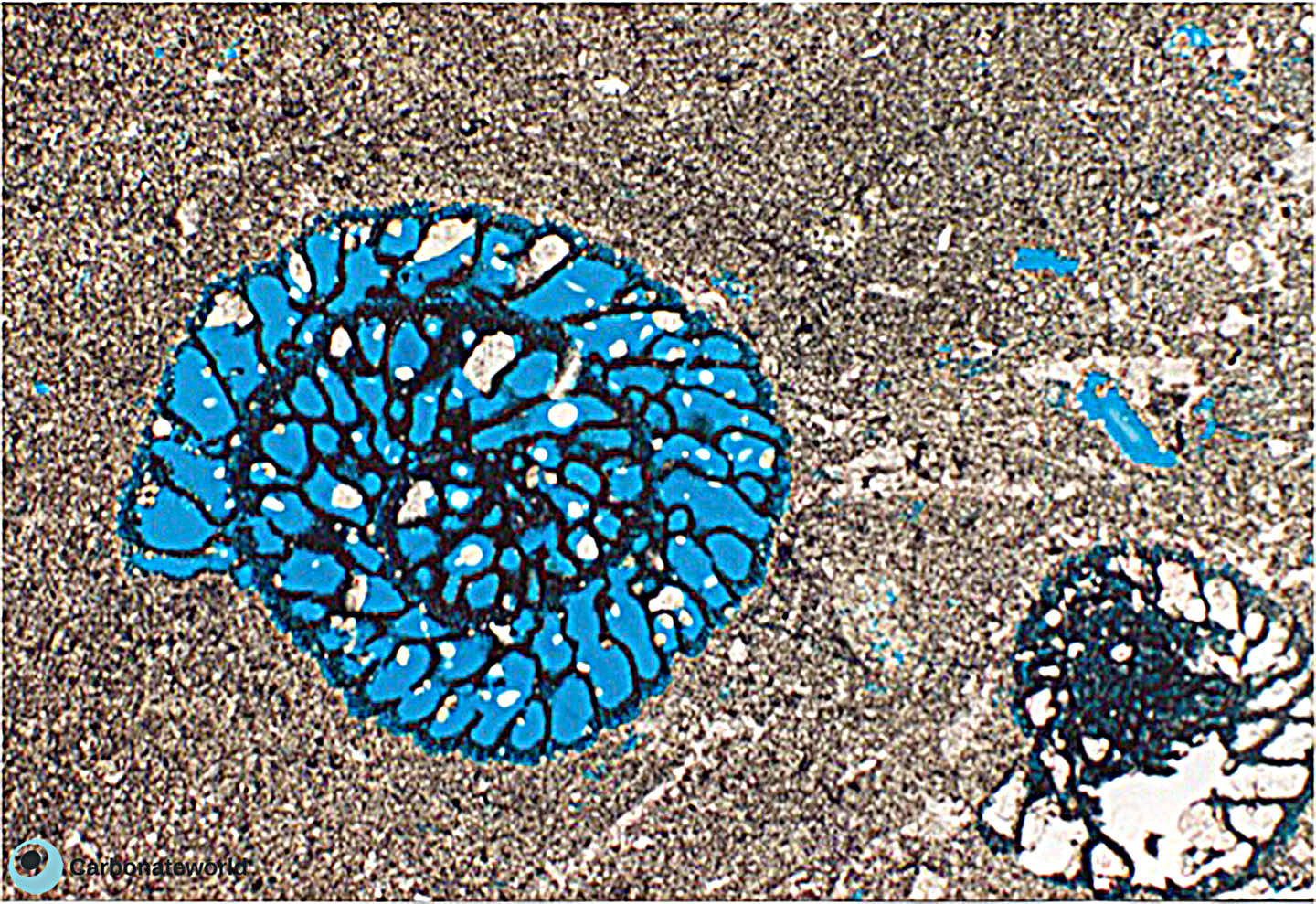
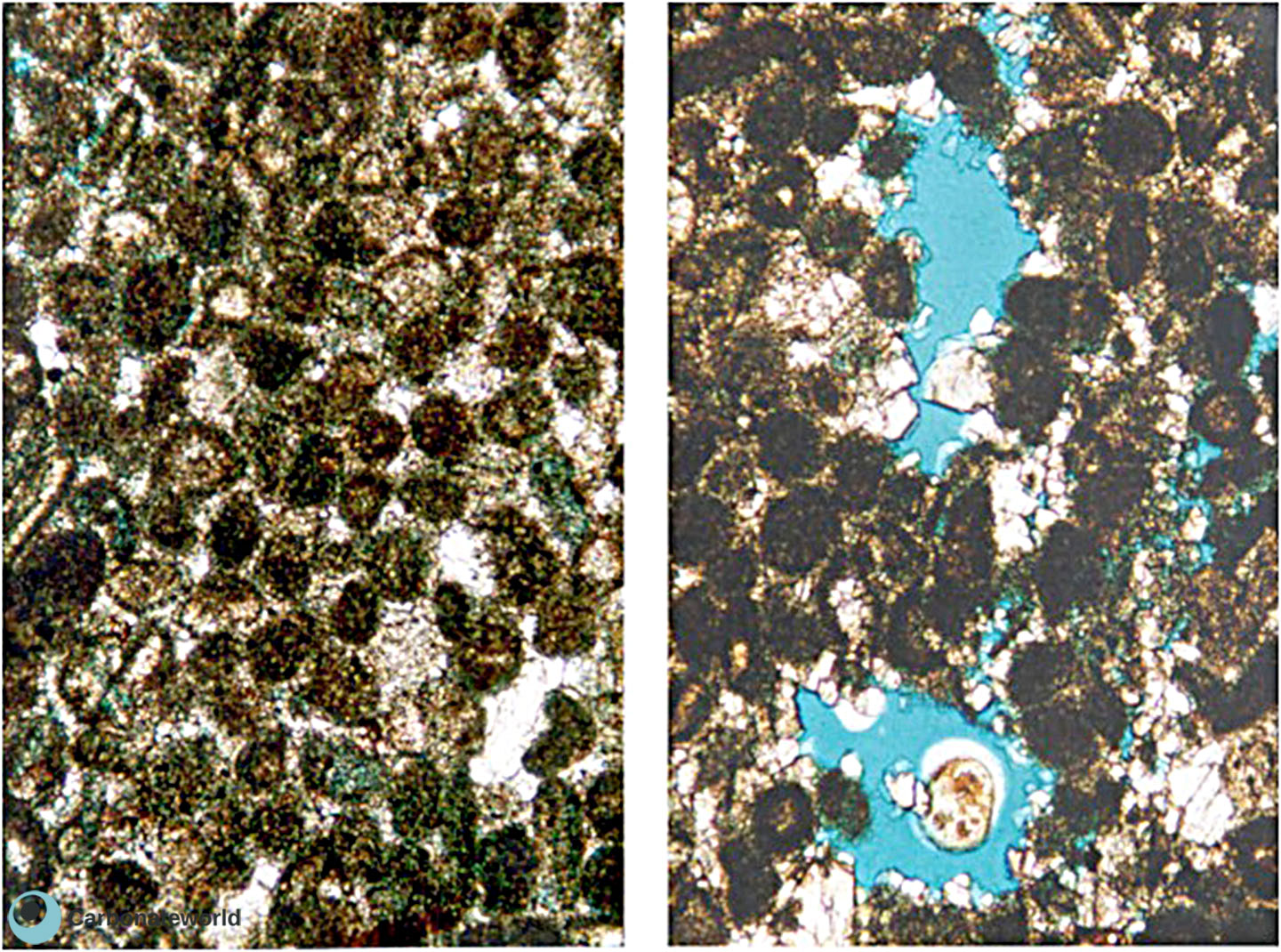
3. Interparticle
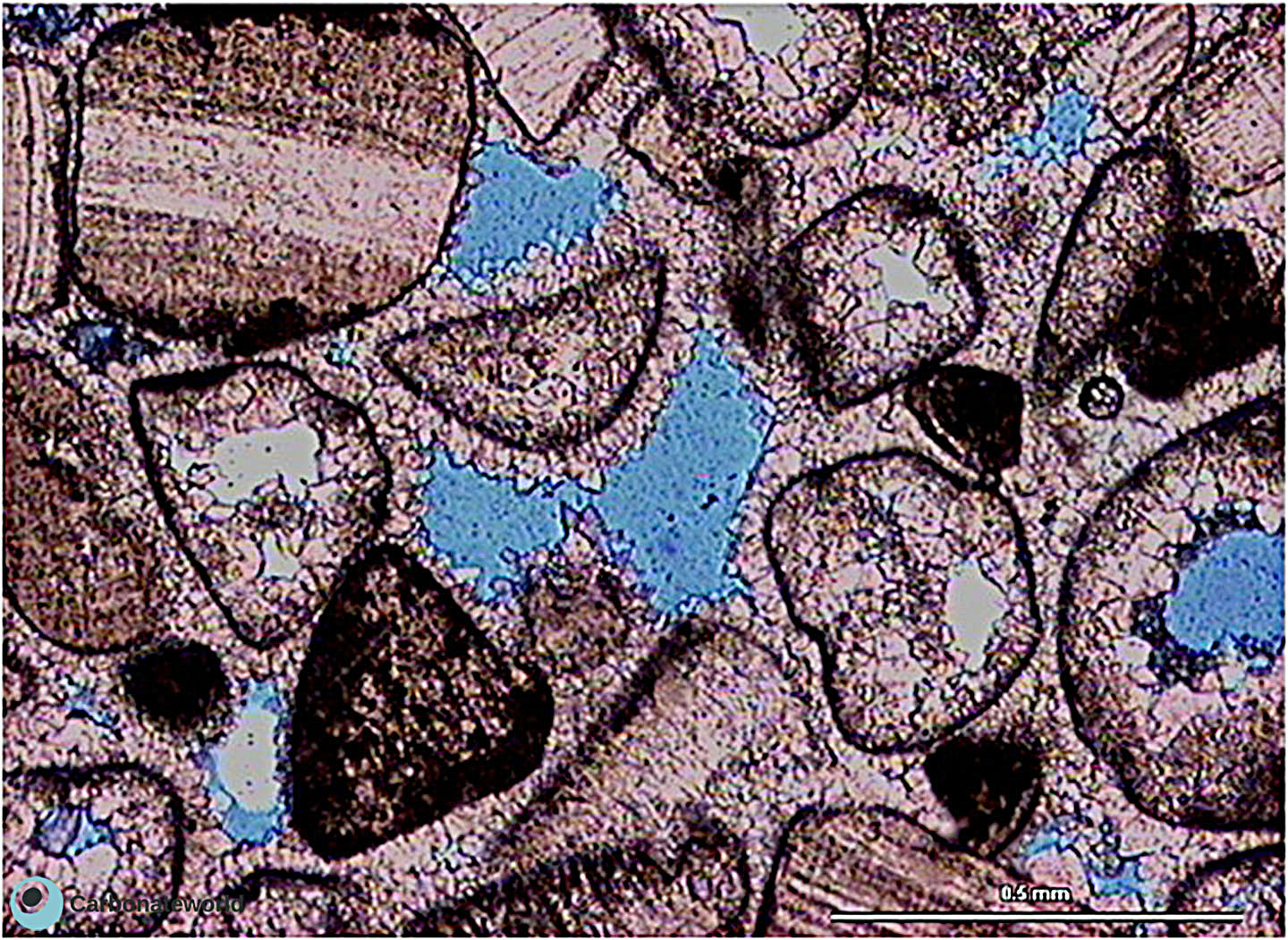
Skeletal grainstone with bioclasts preserved as micrite envelopes due to micritization of the outer rim and dissolution of the skeletal carbonate. Porosity is highlighted by blue epoxy and it is both primary interparticle (intergranular) and secondary mouldic within the grains.
Cretaceous, Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
4. Interparticle
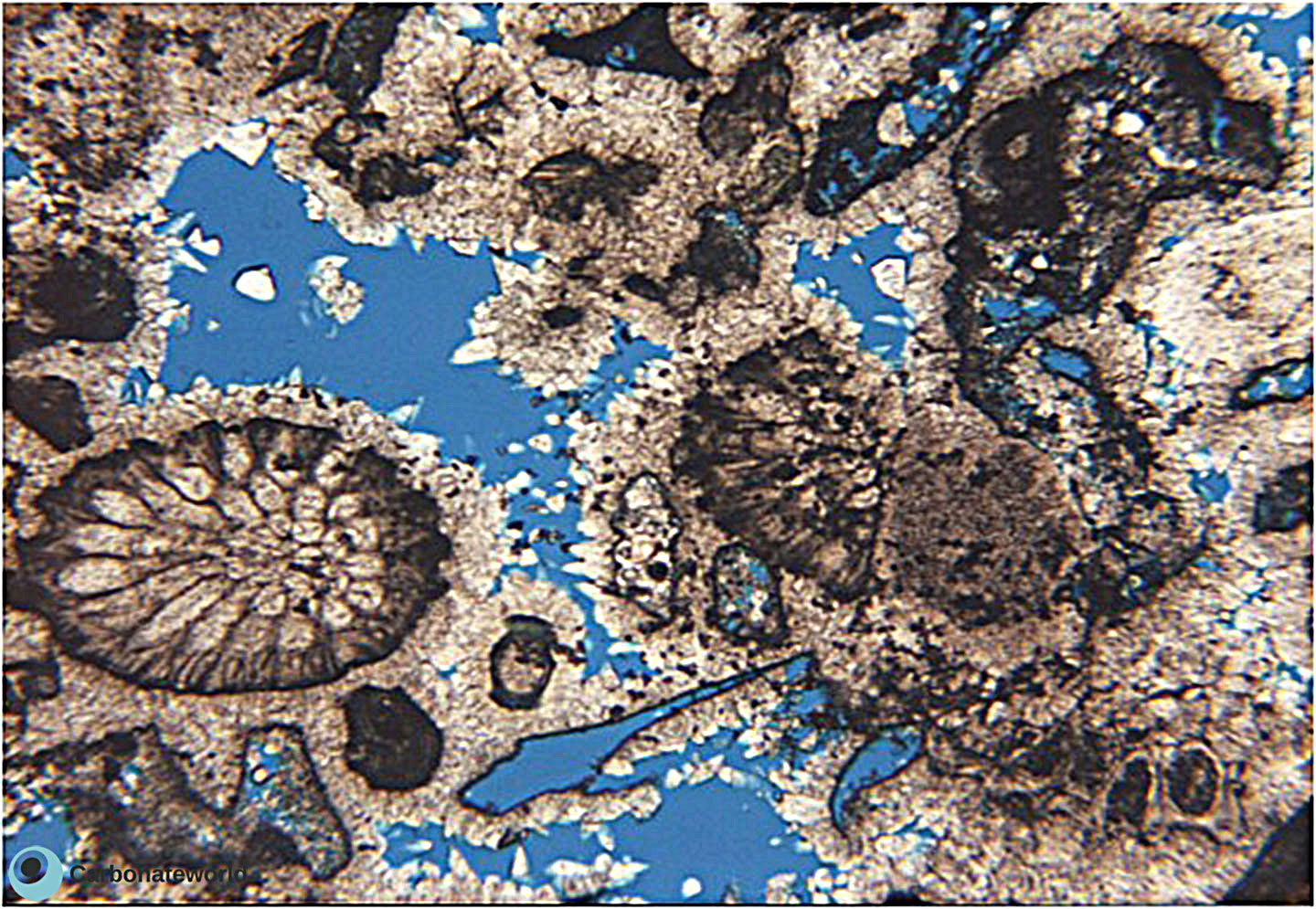
Skeletal grainstone with bryozoans showing primary interparticle (intergranular) porosity (blue epoxy) and minor secondary mouldic porosity due to partial or complete bioclasts dissolution. Field of view approximately 2 mm wide.
Carboniferous, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
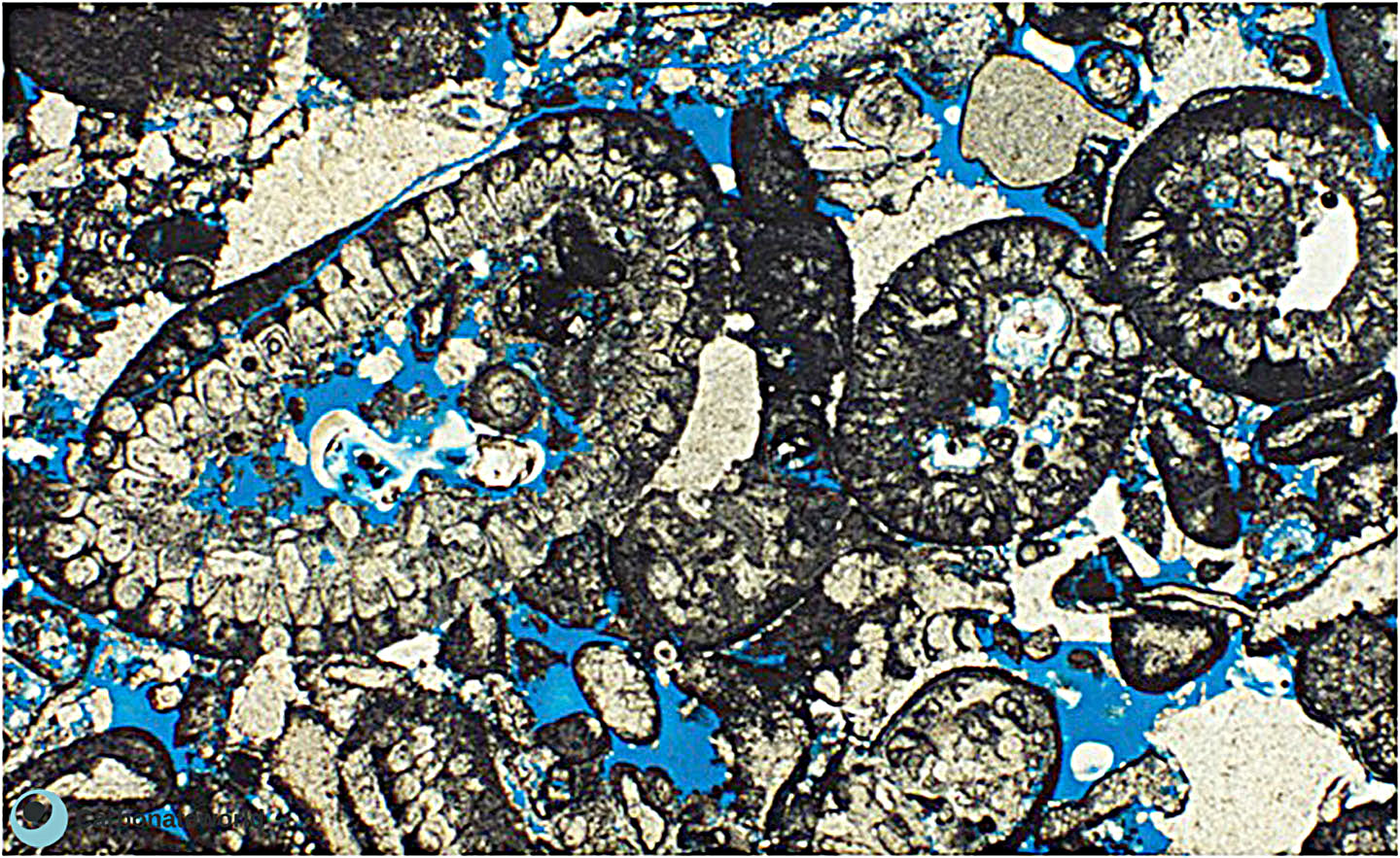
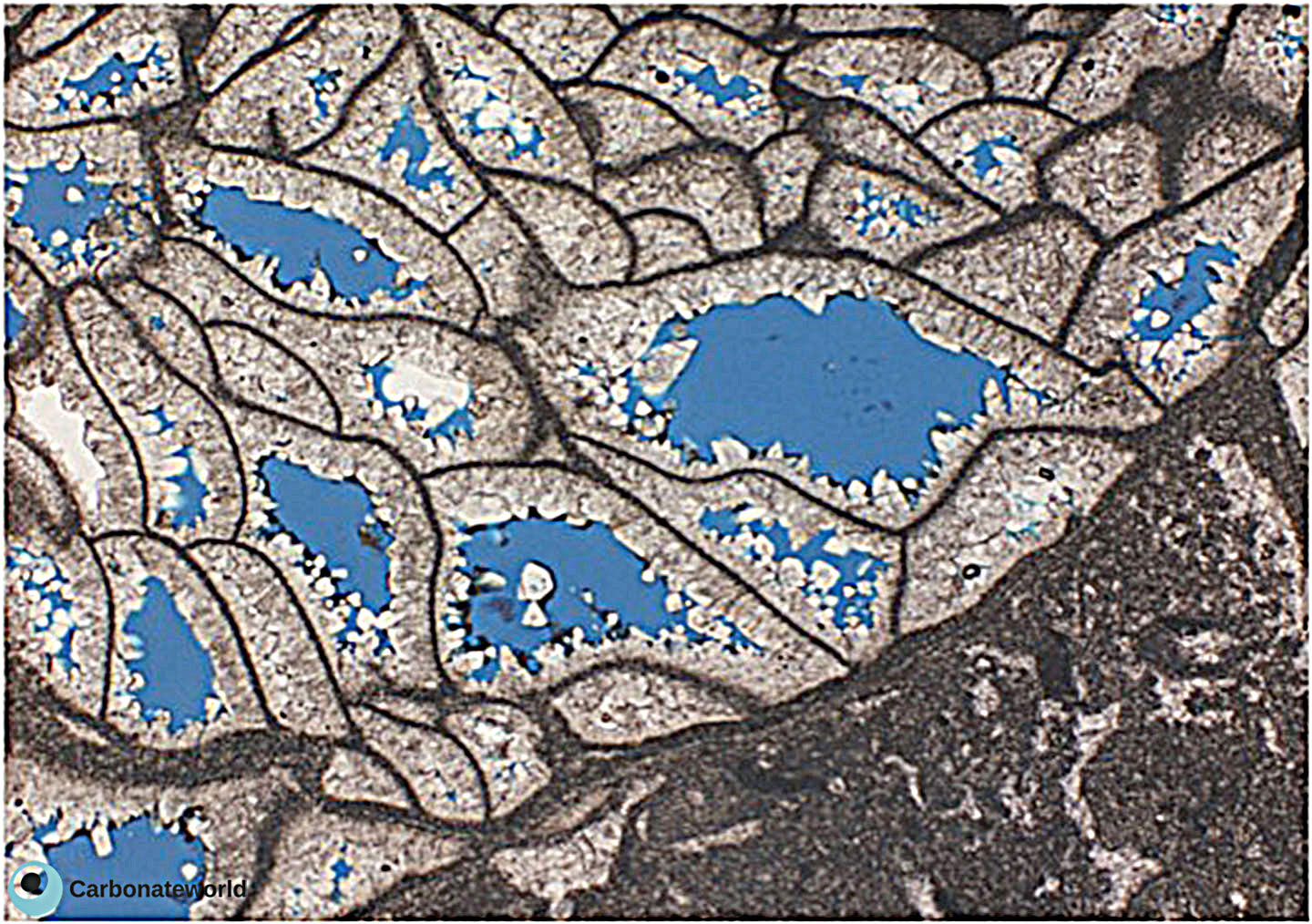
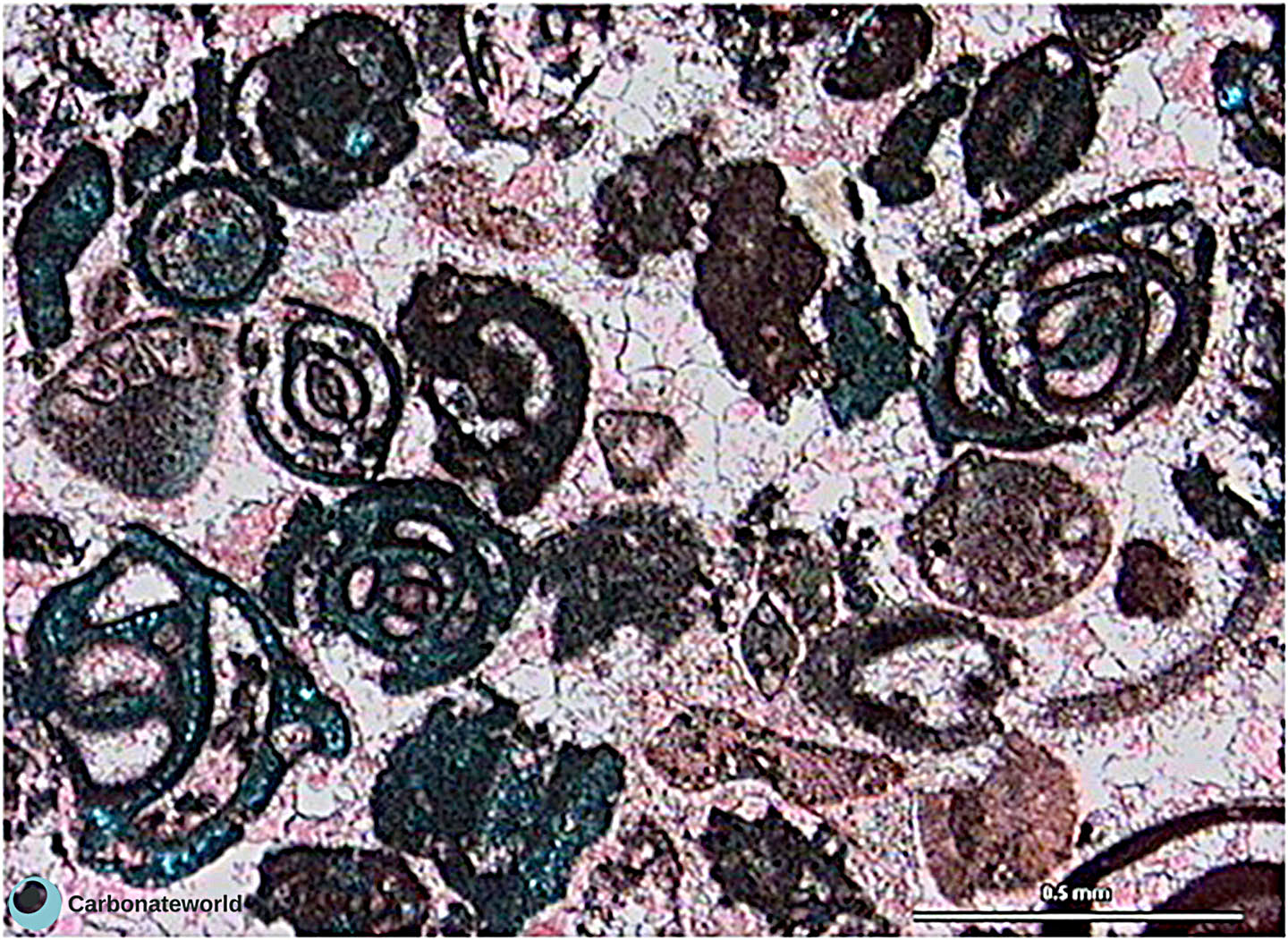
5. Interparticle
Skeletal grainstone rich in fusulinid and staffellid foraminifera. Grains exhibit concave-convex contacts and must have been compacted before cementation. Primary interparticle (intergranular) porosity is scarce. Field of view approximately 4.6 mm wide.
Lower Permian, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
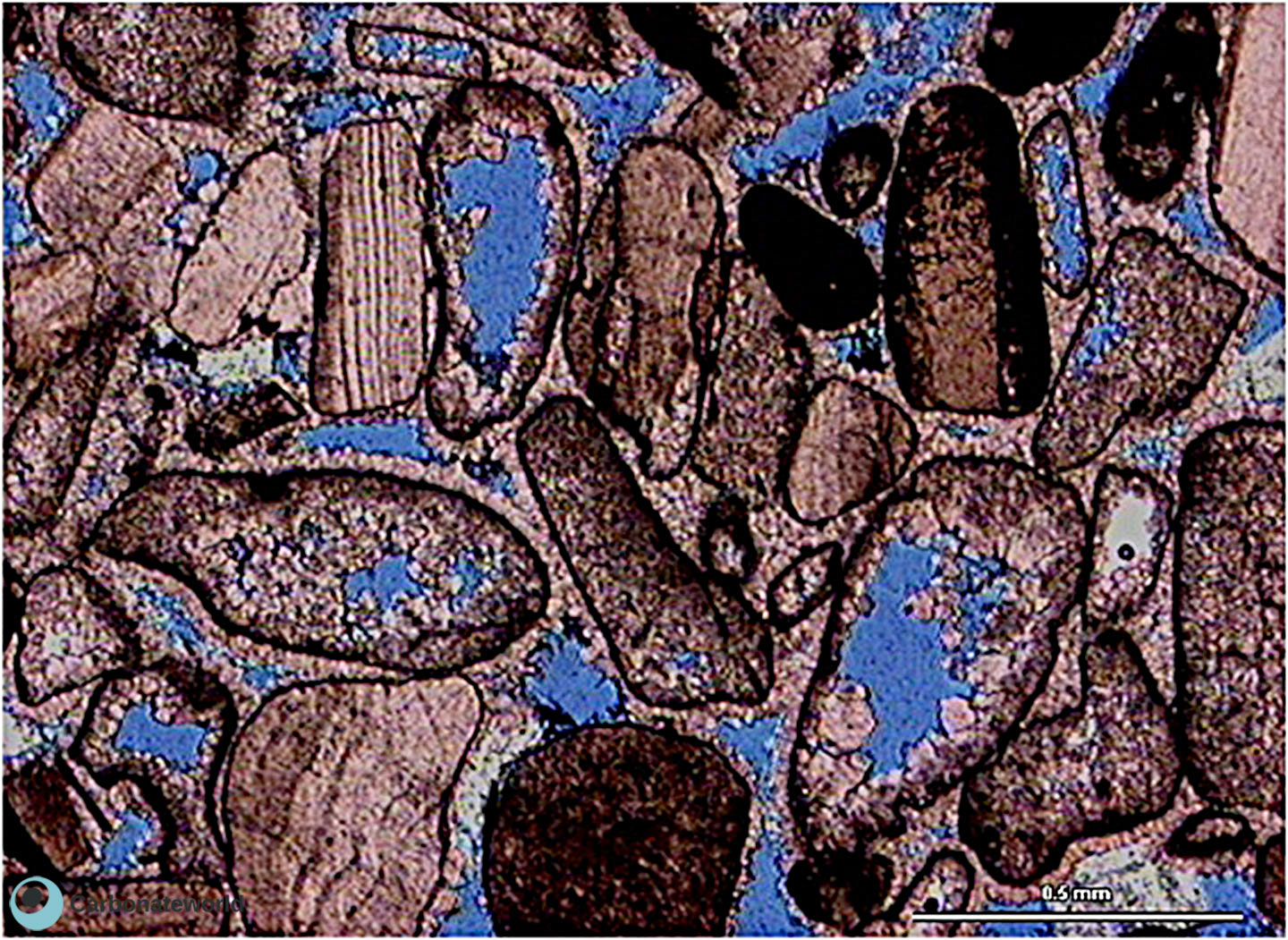
6. Interparticle
Skeletal grainstone with primary interparticle (intergranular) porosity (blue epoxy), minor intraparticle (intragranular) porosity and scarce cementation. Numerous grains have micrite envelopes. Field of view approximately 9 mm wide.
Carboniferous, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
7. Interparticle
Skeletal grainstone with interparticle (intergranular) porosity. Note micrite envelopes on many grains. There is also minor intraparticle (intragranular porosity). Field of view approximately 1.6 mm wide.
Carboniferous, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
8. Interparticle
Primary interparticle (intergranular) porosity in a skeletal grainstone with most of the bioclasts coated by micrite envelopes. There is also minor intraparticle (intragranular) porosity in the benthic foraminifer (Climacammina) in the centre. Field of view approximately 2 mm wide.
Carboniferous, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

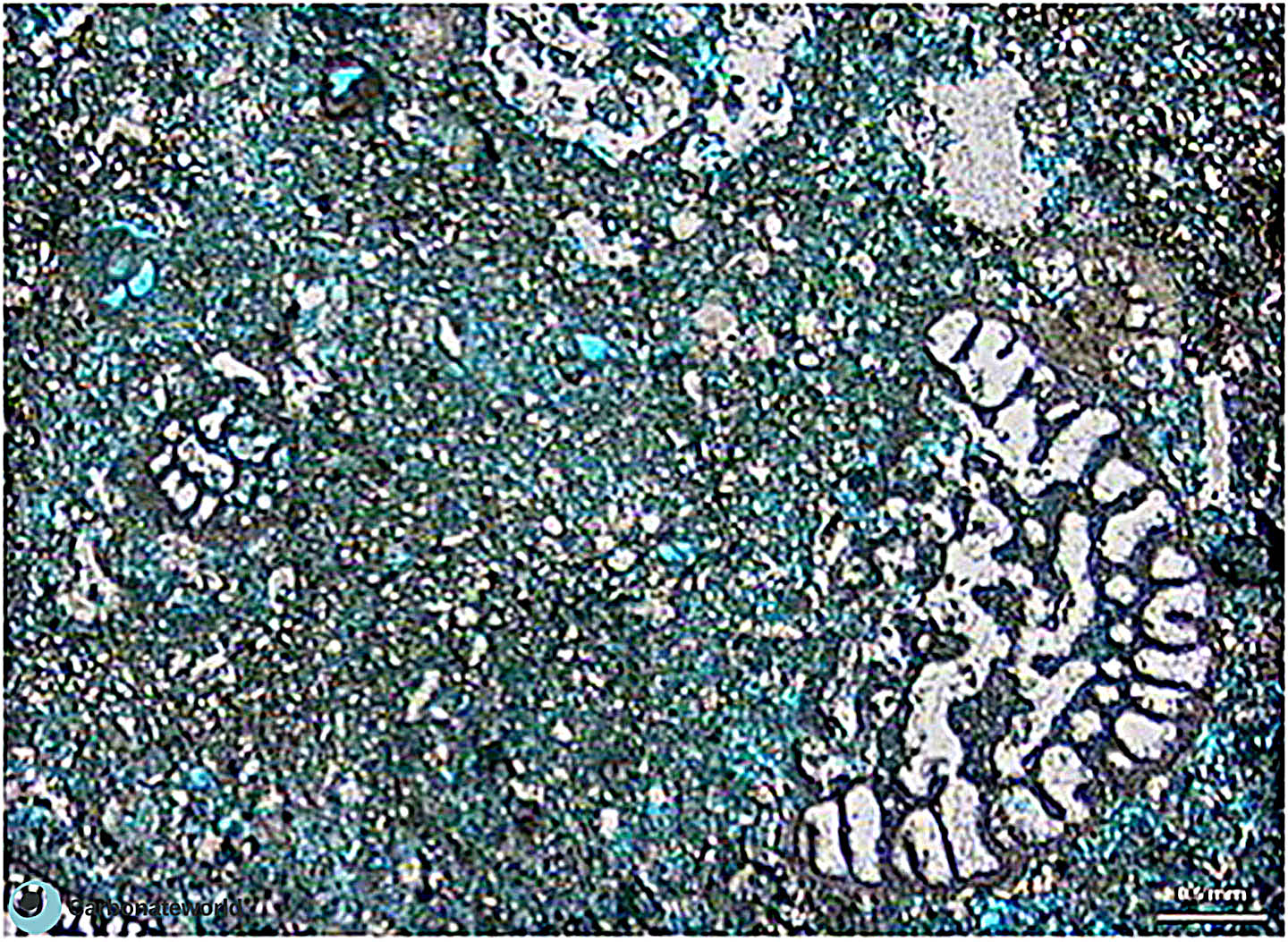
SHOW INFO
9. Interparticle
Primary interparticle (intergranular) porosity in skeletal grainstone with echinoderms, foraminifera and green calcareous algae. The green dasyclad fragment of Koninckopora shows also intraparticle porosity.
Carboniferous, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
10. Interparticle
Skeletal grainstone with echinoderms and calcitic green dasyclad algae (Koninckopora) that exhibit primary intraparticle (intragranular) porosity. Field of view approximately 3 mm wide.
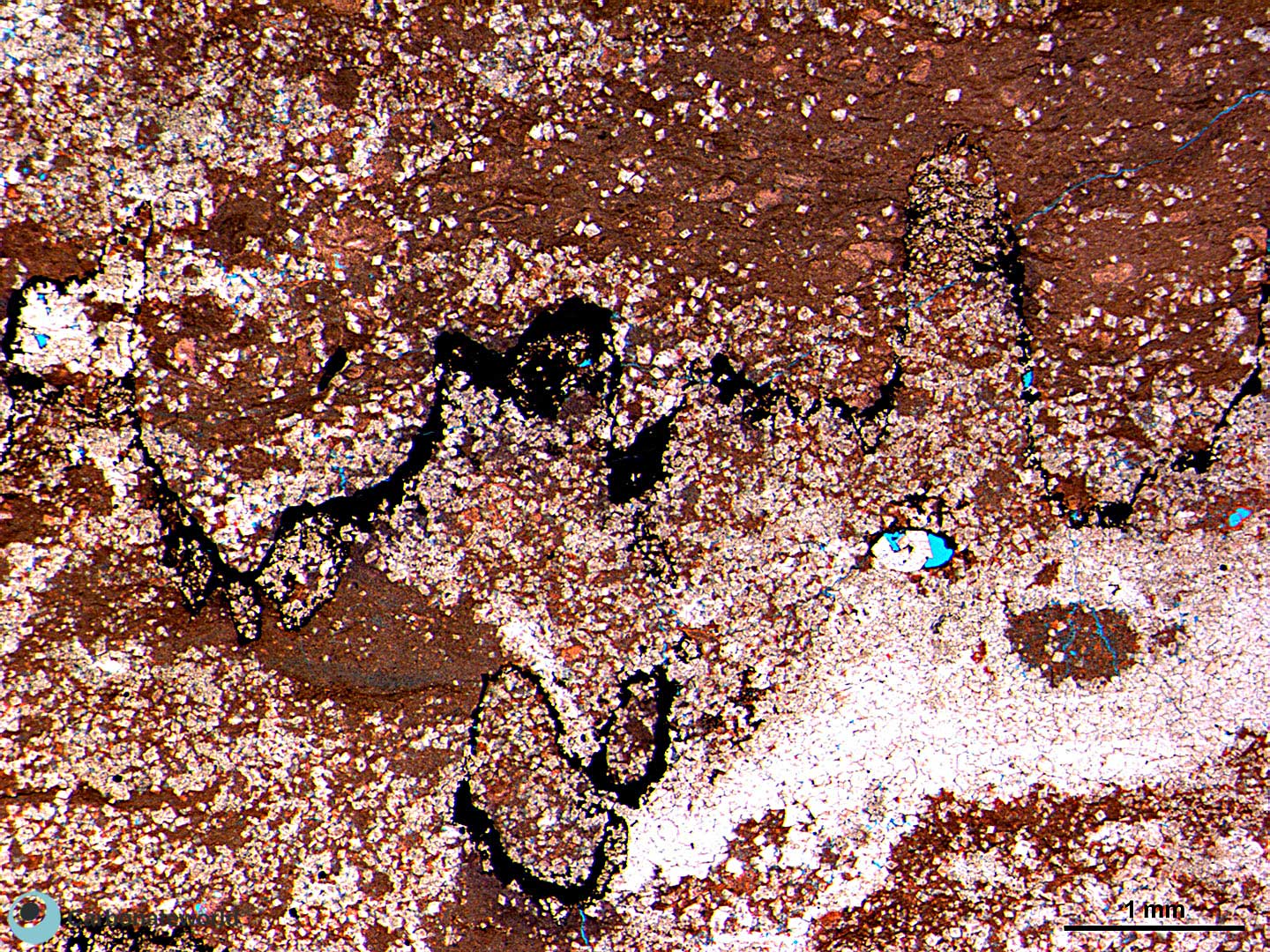
Carboniferous, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
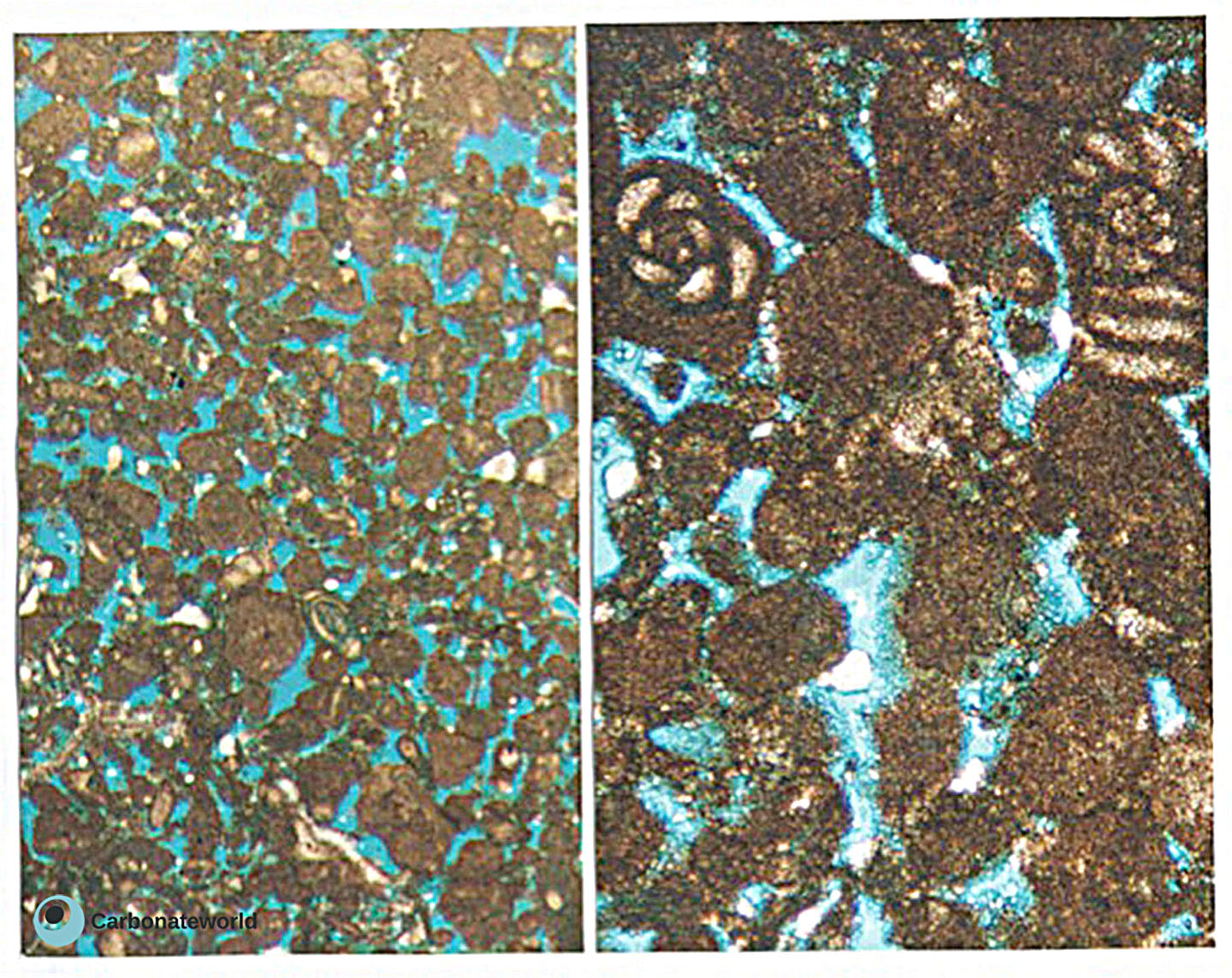
11. Interparticle
Peloidal skeletal grainstone with high interparticle (intergranular) porosity containing miliolid foraminifera typical of restricted (probably with elevated salinities) platform interior lagoons. Field of view approximately 3 mm wide (left) and 1 mm wide (right).
Cretaceous, Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
12. Secondary
Particular type of porosity due to complete dissolution of foraminifer shell with the preservation of remnant “shards” of intraparticle cement after foraminifer test walls have been dissolved.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
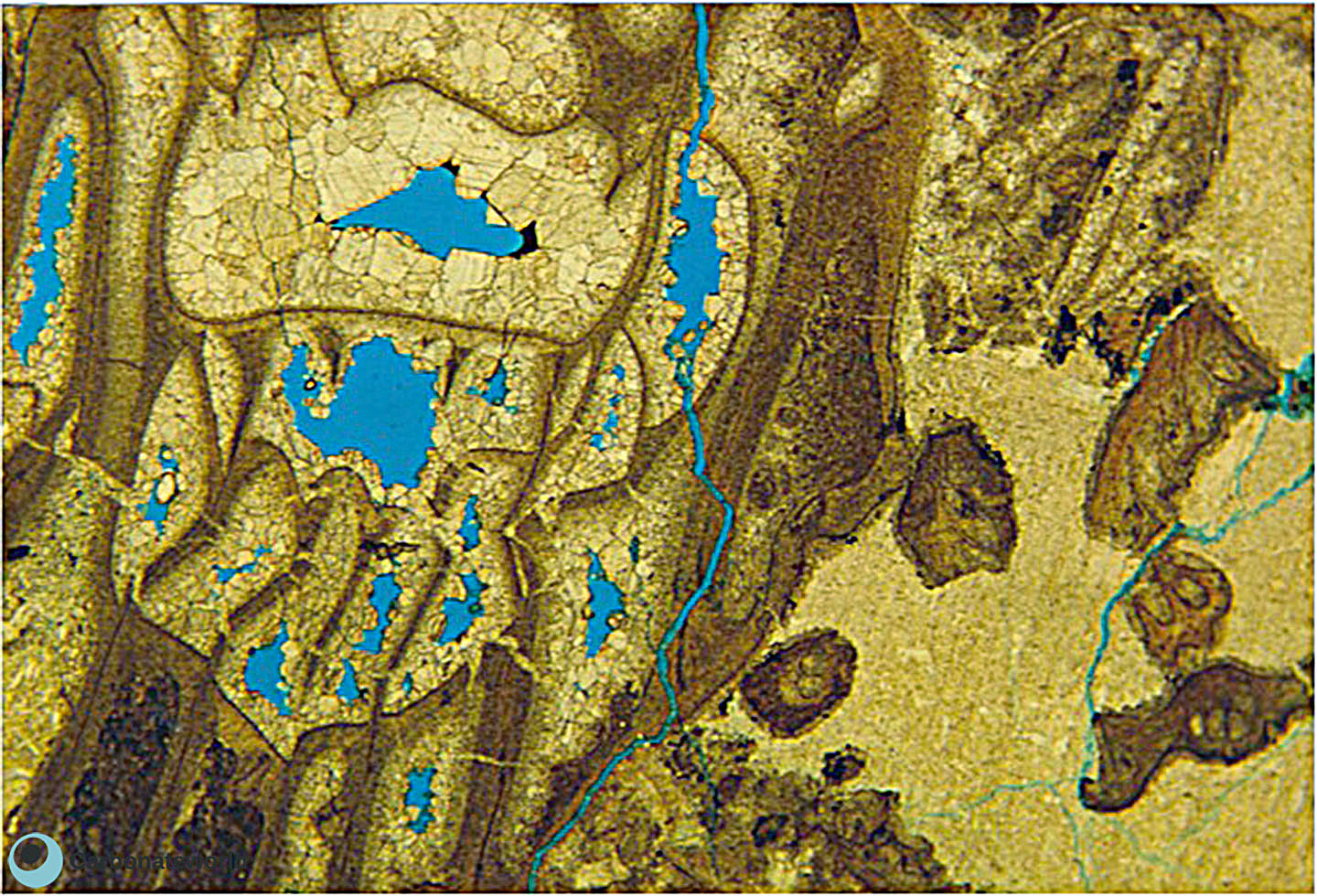
13. Intraparticle
Intraparticle (intragranular) porosity in a fusulinid foraminifer. Micrite matrix has been dolomitized and includes some areas with dissolution vug porosity. Field of view approximately 1 mm wide.
Lower Permian, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
14. Intraparticle
Intraparticle (intragranular) porosity in a rugose coral. Field of view approximately 3 mm wide.
Carboniferous, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
15. Intraparticle
Intraparticle (intragranular) porosity in a rugose coral. Note the cement and bitumen in the intraparticle pore space. Field of view approximately 3 mm wide.
Lower Permian, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
16. Intraparticle/Dissolution
Cross-section of foraminifer showing intraparticle pore space enhanced by secondary dissolution.
Thin section provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
17. Intraparticle/Dissolution
Previous image in cross-polarized light showing the porosity areas of intraparticle and dissolution fully in extinction.
Thin section kindly provided by T. Geel, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
18. Growth framework
Growth framework porosity visible in a polished slab of a red algae bindstone.
Miocene, Mallorca, Spain

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
19. Breccia porosity
Breccia porosity due to intraformational fracturing in a Miocene breccia composed of Mesozoic limestone clasts.
Miocene, Tarragona, Spain

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
20. Fenestral porosity
Fenestral porosity in intertidal facies from Central Oman.
Precambrian, Khufai Formation, Central Oman

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
21. Fenestral porosity
Fenestral porosity in intertidal peloidal grainstone. Field of view approximately 3 mm wide.
Precambrian, Khufai Formation, Central Oman

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
22. Fenestral porosity
Fenestral porosity in intertidal peloidal grainstone. Field of view approximately 1 mm wide.
Precambrian, Khufai Formation, Central Oman

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
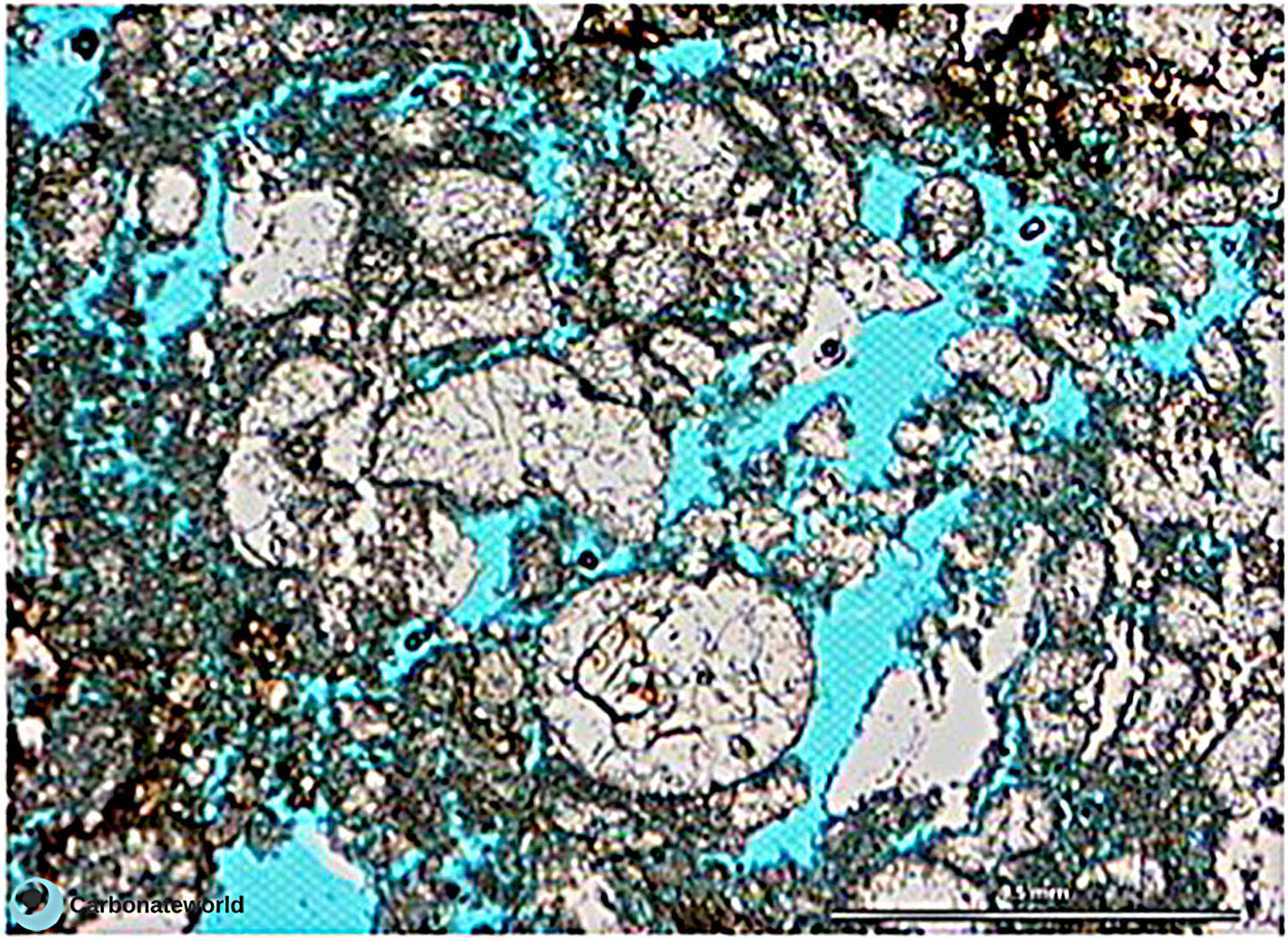
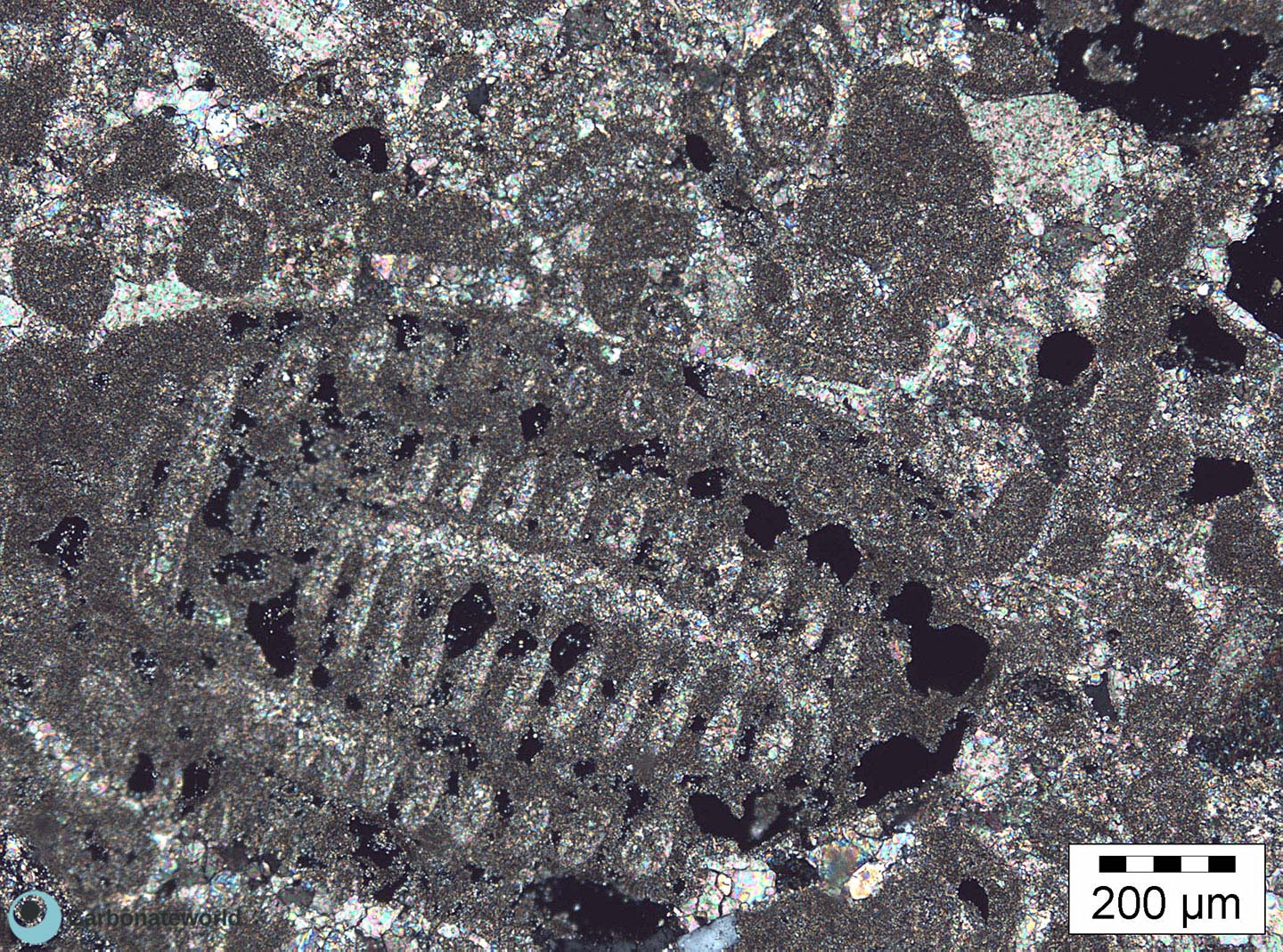
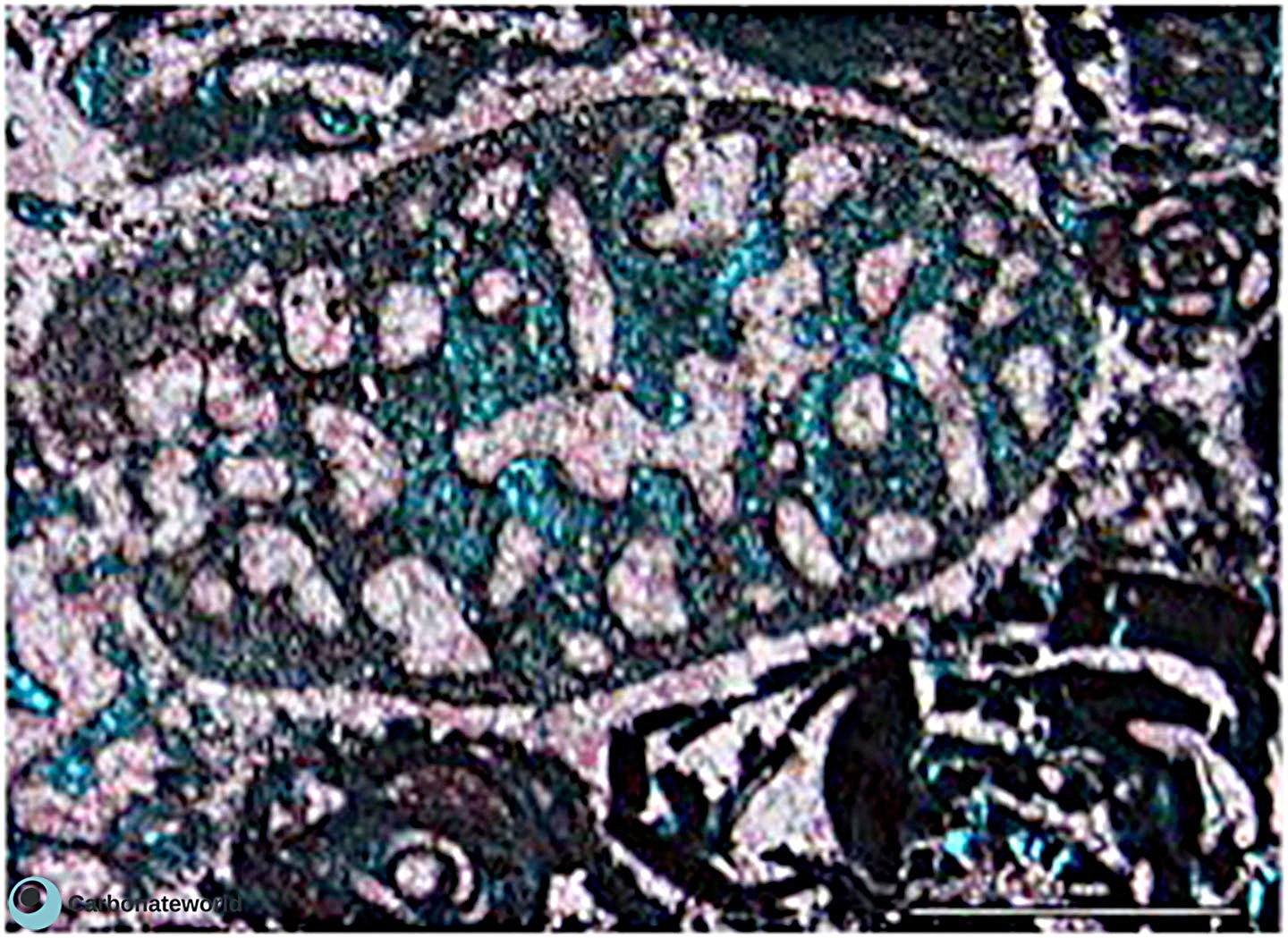
23. Biomouldic
Skeletal grainstone with fusulinid and bryozoan fragments and a bivalve biomould preserved by the micrite envelope on the outer shell rim. Field of view approximately 9 mm wide.
Lower Permian, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
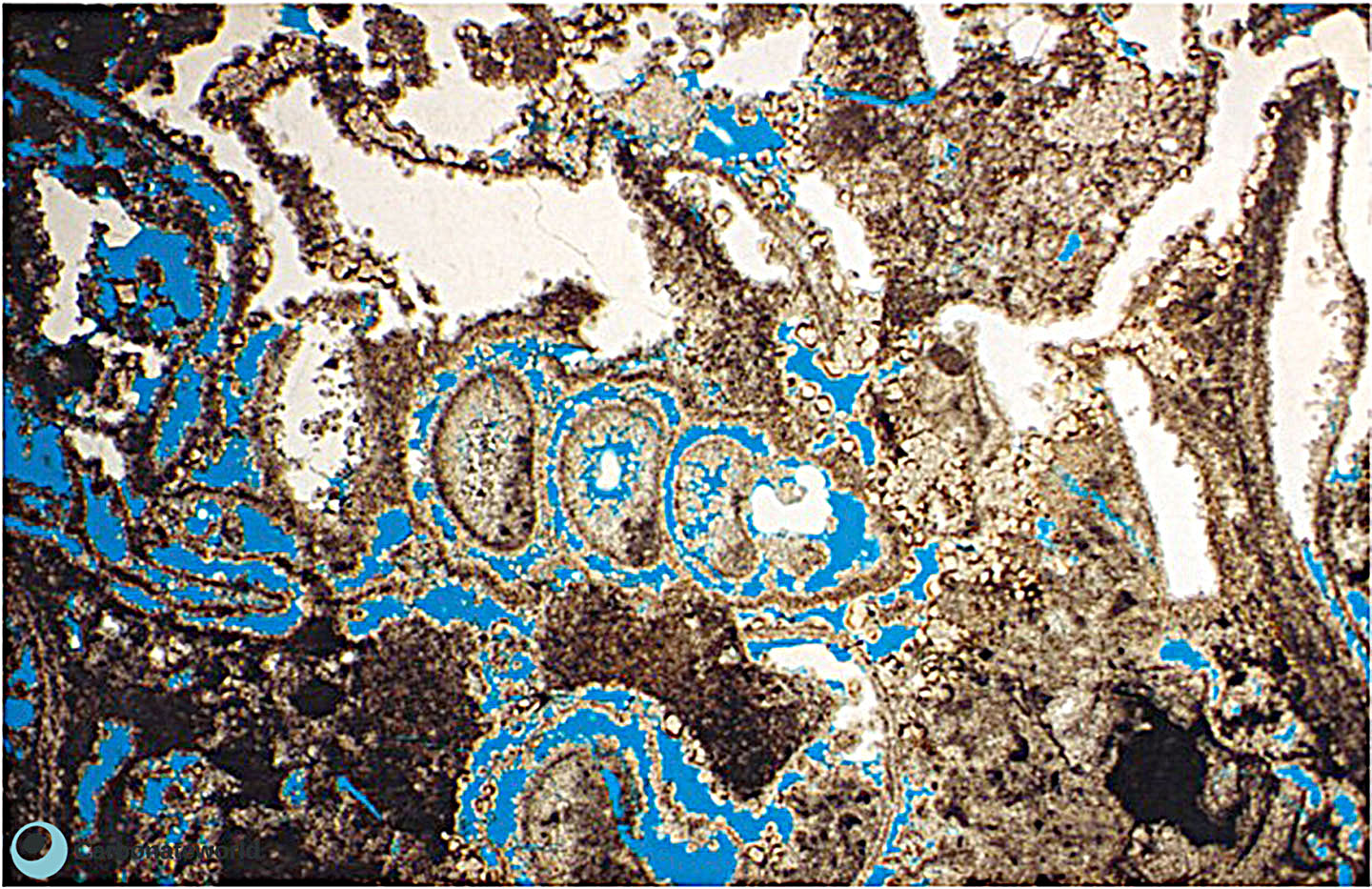
24. Biomouldic
Secondary porosity put in evidence by the blue epoxy resin with preferential removal of walls of coskinolinid foraminifer to produce mouldic porosity. The intraparticle space is filled by undissolved cement.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
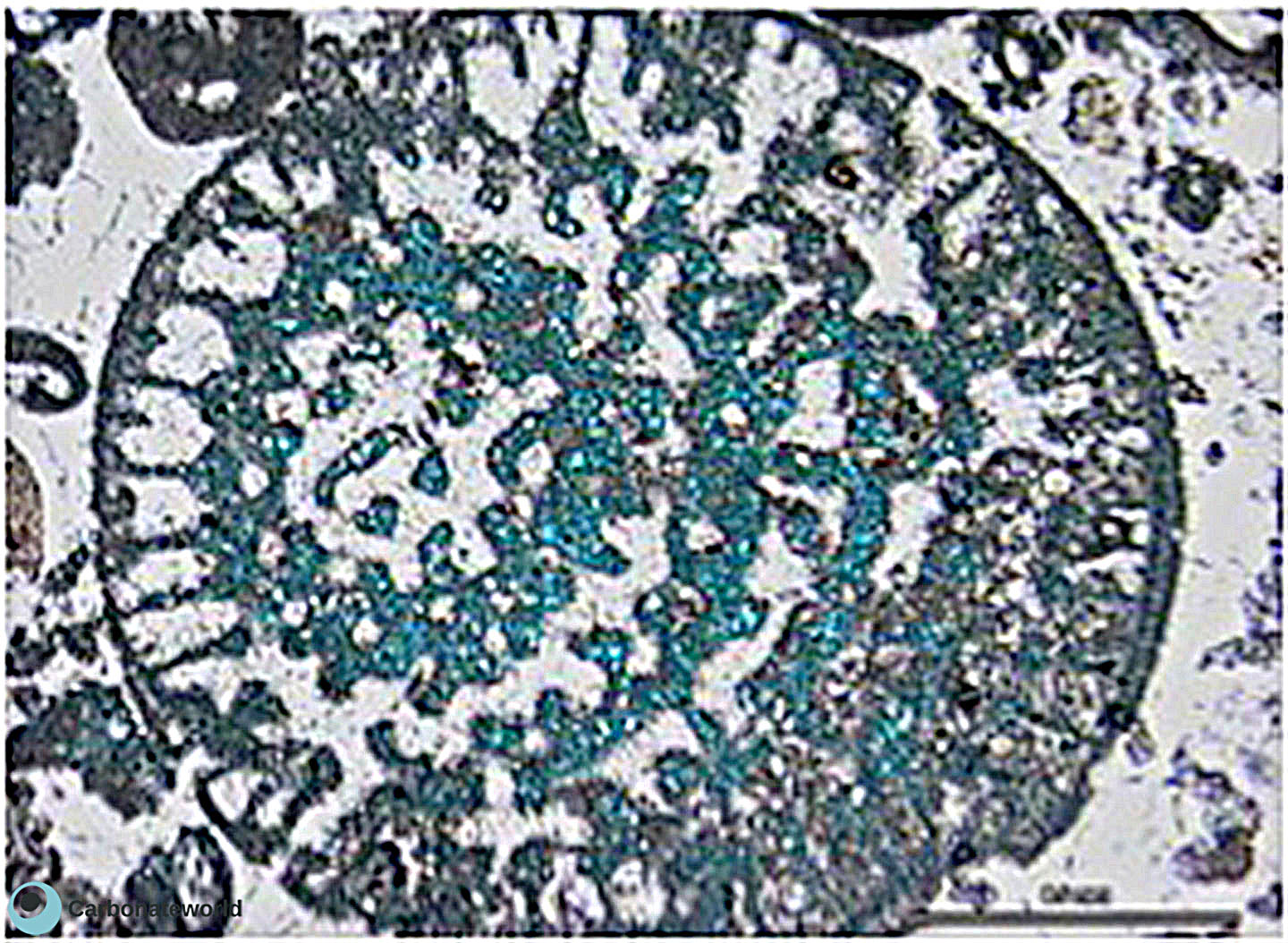
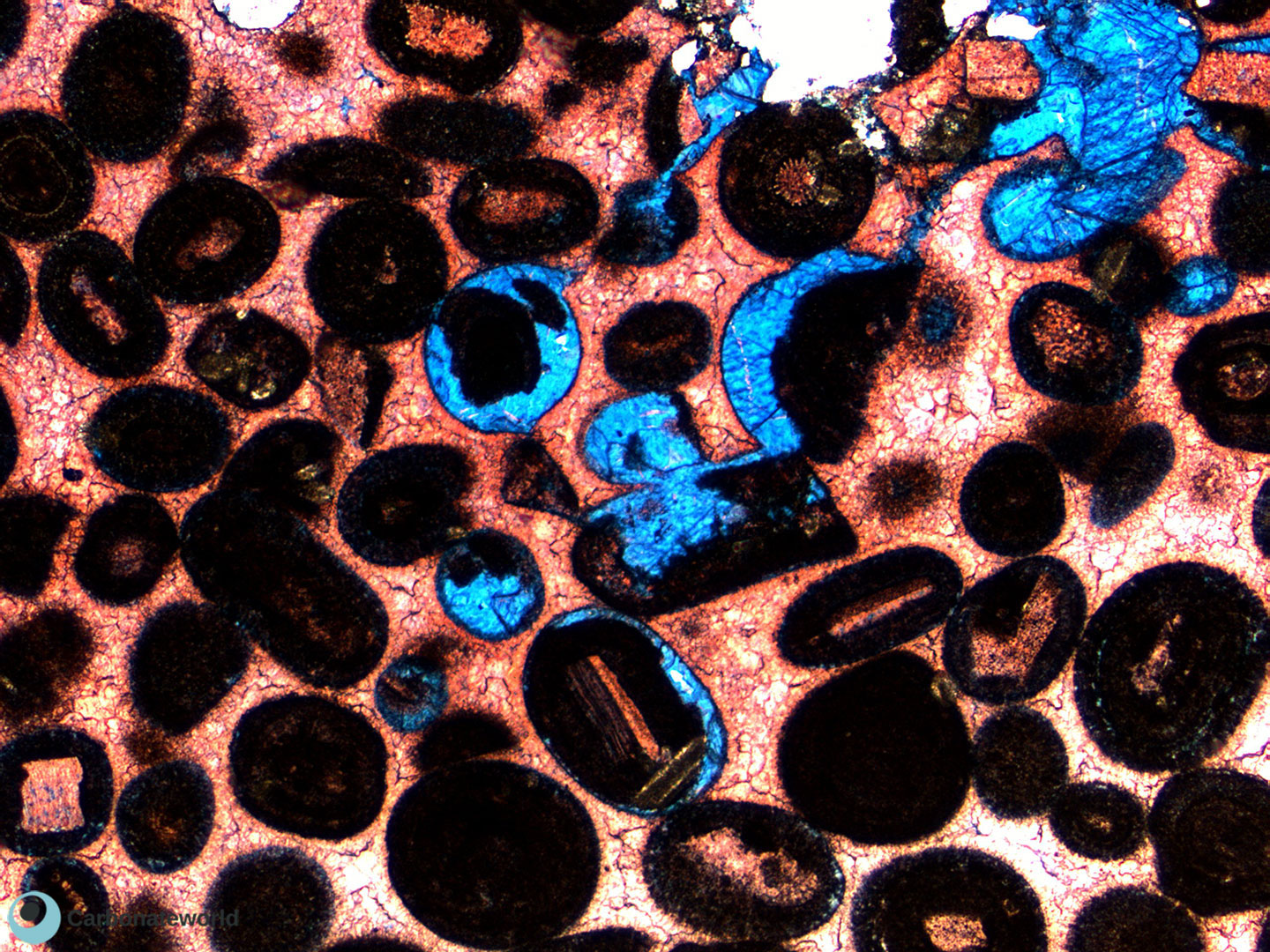
25. Biomouldic
Mouldic porosity due to dissolution of coskinolinid foraminifer walls. The intraparticle space is filled by undissolved cement.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
26. Biomouldic
Mouldic porosity due to dissolution of coskinolinid foraminifer walls. The intraparticle space is filled by undissolved cement.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
27. Biomouldic
Mouldic porosity due to dissolution of gastropods. Field of view approximately 3 mm wide.
Carboniferous, Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
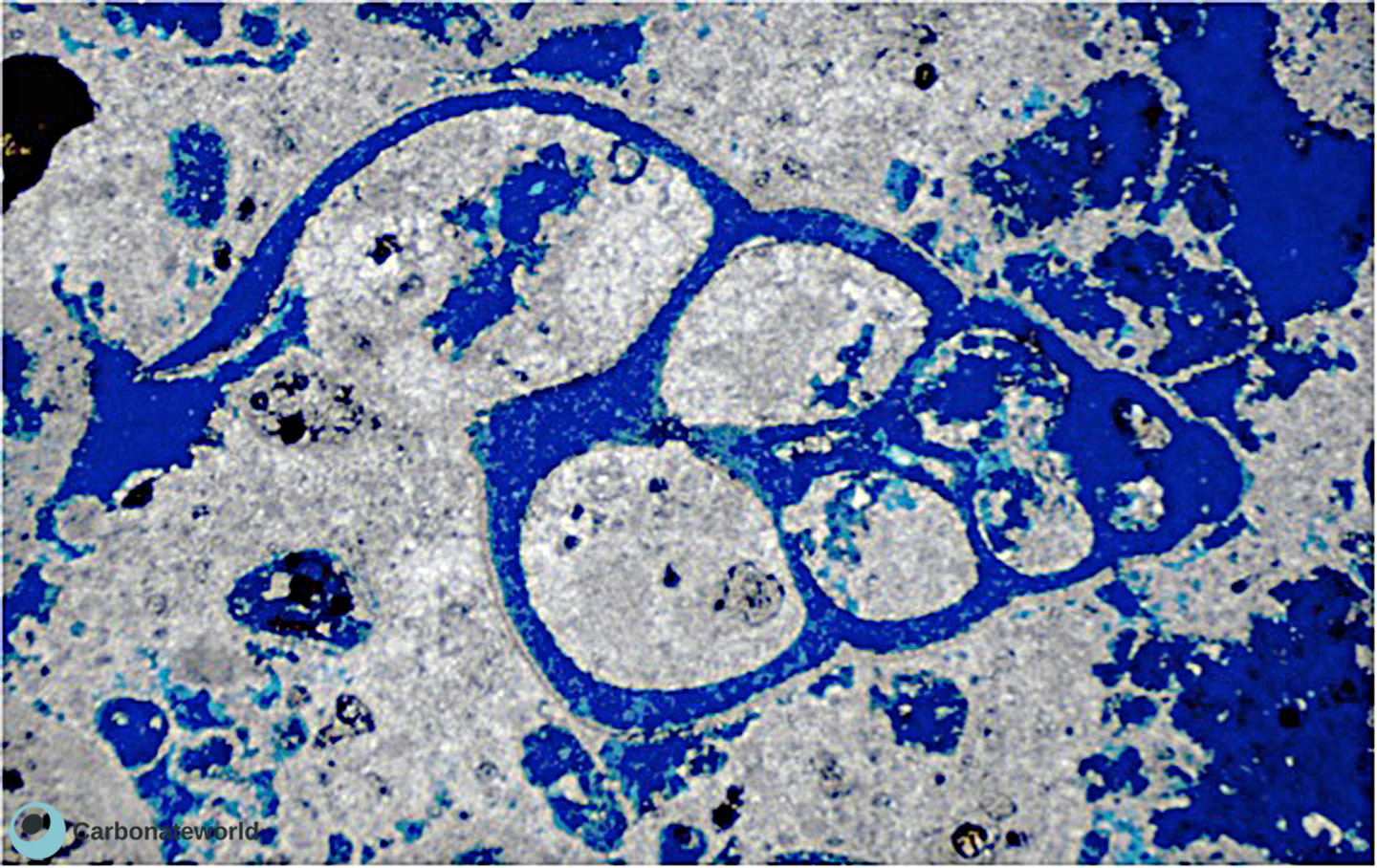
28. Biomouldic
Mouldic secondary porosity due to dissolution of a gastropod. Field of view approximately 3 mm wide.
Miocene, Mallorca, Spain

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
29. Biomouldic
Grainstone of miliolid foraminifera that have been partly to completely corroded with removal of the calcitic shells.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
30. Biomouldic
Sparite cement on a micrite envelope. The original aragonite of the mollusc shell was leached creating mouldic porosity.
Upper Cretaceous (Turonian), Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
31. Biomouldic
Rims of sparite cement on shell fragments. Note the micrite envelopes. The original aragonite of the mollusc shells was leached creating mouldic porosity. Intergranular porosity is also seen.
Upper Cretaceous (Turonian), Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
32. Biomouldic
Mouldic porosity in rudist bivalve grainstone. Field of view approximately 2 mm wide.
Upper Cretaceous (Coniacian), Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
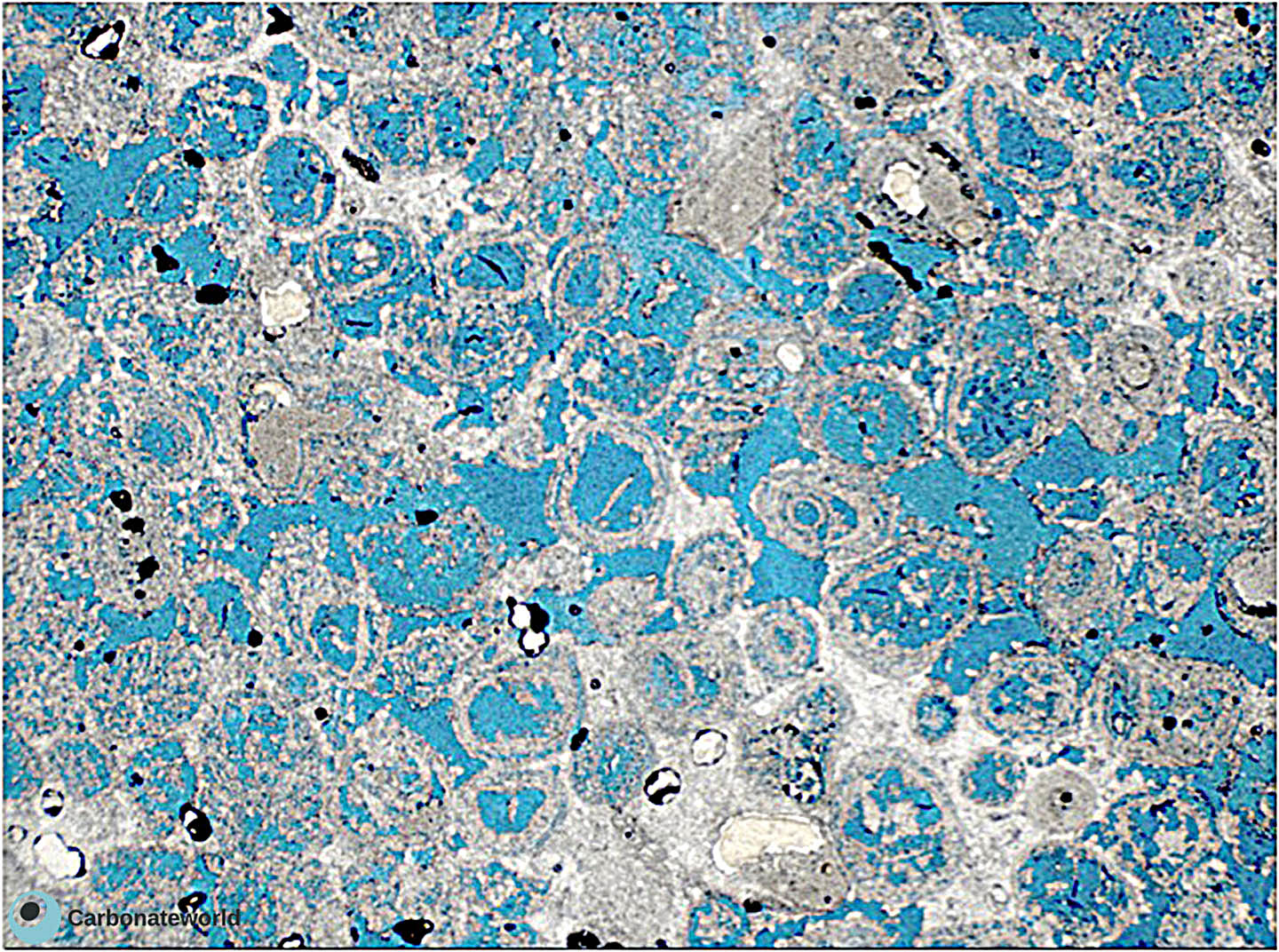
33. Oomouldic
Oomoulds due to dissolution of aragonitic ooids. Field of view approximately 6 mm wide.
Miocene, Mallorca, Spain

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
34. Oomouldic
Ooidal grainstone where ooids were dissolved and the oomouldic porosity was filled by late burial cement (ferroan calcite, blue staining with K ferricyanide).

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
35. Mouldic/Interparticle
Skeletal grainstone containing shelter, interparticle and mouldic porosity. Field of view approximately 9 mm wide.
Carboniferous (Visean), Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
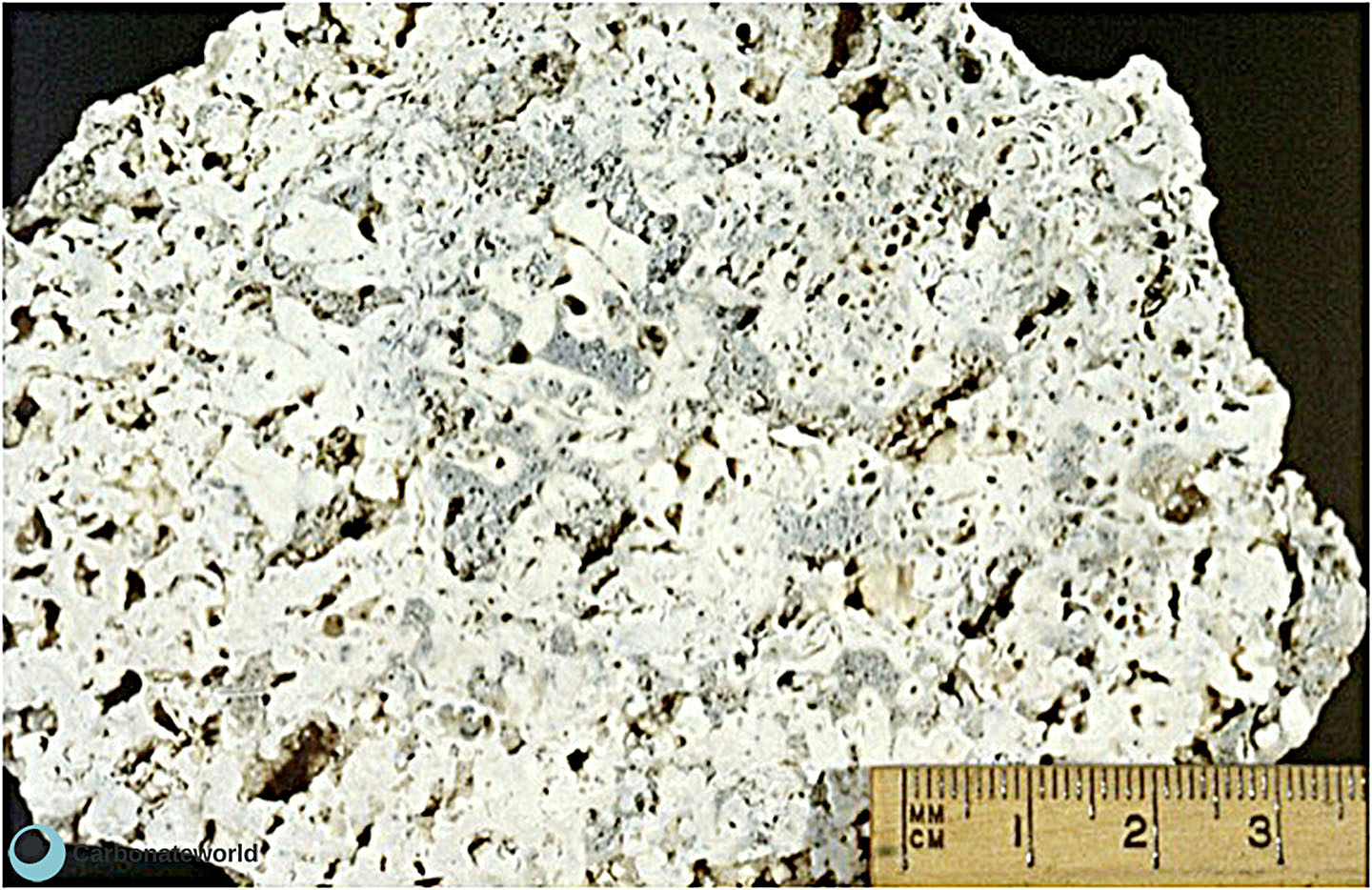
36. Cavernous
Cavernous porosity due to limestone dissolution by meteoric water.

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
37. Late leaching
At first this appears to be primary intraparticle porosity in the stereom of an echinoderm fragment, but the porosity has been created by the selective, late stage dissolution of micrite that had filled the once porous grain.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
38. Late leaching
Corroded echinoderm fragment with remnant patches of matrix in the stereom and dissolved micrite matrix producing vug porosity.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
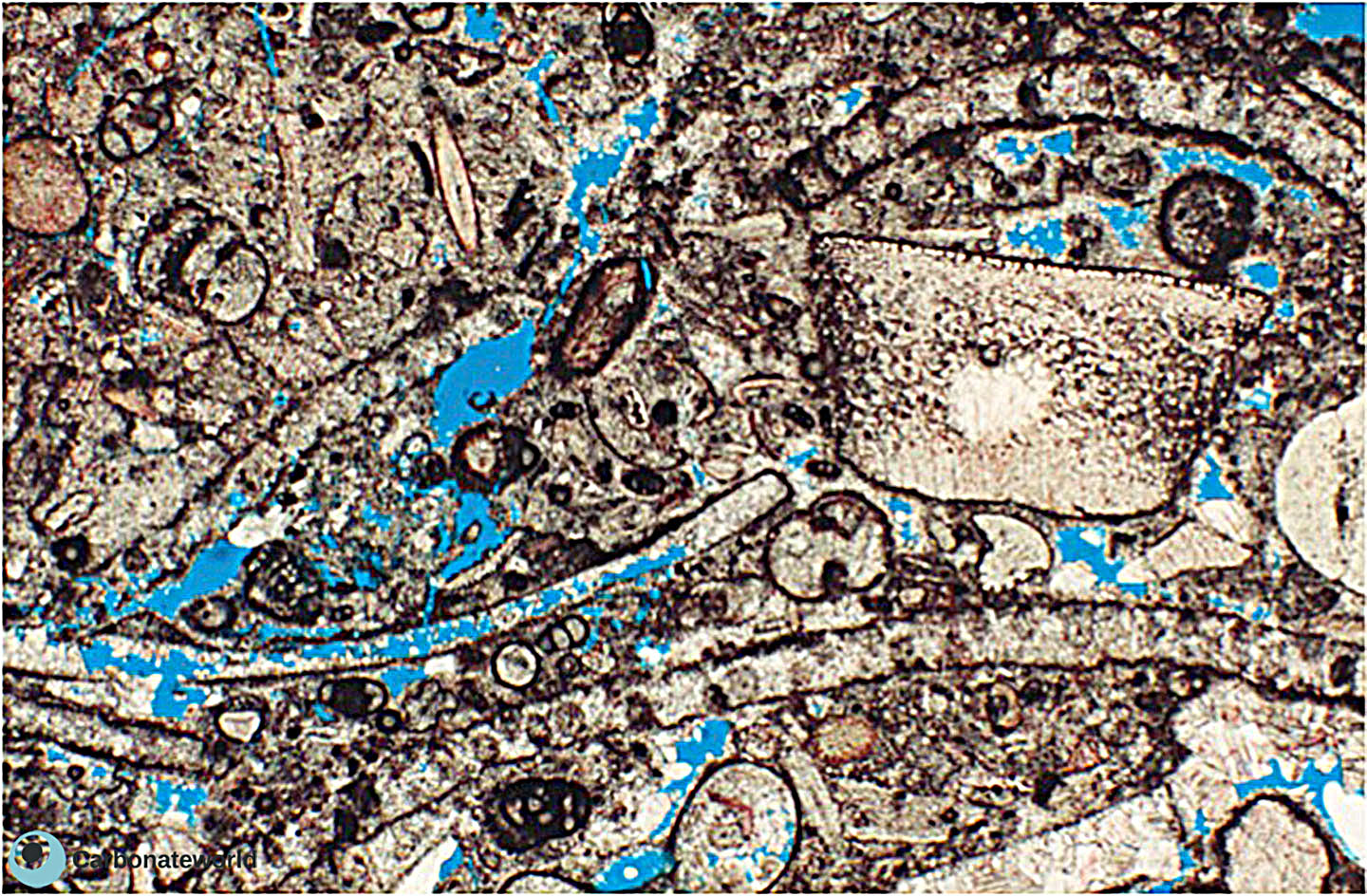
39. Dissolution
Extensive dissolution of the sparry calcite intragranular cements and micritic foraminifer test walls.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
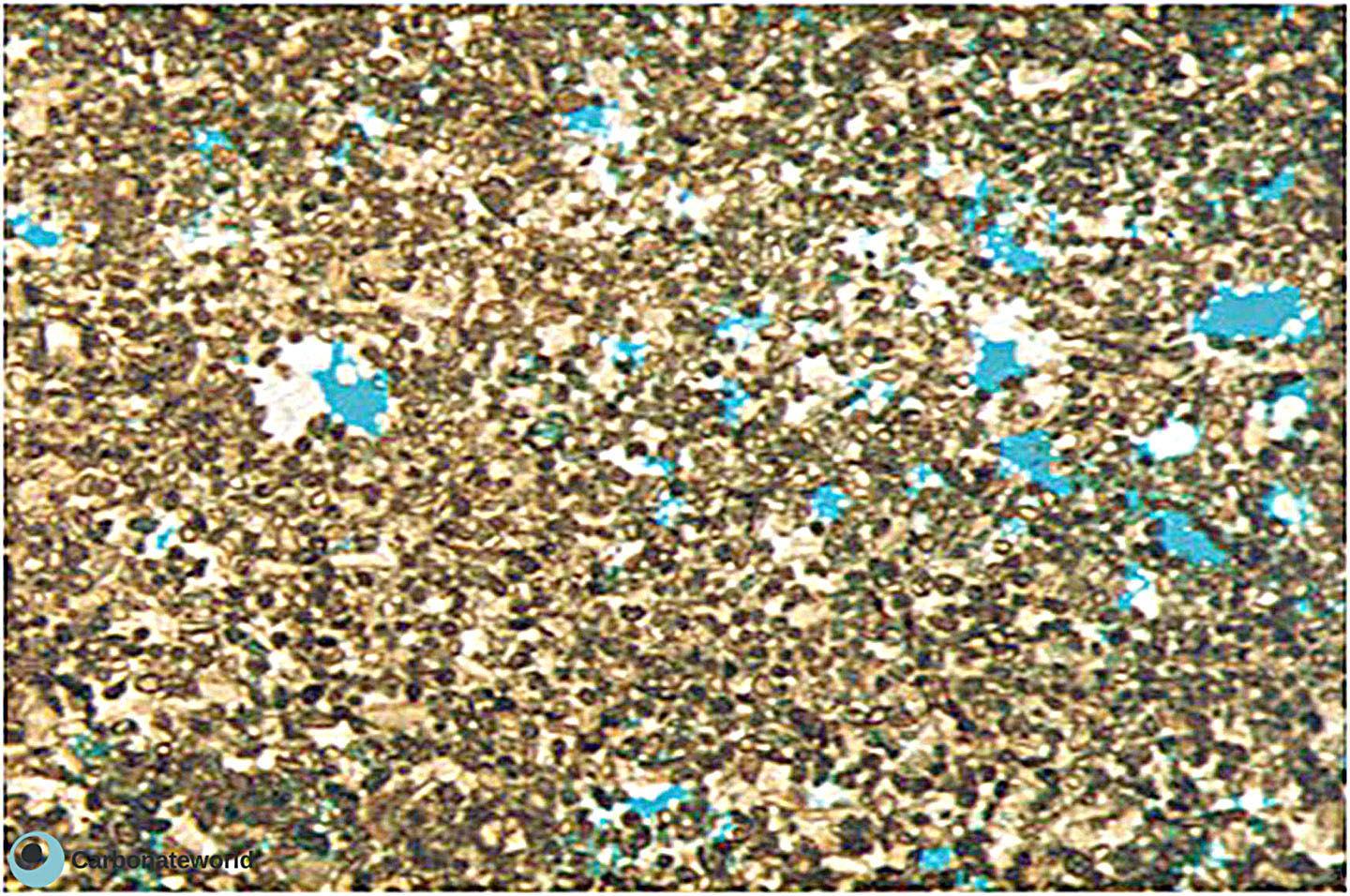
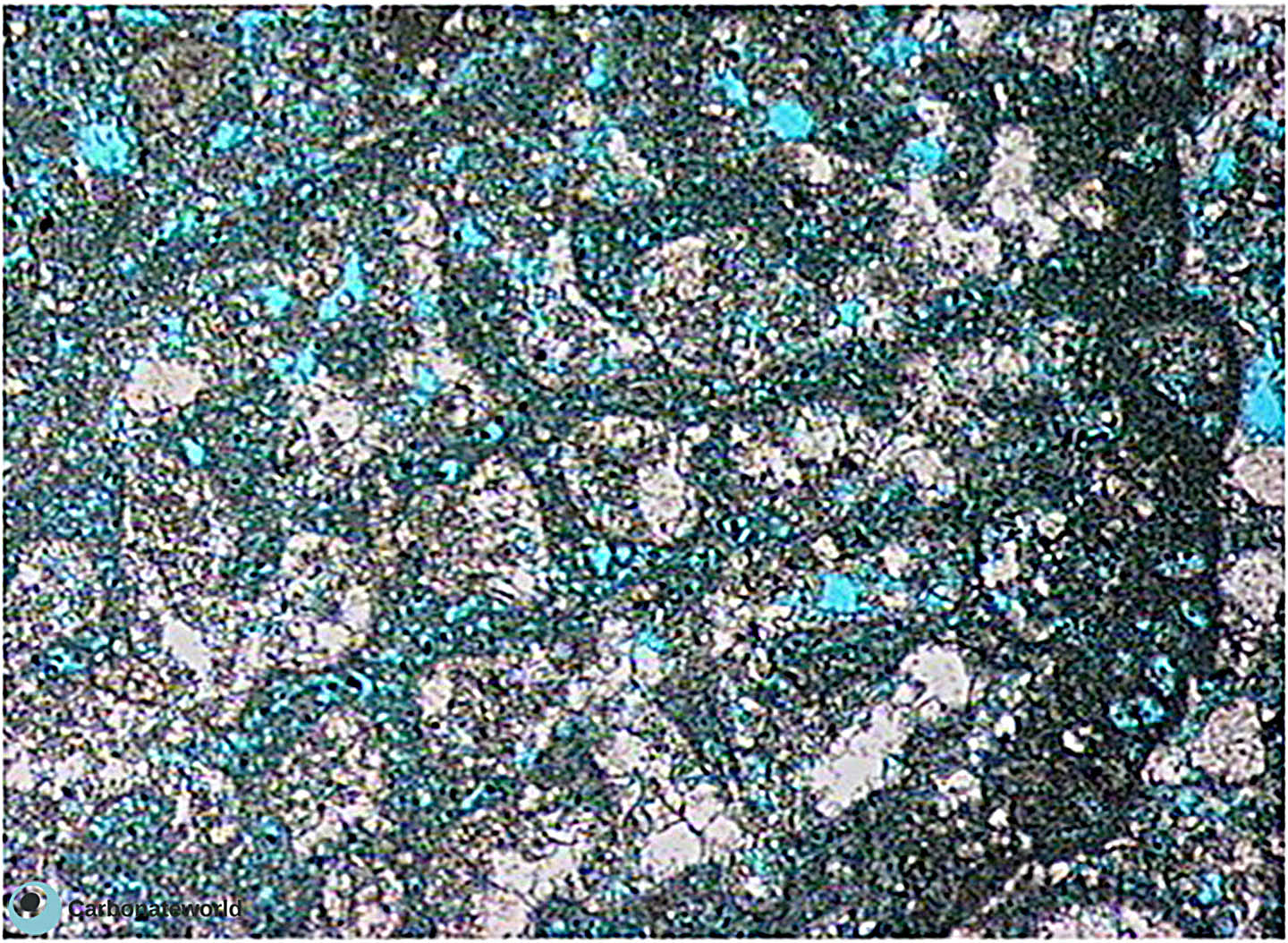
40. Microporosity
Irregular microporosity within the micrite matrix in foraminifer packstone with Coskinolina.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
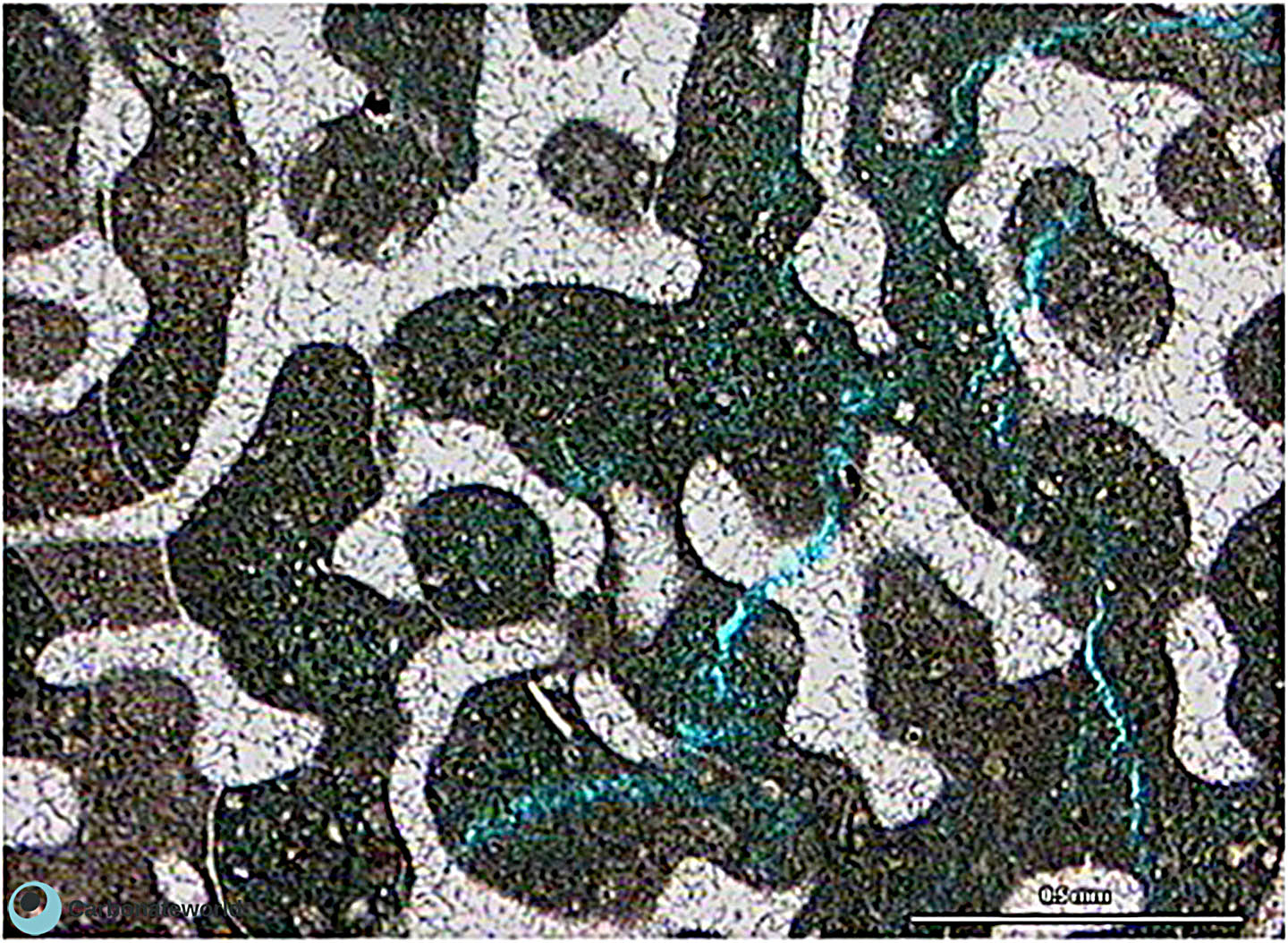
41. Microporosity
Microporosity in the walls of Coskinolina foraminifer and in the cement precipitated in the interparticle space of the foraminifer chambers. The walls are nearly 60 microns thick.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
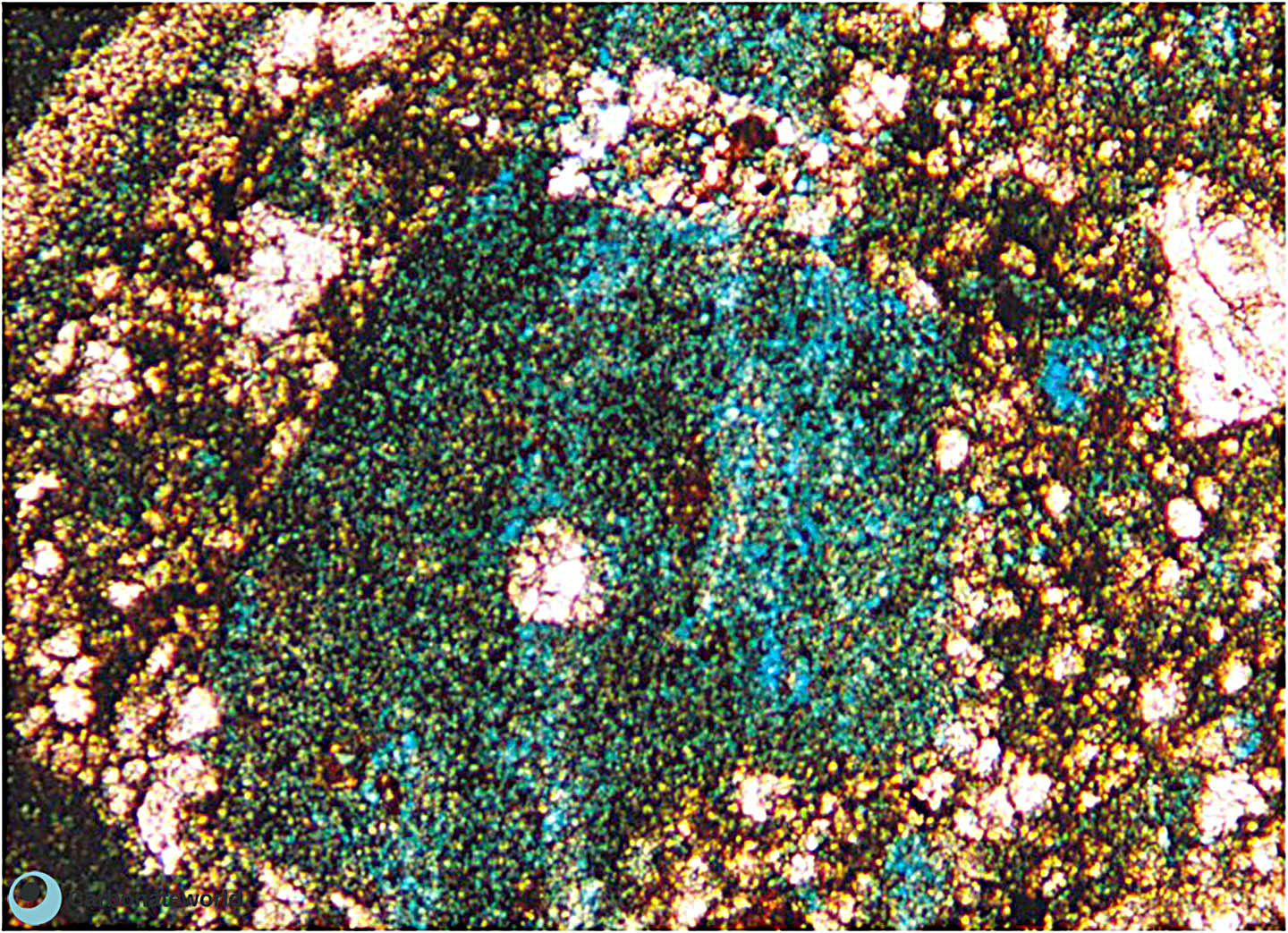
42. Microporosity
Microporosity and fine fracture porosity in the micrite matrix filling the cavities in a coral; the former aragonitic corallite walls were replaced by calcite spar but exhibit no porosity.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
43. Microporosity
Microporosity in a skeletal grain; field of view 0.3 mm.
Upper Cretaceous, Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
44. Microporosity
SEM image of microporosity in Mississippian (Visean) micrite.
Carboniferous, Mississippian (Visean), Karachaganak Field, Kazakhstan

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
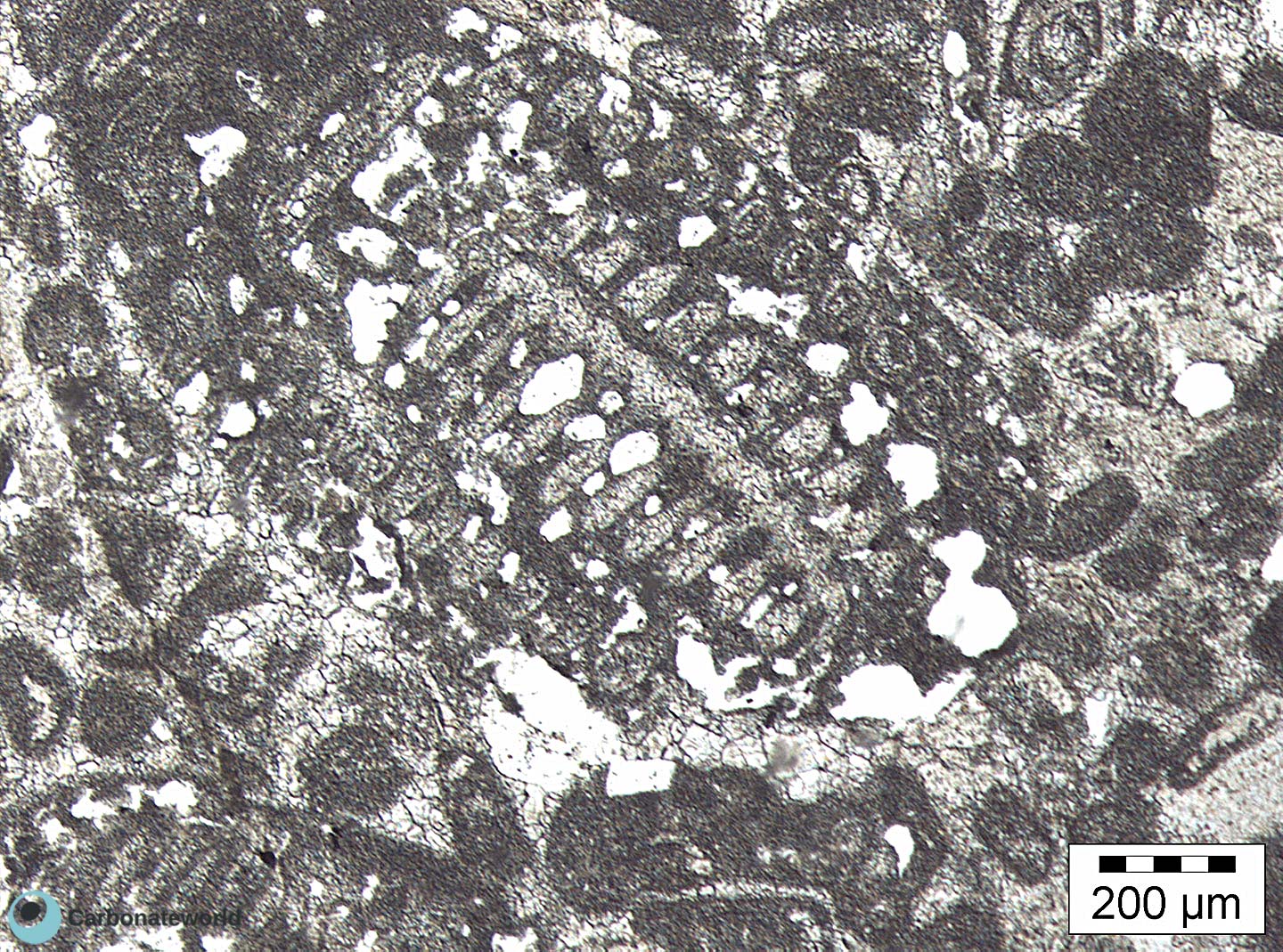
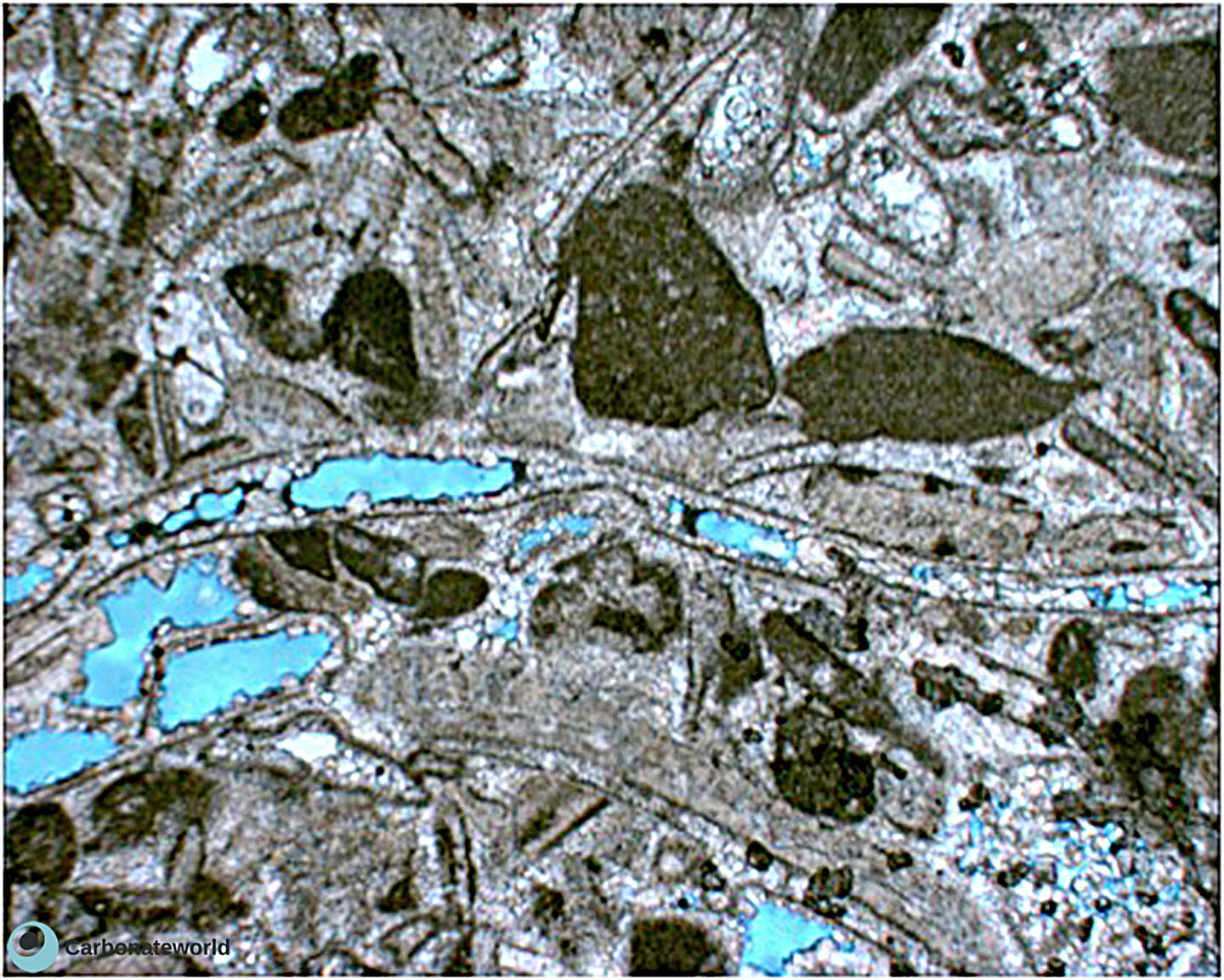
45. Stylolite dissolution
Late corrosion porosity along stylolite.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
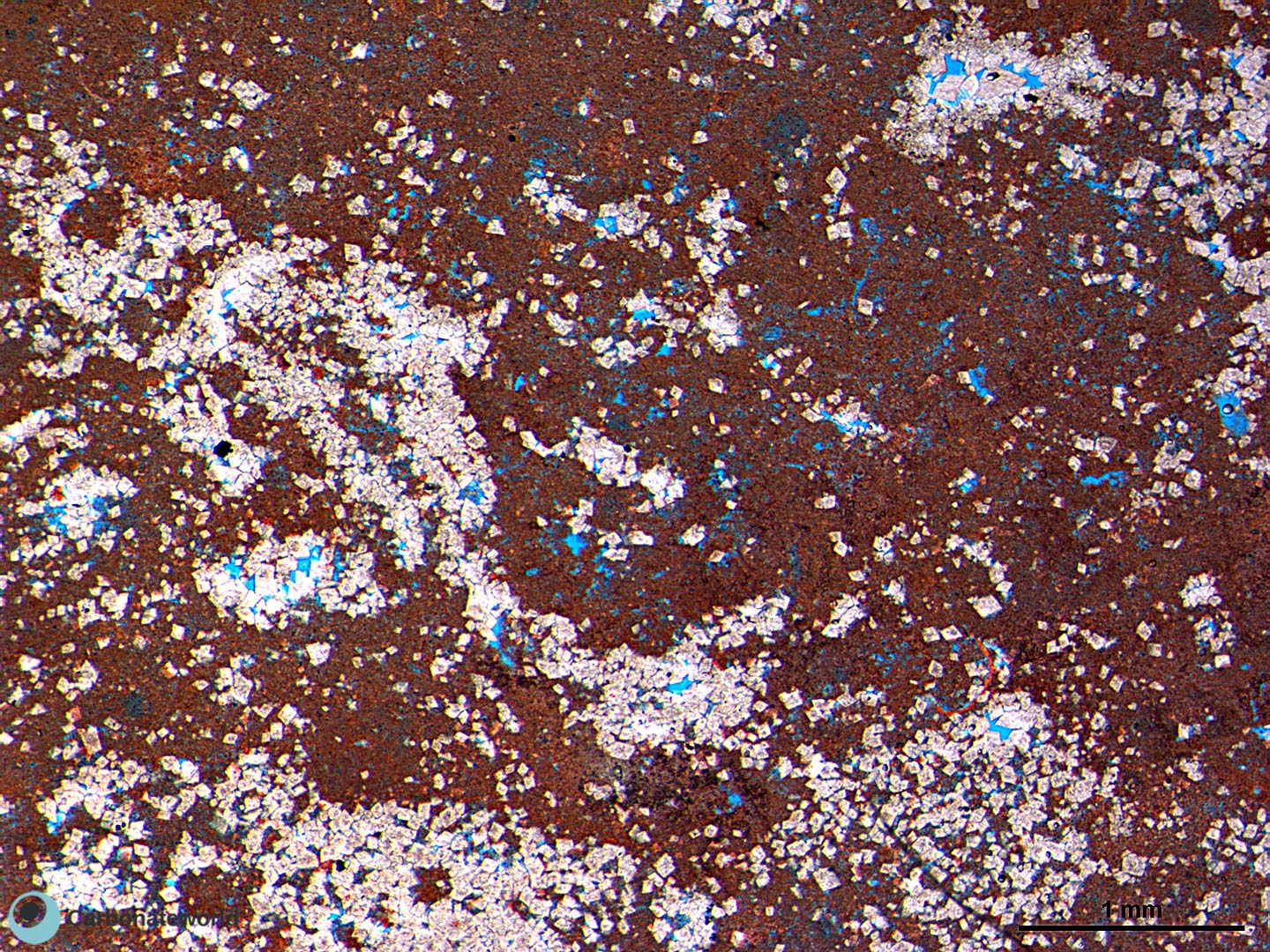
46. Matrix dissolution
Micrite matrix partly replaced by a hypidiotopic mosaic of dolomite (white). Micrite has been partly dissolved and exhibits secondary porosity (blue epoxy).

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
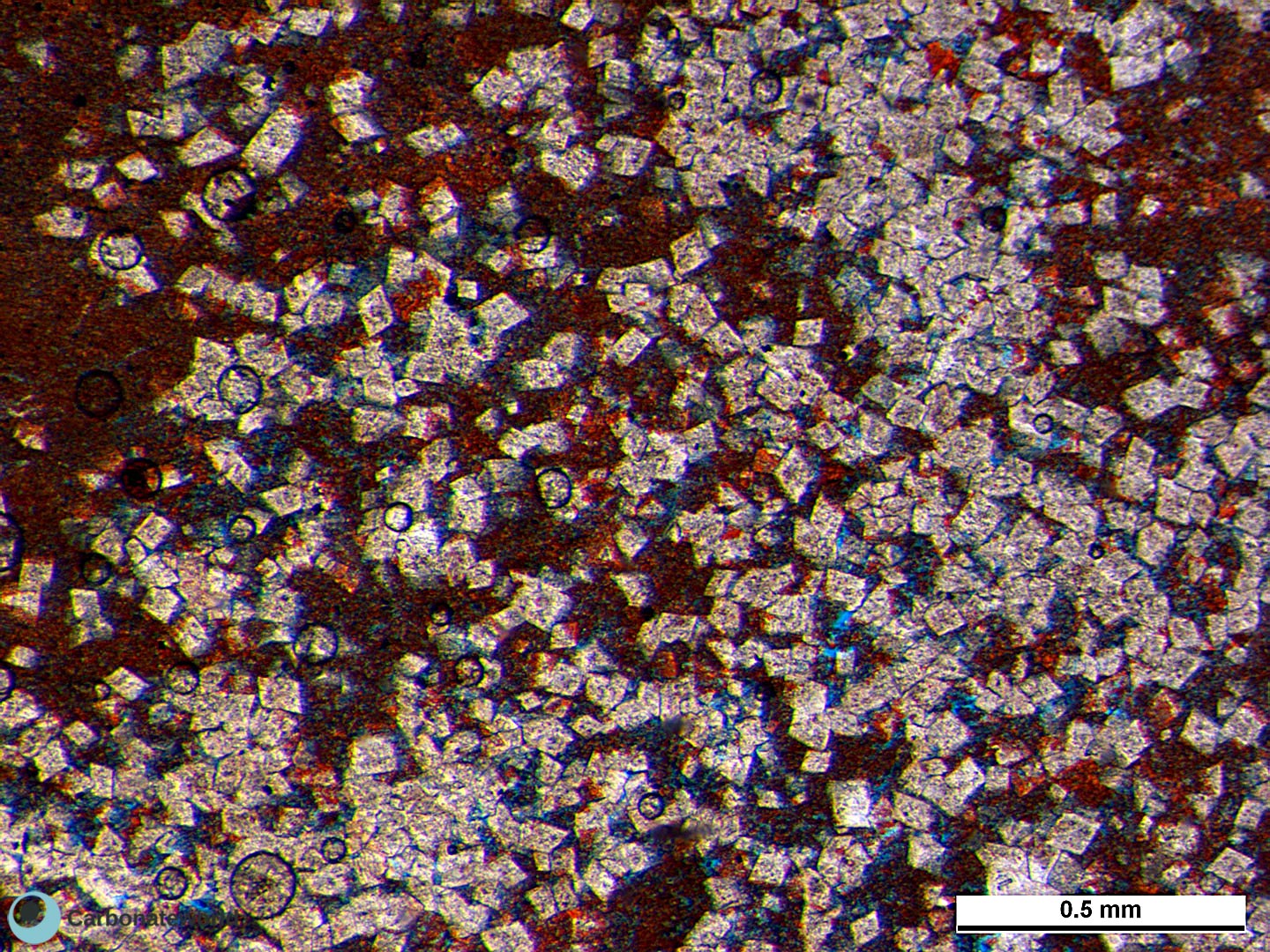
47. Dissolution/Intercrystalline
Idiotopic (planar-e) mosaic of (euhedral) dolomite rhomb crystals (white) replacing micrite. The blue areas are secondary porosity between the dolomite crystals (intercrystalline) due to micrite dissolution.

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
48. Dissolution/Stylolite
Hypidiotopic mosaic of (subhedral, planar-s) dolomite rhomb crystals (white) replacing a skeletal packstone. The blue areas are secondary porosity due to dissolution associated with stylolite formation.

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
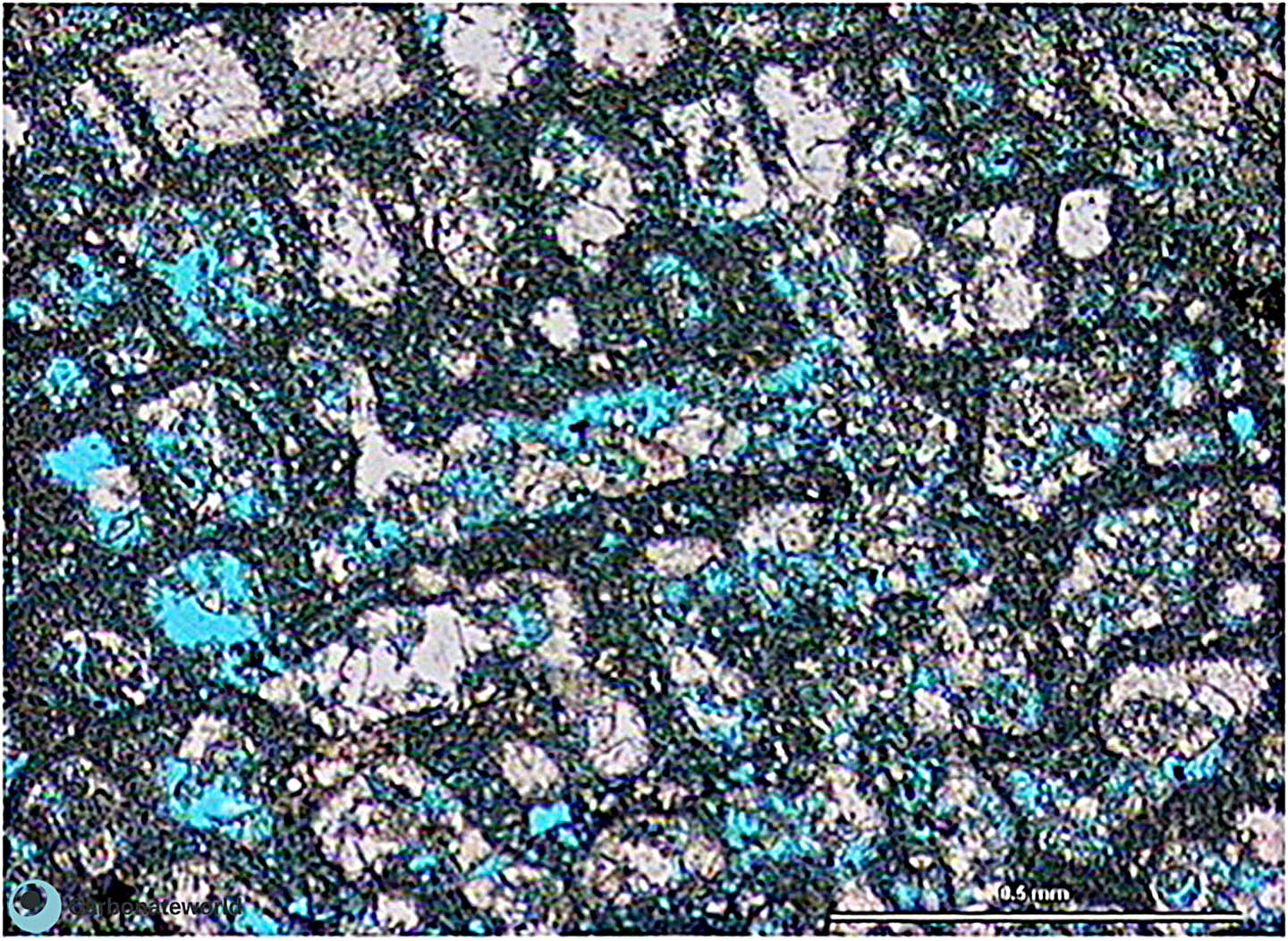
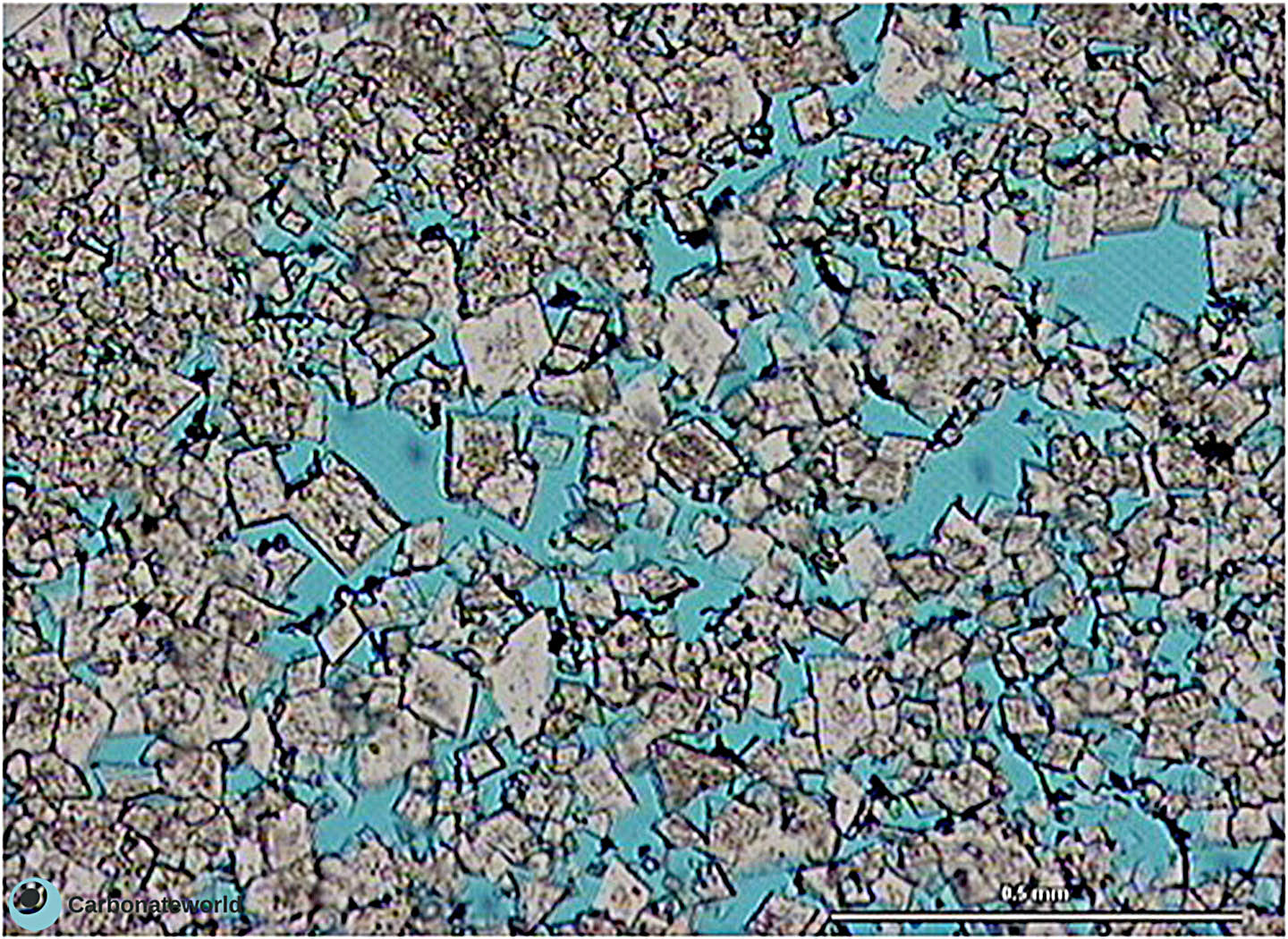
49. Intercrystalline
Intercrystalline porosity in dolomite planar-e (euhedral) idiotopic mosaic.
Upper Cretaceous, Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
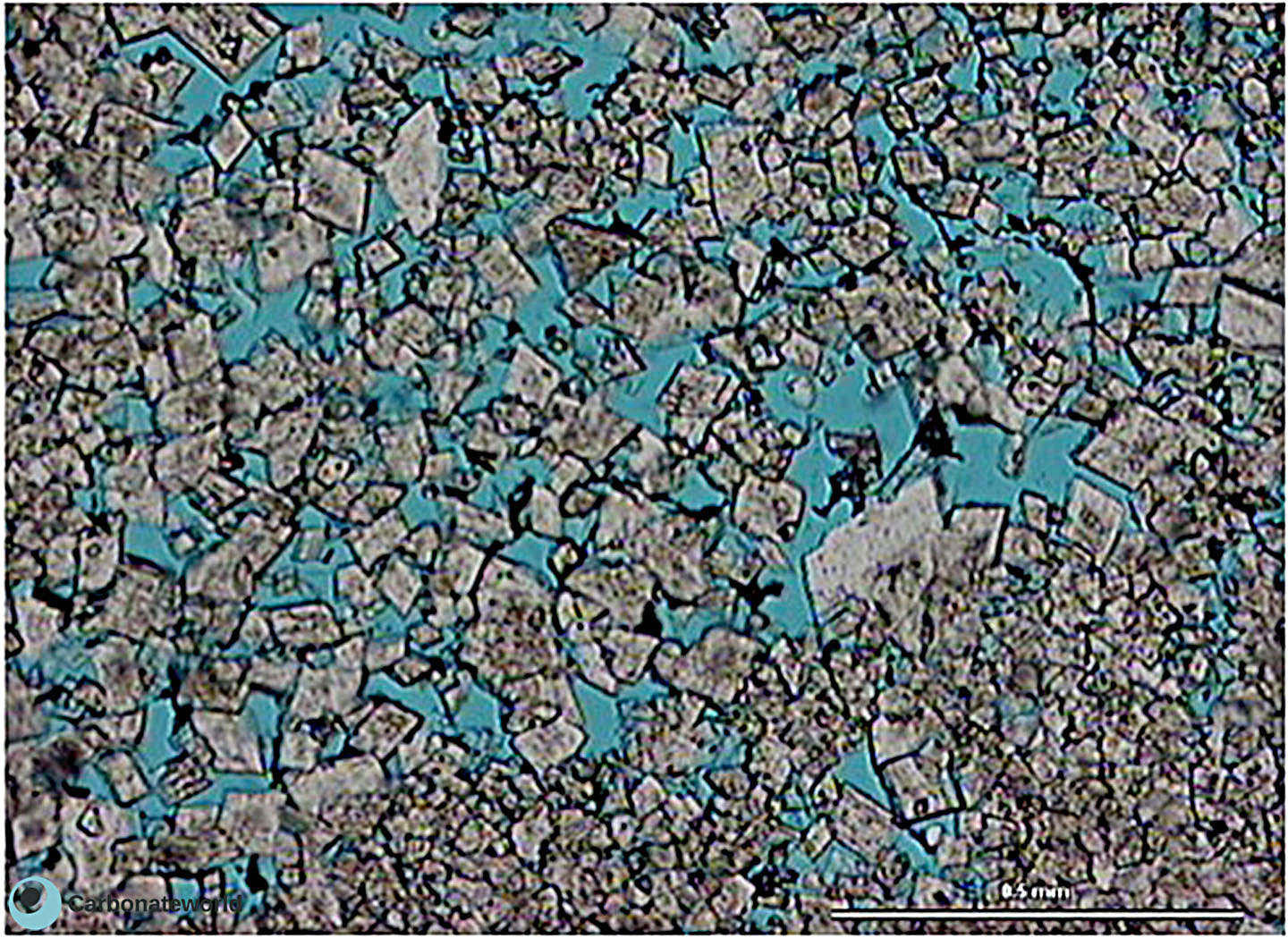
50. Intercrystalline
Intercrystalline porosity in dolomite planar-e (euhedral) idiotopic mosaic.
Upper Cretaceous, Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
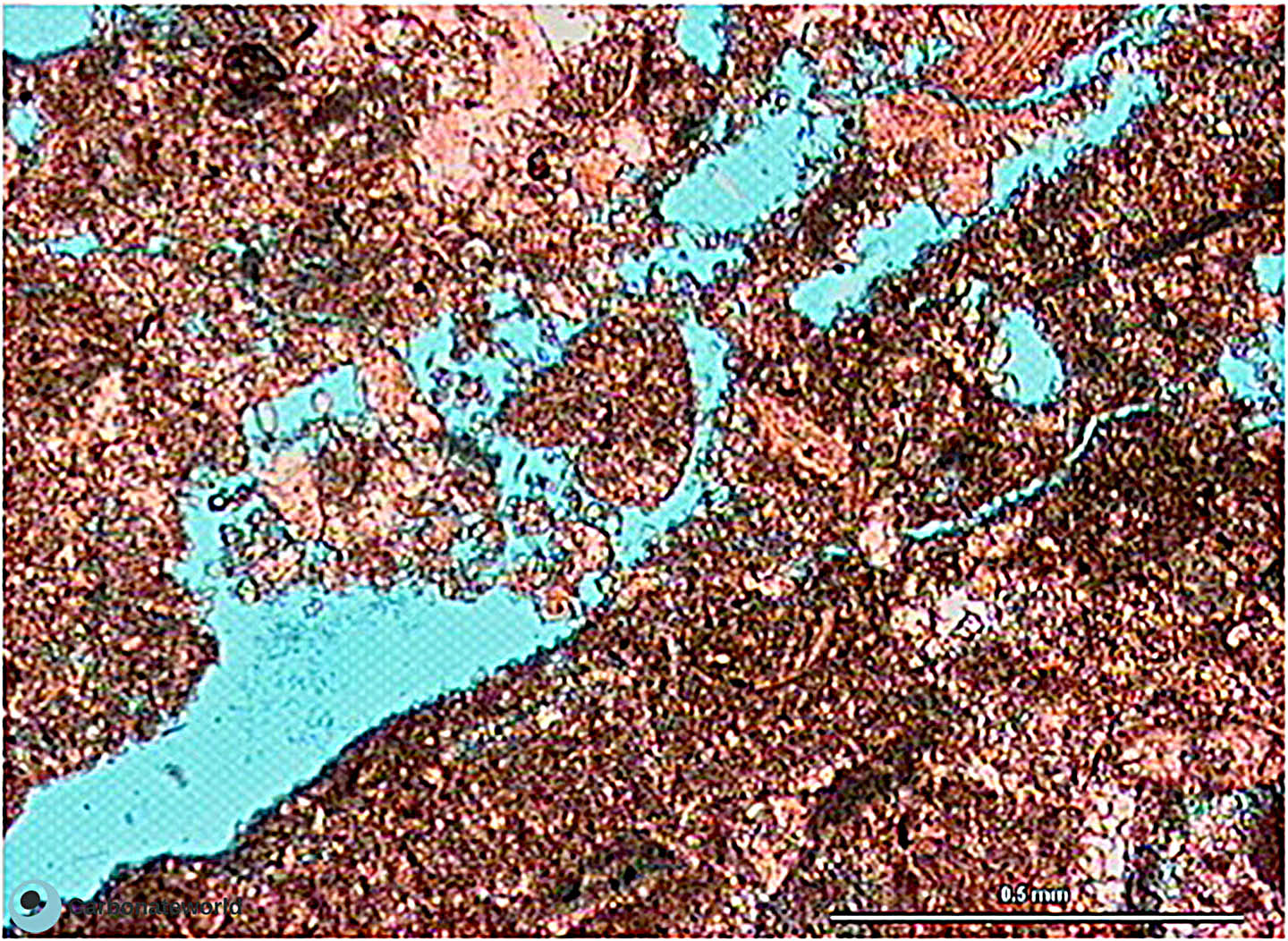
51. Fracture/Dissolution
Late corrosion porosity along fractures.
Eocene, Mukta Field, offshore India

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
IMAGE INDEX
1. Interparticle
2. Interparticle
3. Interparticle
4. Interparticle
5. Interparticle
6. Interparticle
7. Interparticle
8. Interparticle
9. Interparticle
10. Interparticle
11. Interparticle
12. Secondary
13. Intraparticle
14. Intraparticle
15. Intraparticle
16. Intraparticle/Dissolution
17. Intraparticle/Dissolution
18. Growth framework
19. Breccia porosity
20. Fenestral porosity
21. Fenestral porosity
22. Fenestral porosity
23. Biomouldic
24. Biomouldic
25. Biomouldic
26. Biomouldic
27. Biomouldic
28. Biomouldic
29. Biomouldic
30. Biomouldic
31. Biomouldic
32. Biomouldic
33. Oomouldic
34. Oomouldic
35. Mouldic/Interparticle
36. Cavernous
37. Late leaching
38. Late leaching
39. Dissolution
40. Microporosity
41. Microporosity
42. Microporosity
43. Microporosity
44. Microporosity
45. Stylolite dissolution
46. Matrix dissolution
47. Dissolution/Intercrystalline
48. Dissolution/Stylolite
49. Intercrystalline
50. Intercrystalline
51. Fracture/Dissolution


Interparticle porosity

Fibrous marine cement

Interparticle porosity

Fibrous marine cement

Interparticle porosity

Micrite envelope

Bryozoan

Biomould
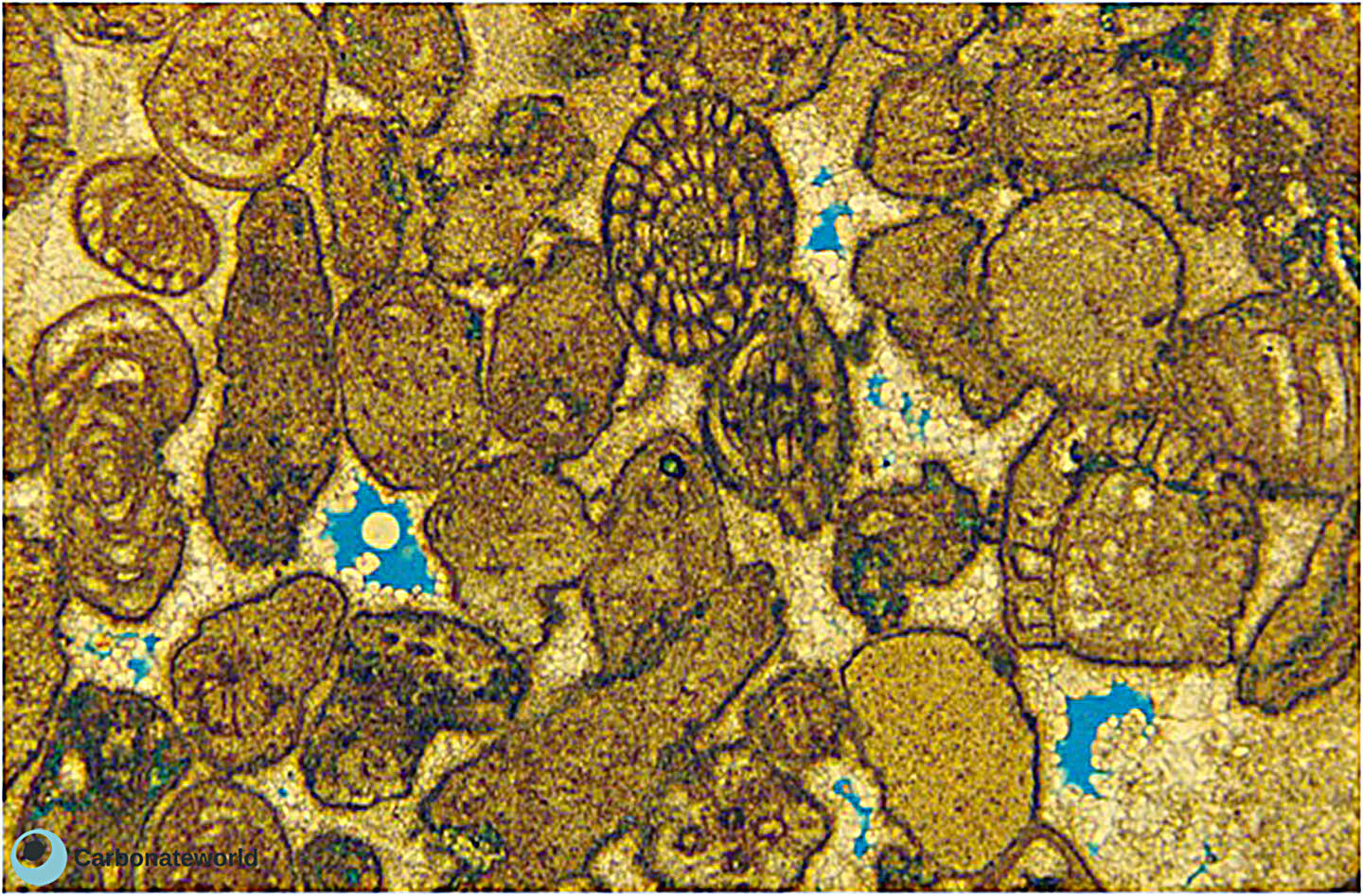

Fusulinid

Interparticle porosity
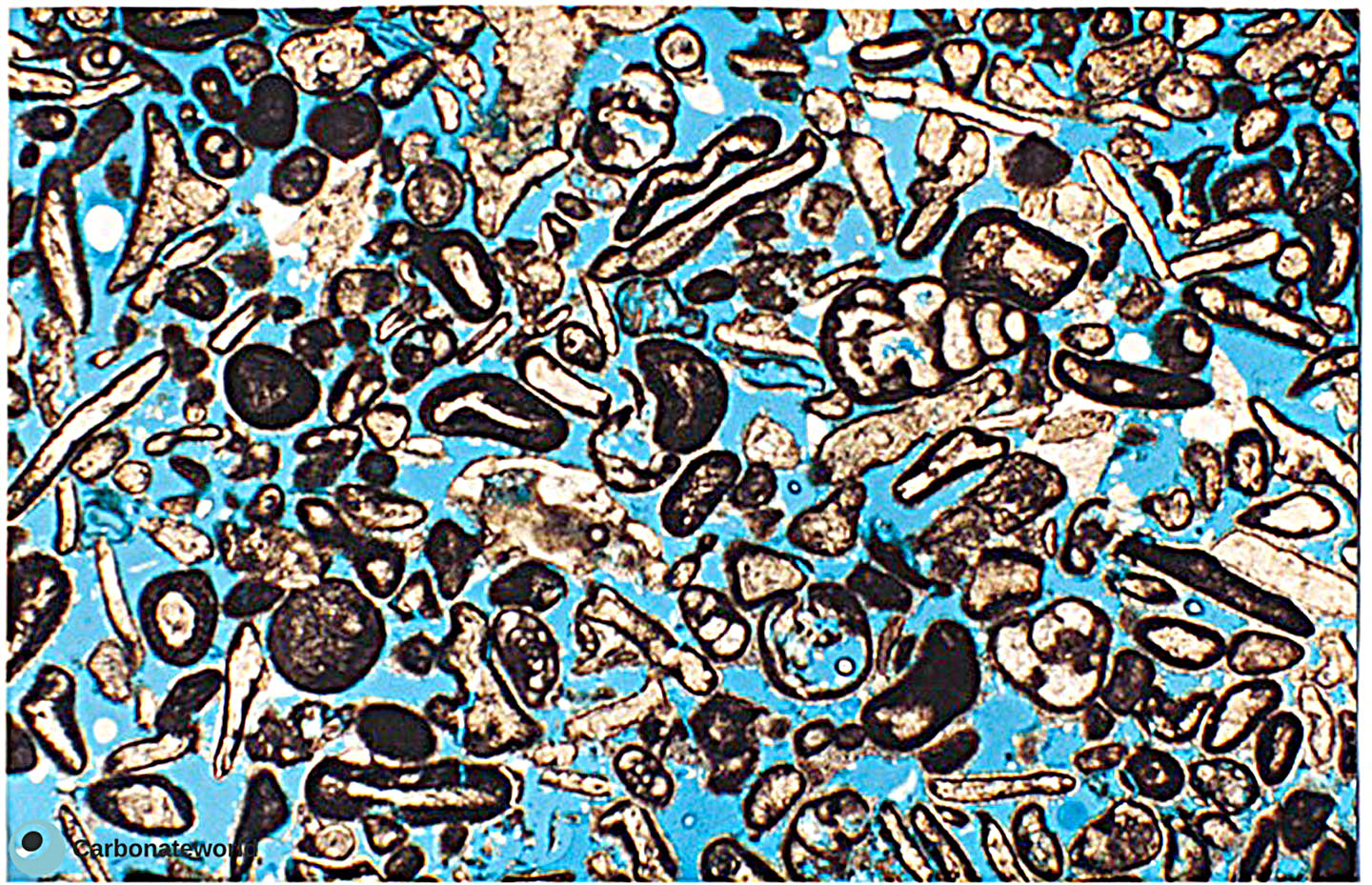

Interparticle porosity

Intraparticle porosity
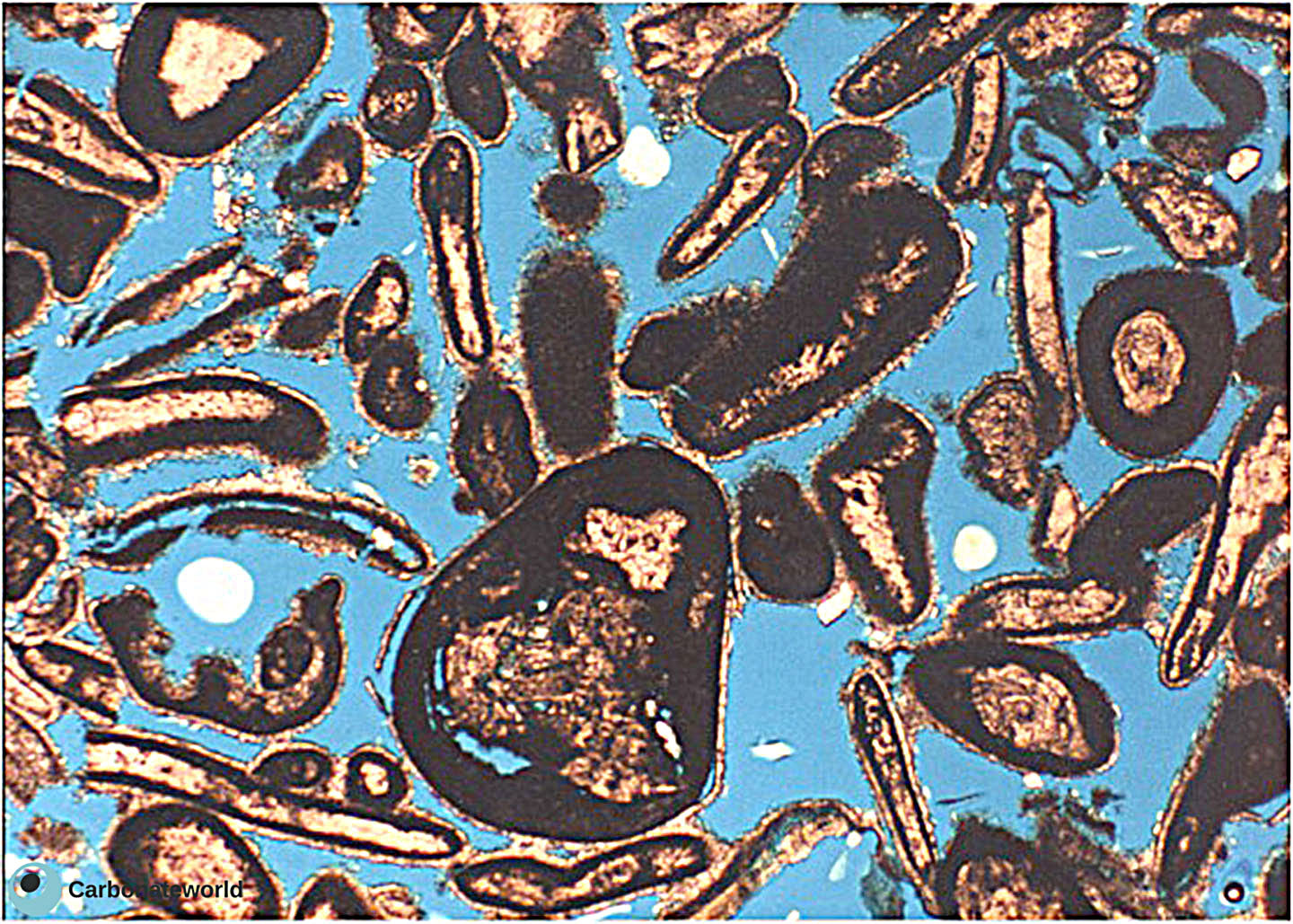

Micrite envelopes

Interparticle porosity
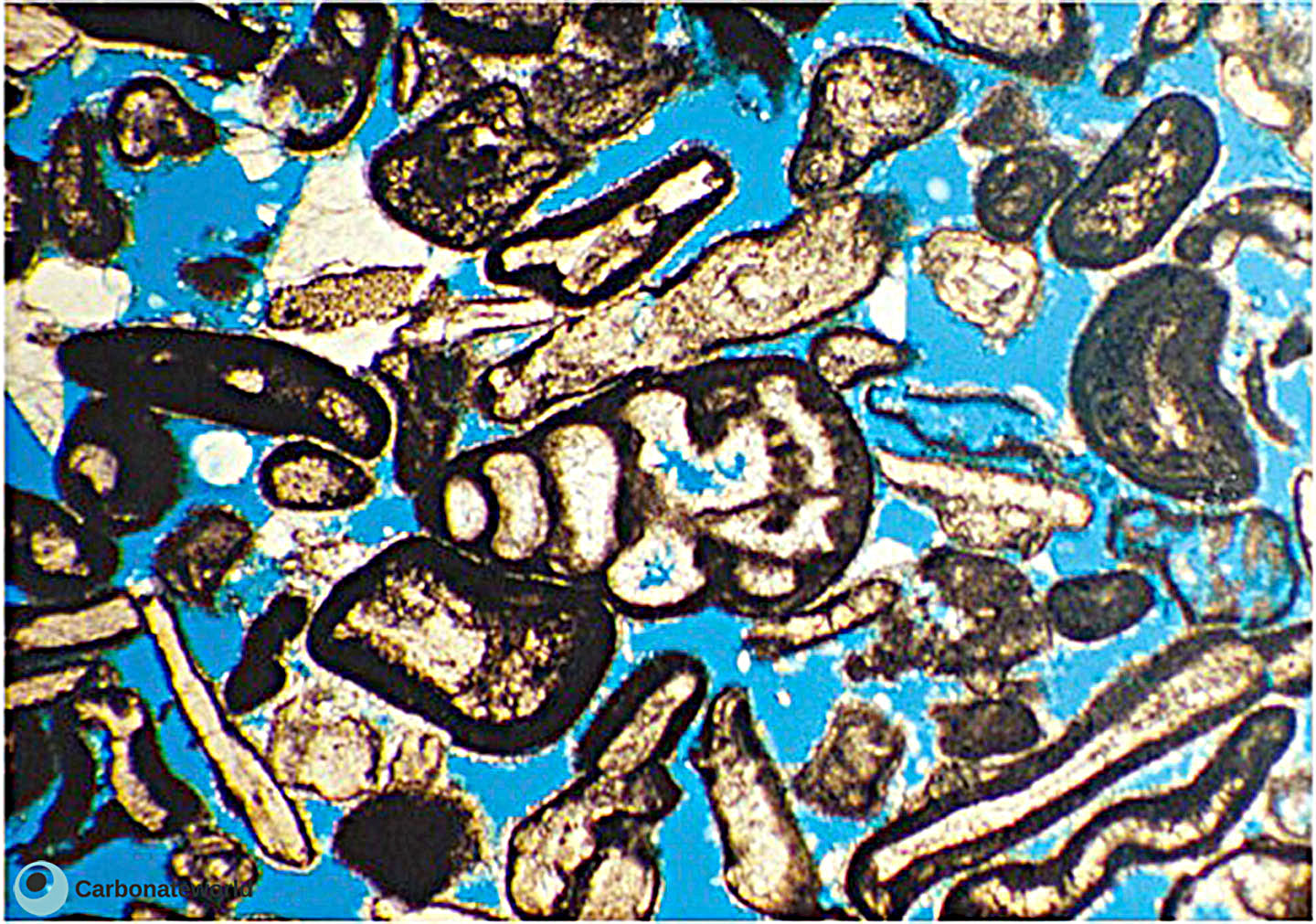

Intraparticle porosity

Interparticle porosity

Echinoderm

Koninckopora

Interparticle porosity

Intraparticle porosity

Koninckopora

Interparticle porosity

Dissolution porosity

Intraparticle cement preserved after dissolution

Fusulinid

Porosity in dolomitized matrix


Intraparticle porosity

Intraparticle porosity

Fracture porosity

Secondary porosity enhancing intraparticle pore space


Secondary porosity enhancing intraparticle pore space


Growth framework porosity
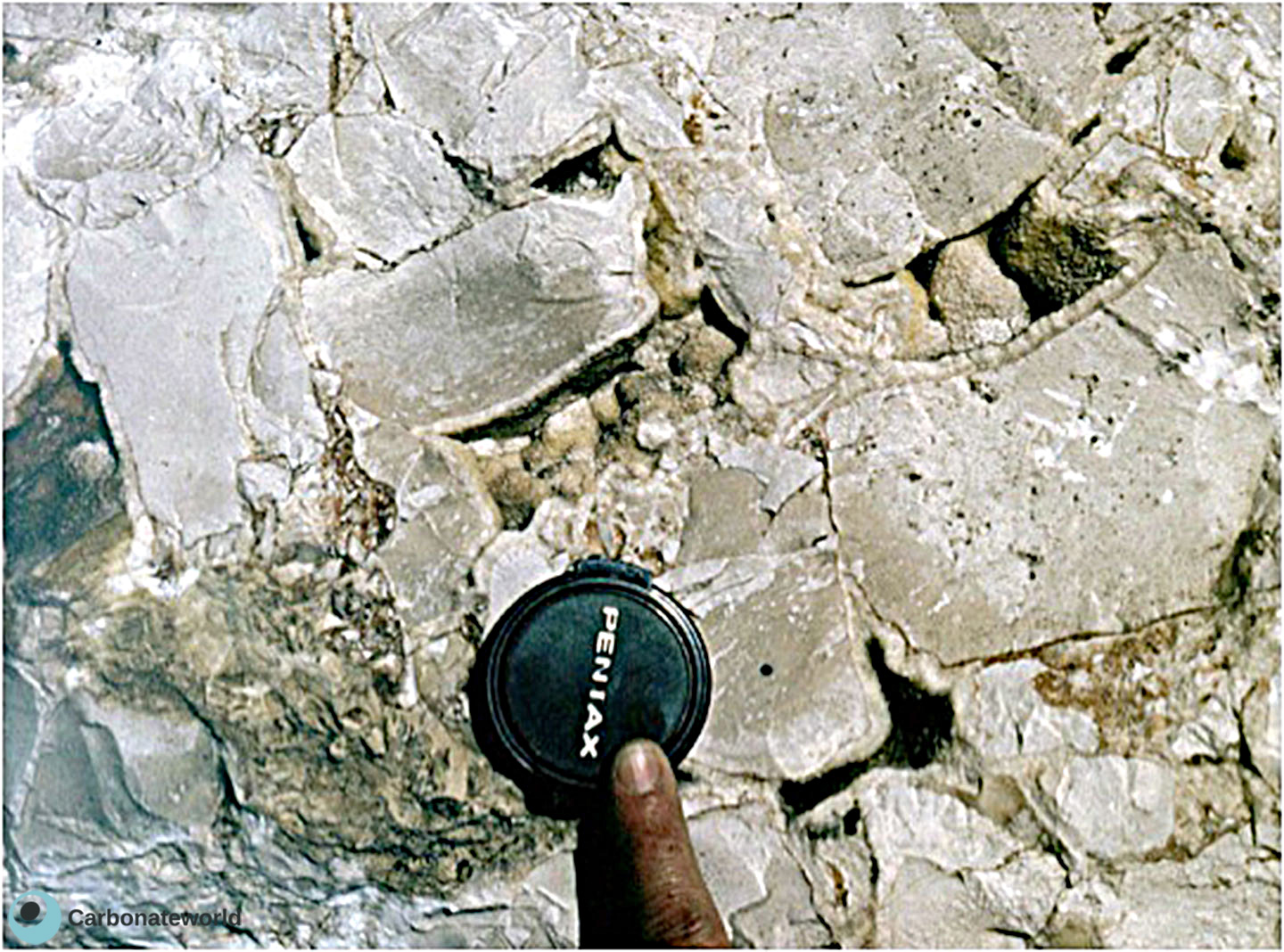


Breccia porosity
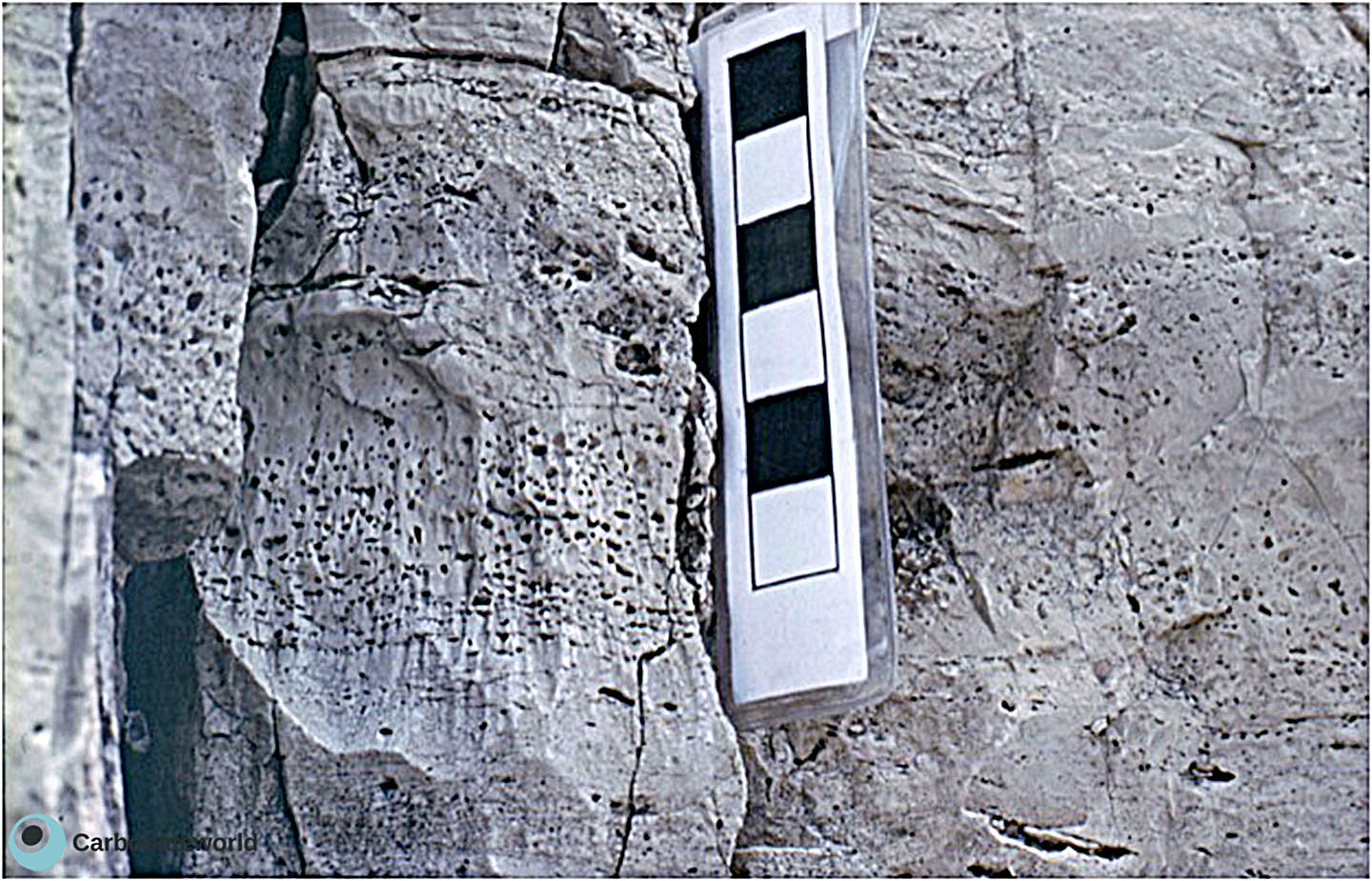


Fenestral porosity

Fenestral porosity

Fenestral porosity


Biomouldic porosity

Dissolution of coskinolinid wall
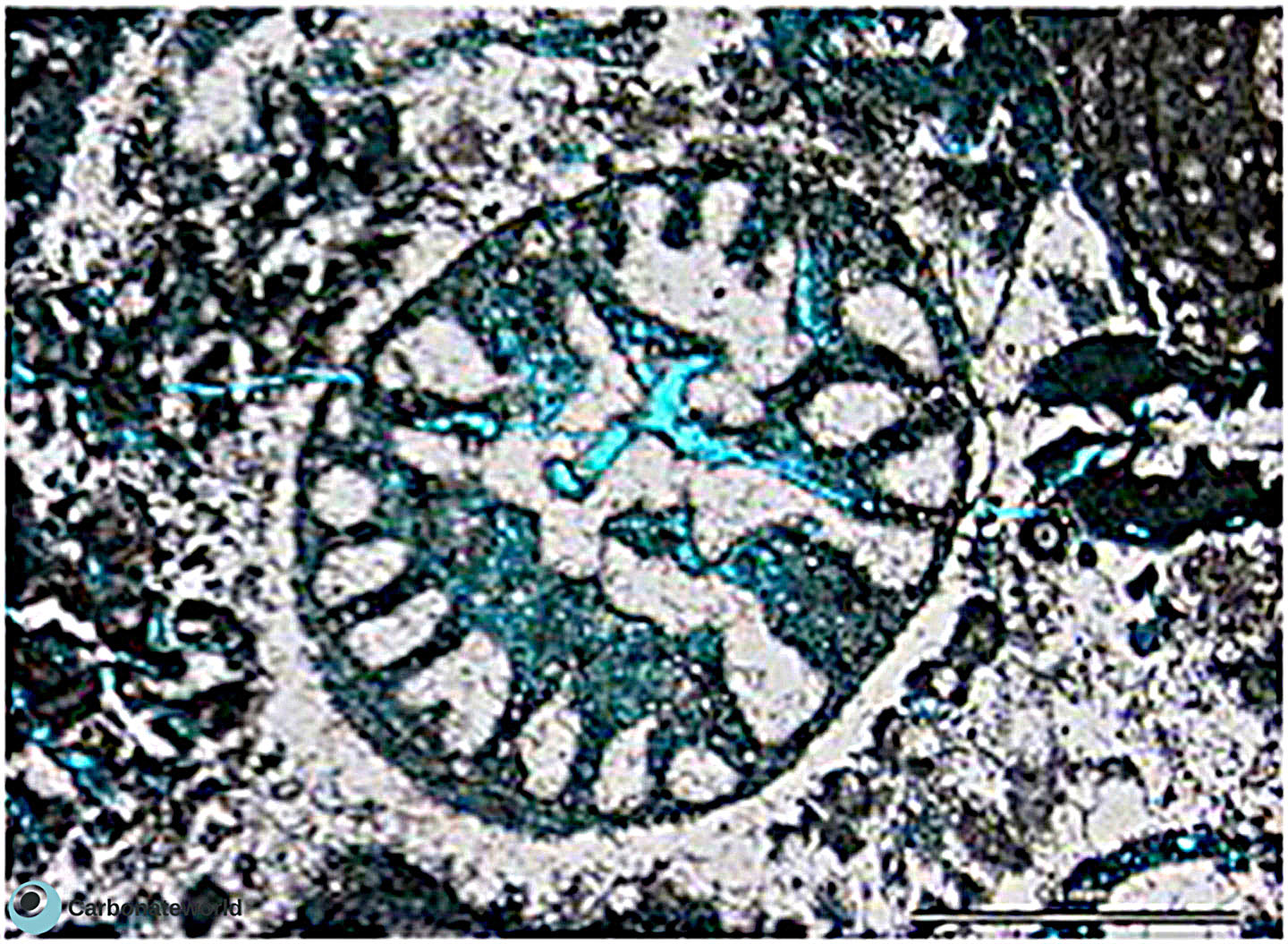


Dissolution of foraminifer wall

Cement in intraparticle space

Dissolution of foraminifer wall

Mould of gastropod

Mould of gastropod

Biomouldic porosity
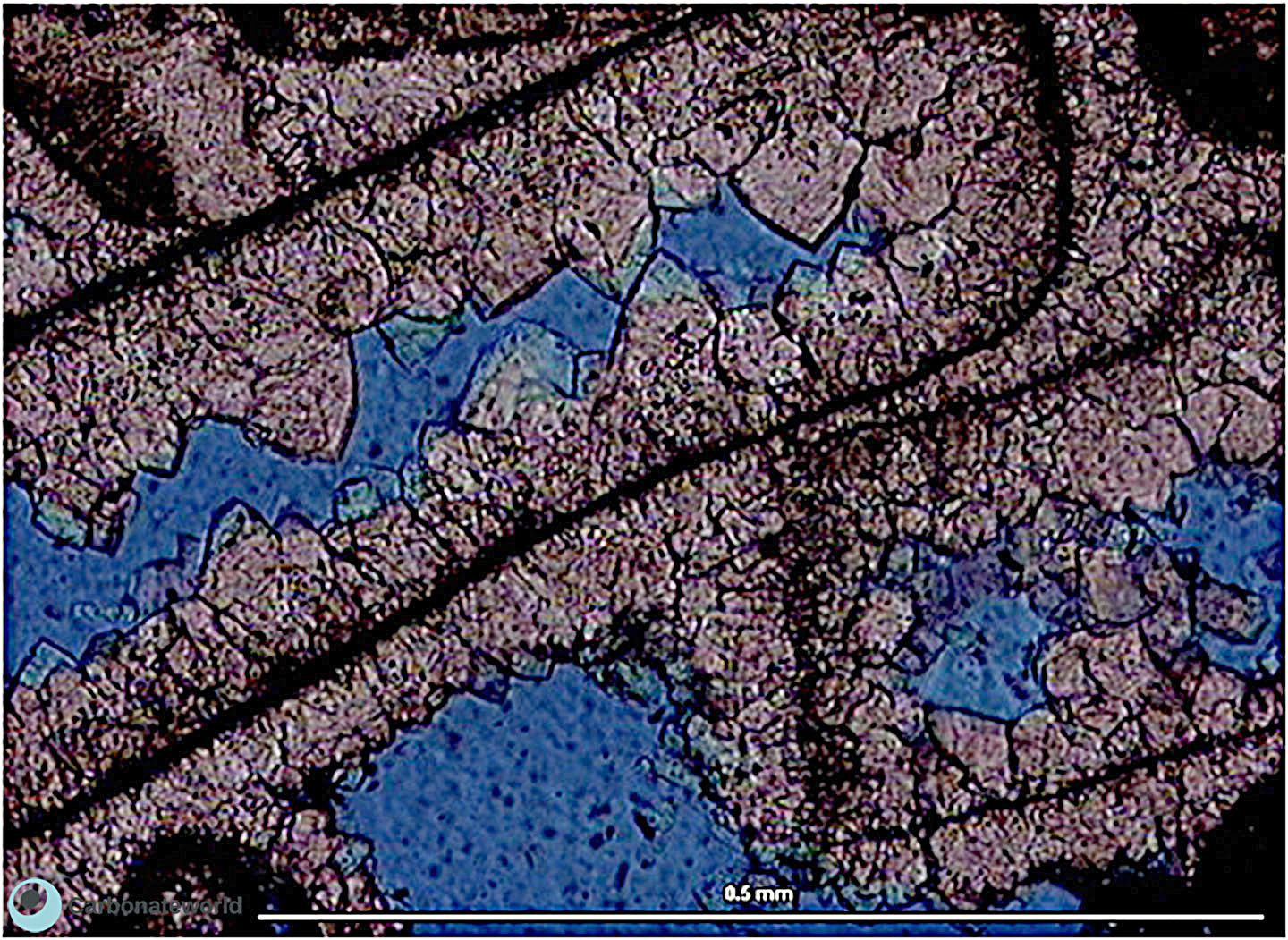


Biomouldic porosity

Sparite cement

Mouldic porosity

Interparticle porosity

Biomouldic porosity

Oomouldic porosity

Oomouldic porosity filled by ferroan calcite

Biomouldic porosity

Interparticle porosity
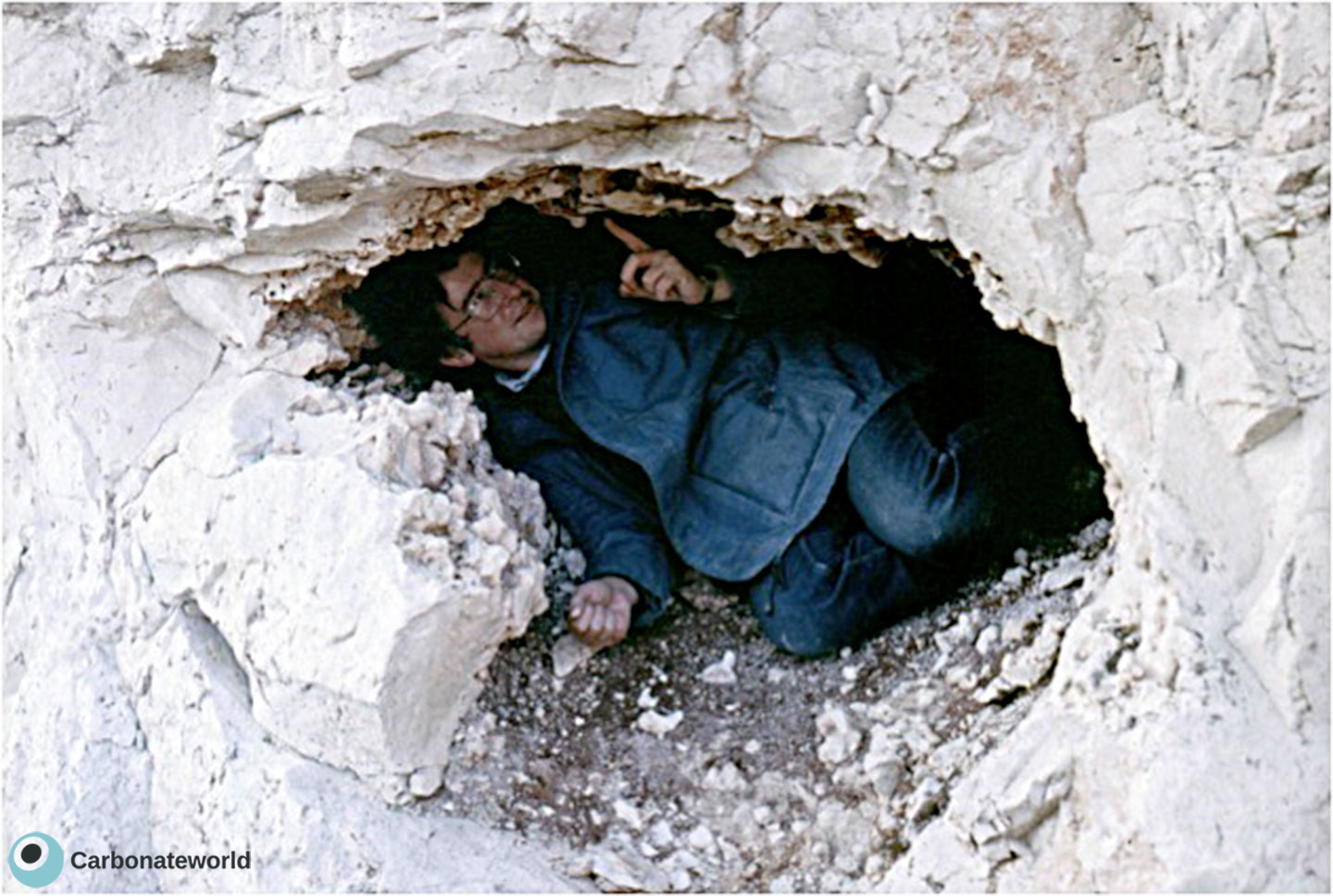


Man-size cavern porosity
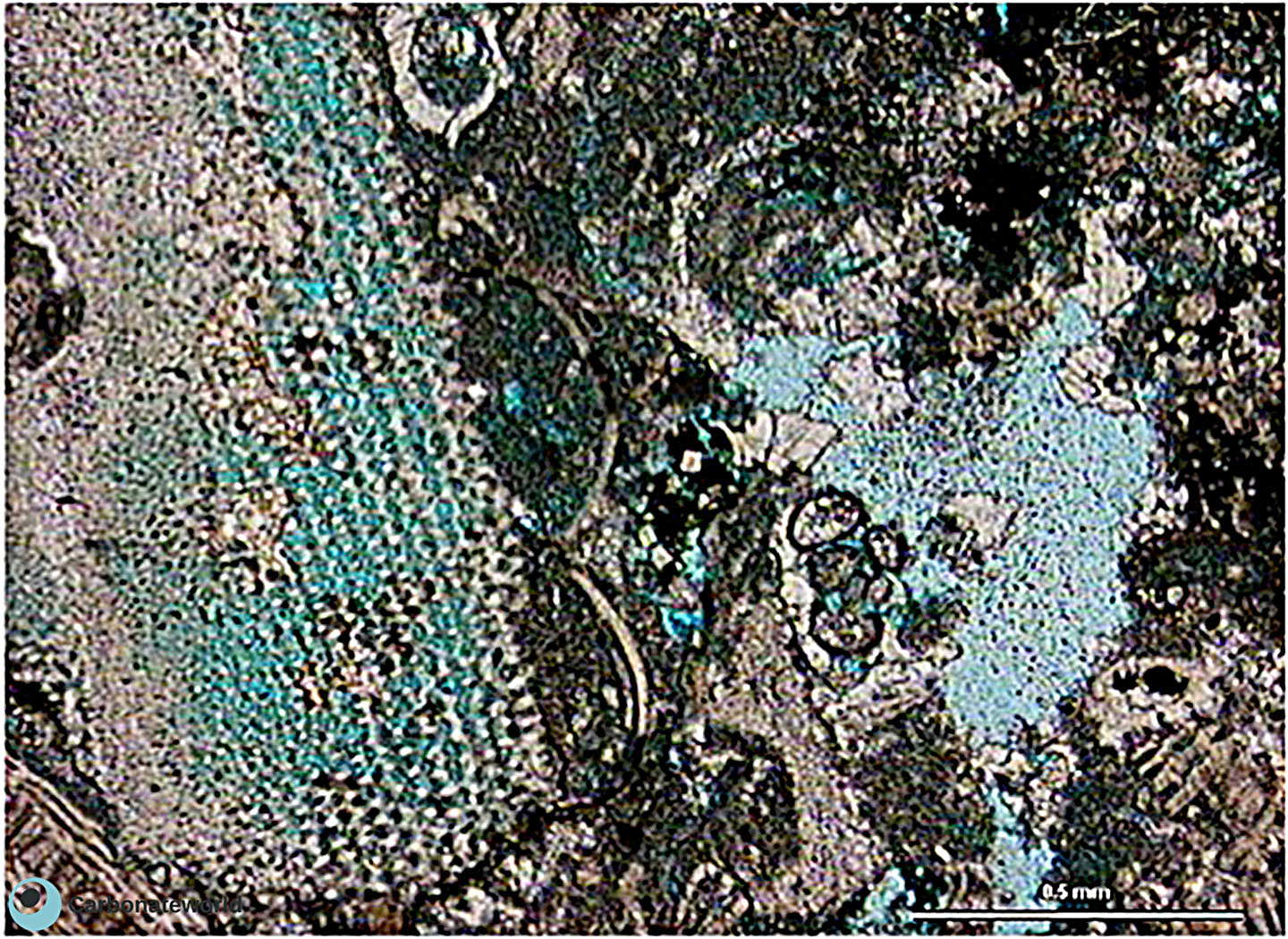



Porosity in echinoderm stereom

Porosity due to micrite dissolution

Dissolution of foraminifer walls

Dissolution of calcite in intraparticle space

Microporosity in micrite

Microporosity

Coral wall

Microporosity and fracture in filling micrite

Microporosity
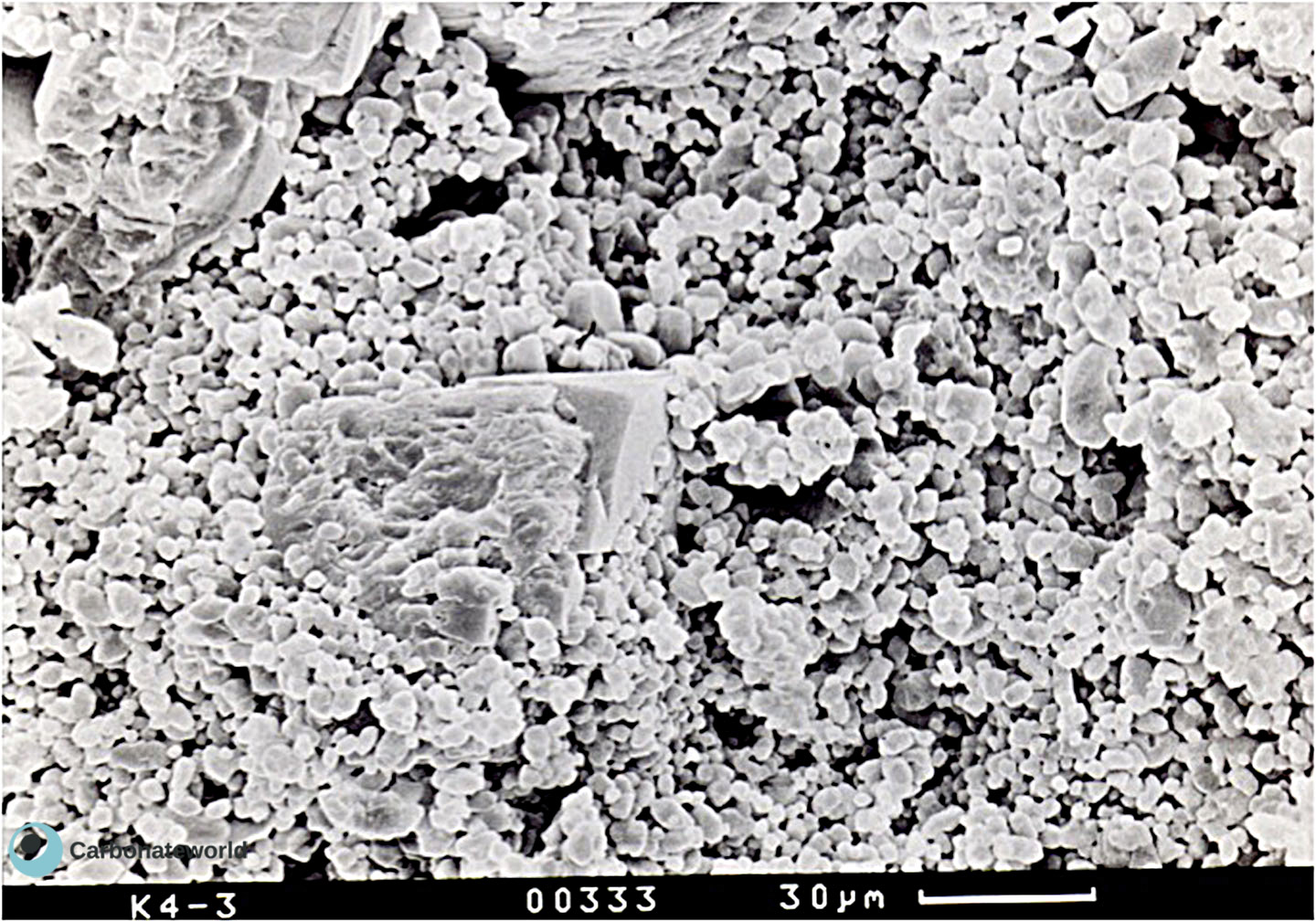


Microporosity
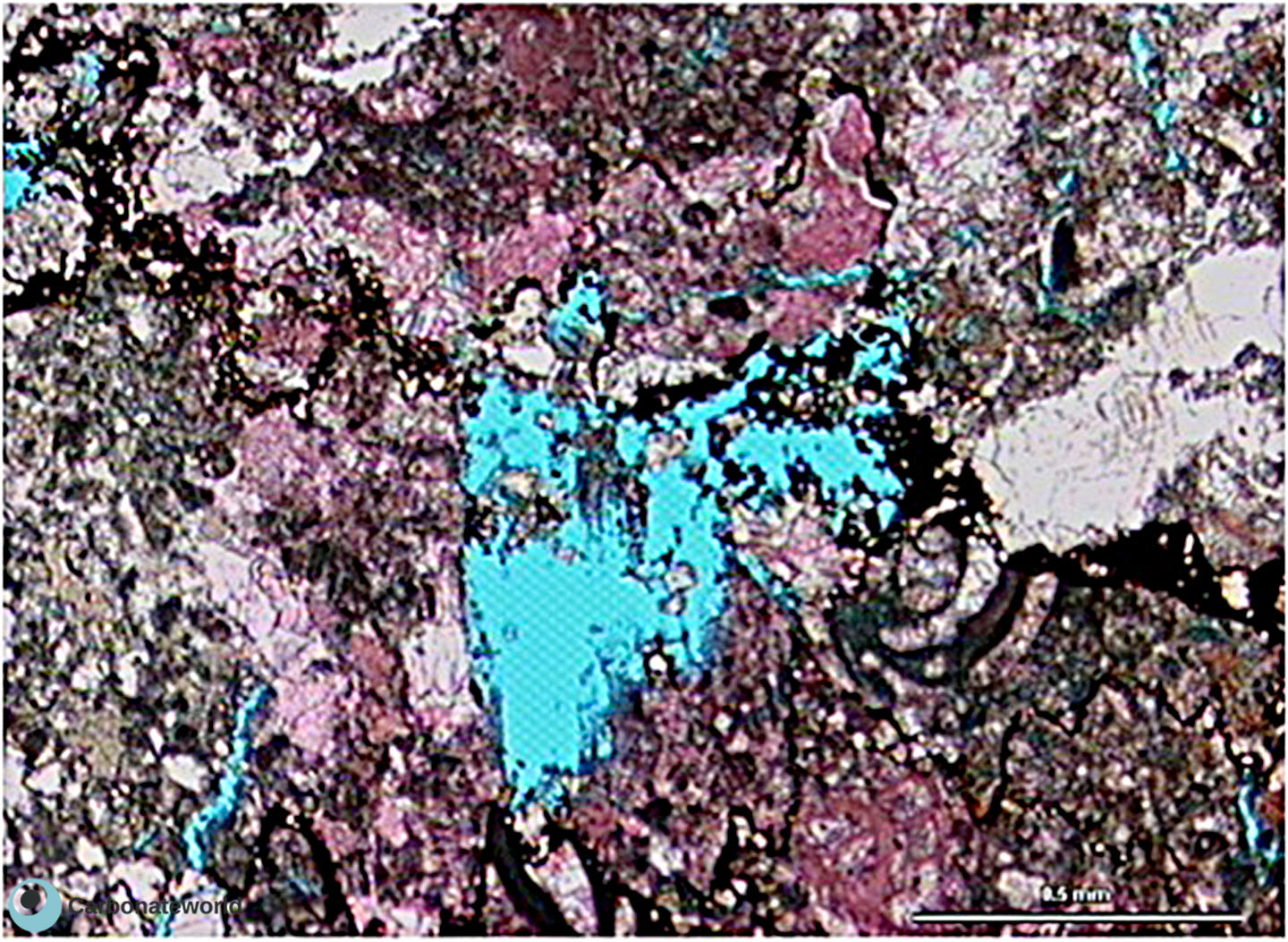


Dissolution linked to stylolite

Secondary porosity in micrite

Dolomite

Secondary intercrystalline porosity


Stylolite


Intercrystalline porosity

Dolomite


Dolomite


Fracture enlarged by late leaching