Staining Techniques
1. Dedolomite
Staining technique puts in evidence the process of dedolomitization. The dolomite rhomb in the image is affected by alteration and transformation into calcite as shown by the pink patches (calcite) within the dolomite crystal (white).
Mississippian, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
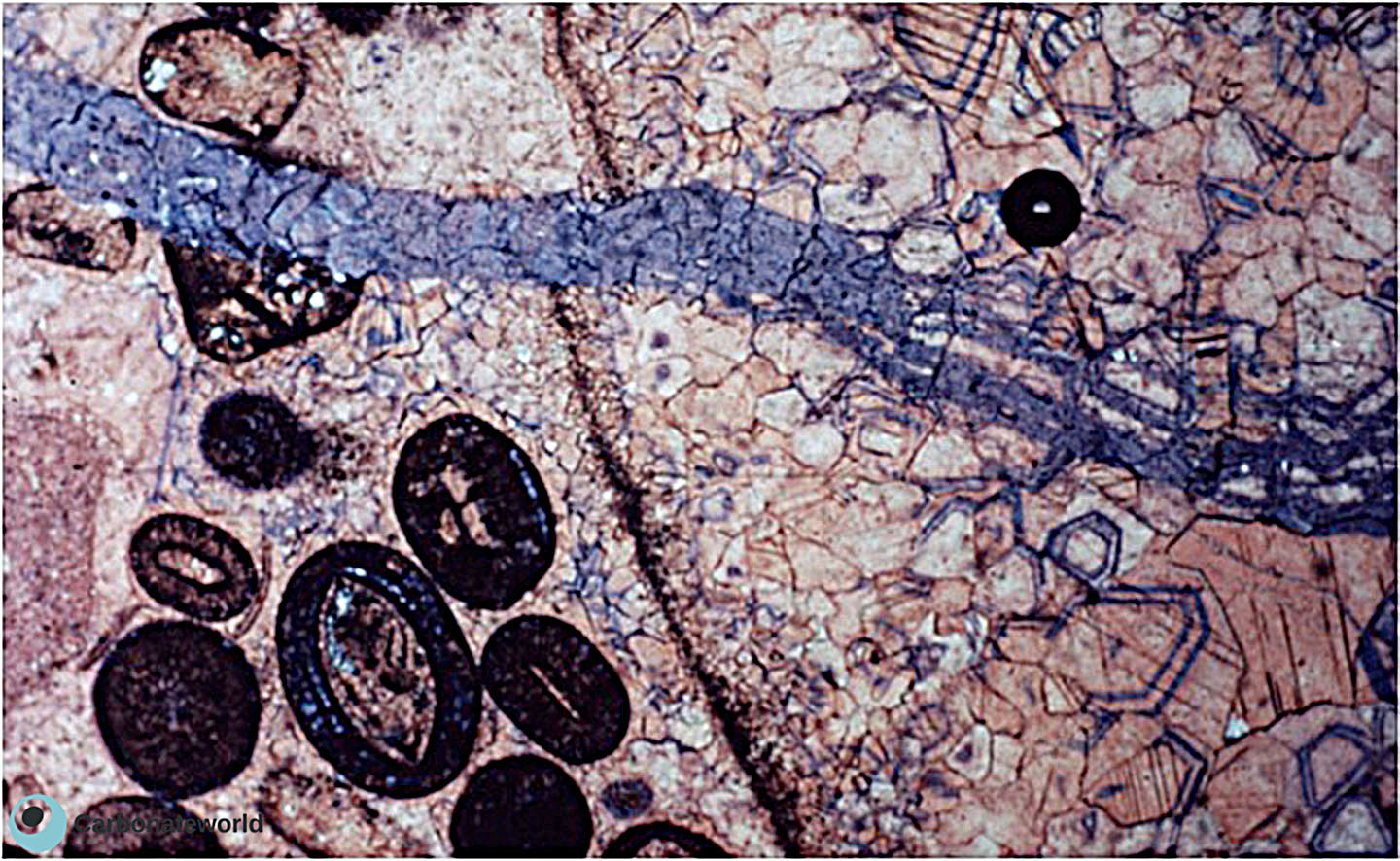
2. Zoned cement
Stained thin section showing zoned cement followed by dissolution of calcite and dickite precipitation.
Cretaceous, Miskar Field, offshore Tunisia

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
3. Ferroan calcite
Non-ferroan calcite walls (pink with staining by alizarin red) of Silurian coral and first generation cement followed by burial ferroan cement (blue with K ferricyanide staining). Field of view approximately 6 mm.

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
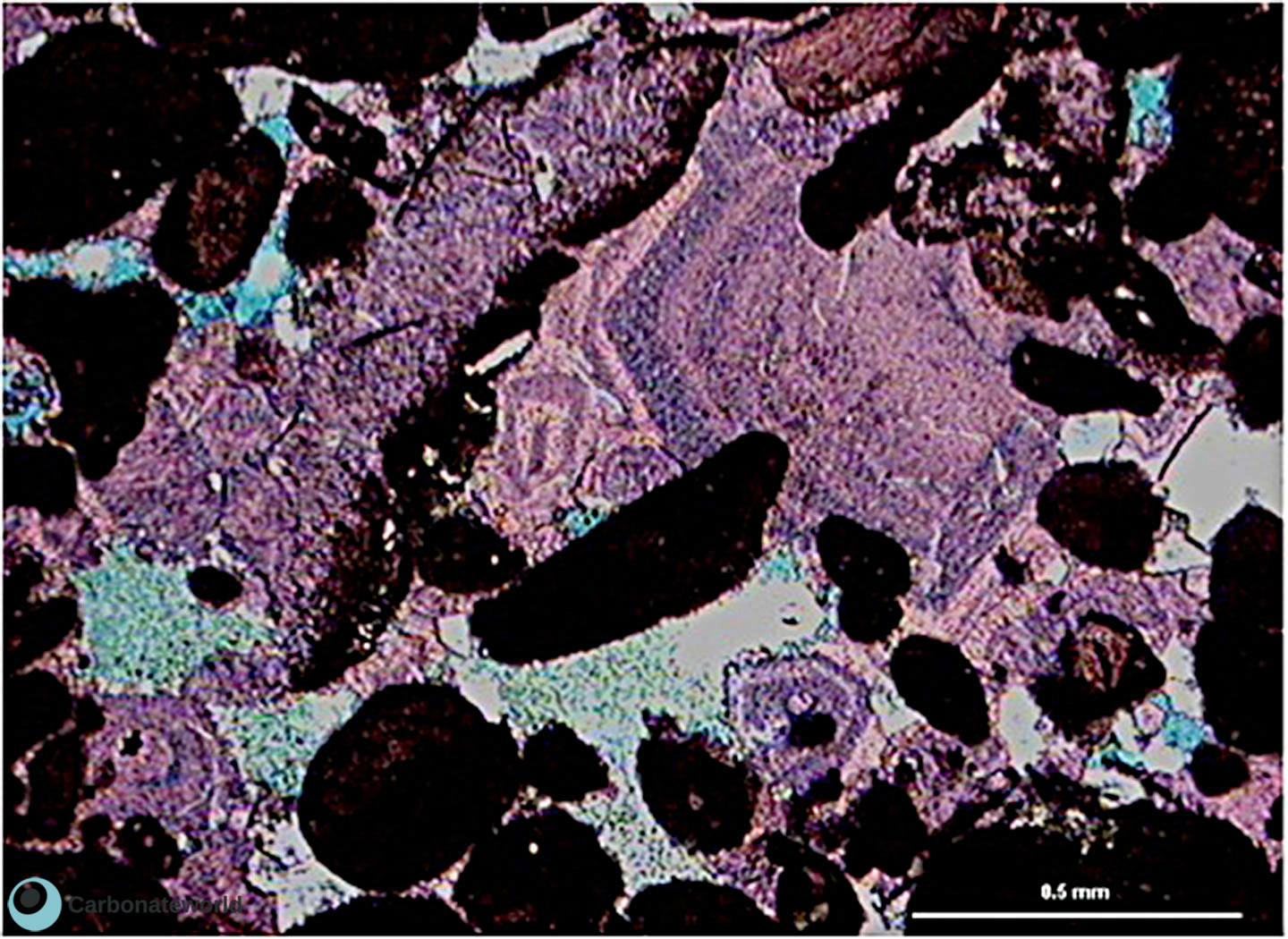
4. Replaced ooids
Ooids replaced by ferroan calcite (stained blue): this probably reflects the fact that the original ooids were composed of HMC (high Mg-calcite), which converted to low Mg calcite and incorporated ferrous iron under reducing conditions. The multi-coloured forms were probably bimineralic (LMC and HMC). Field of view approximately 3 mm wide.
Mississippian, Blaen Onnen Oolite, Brynmawr, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
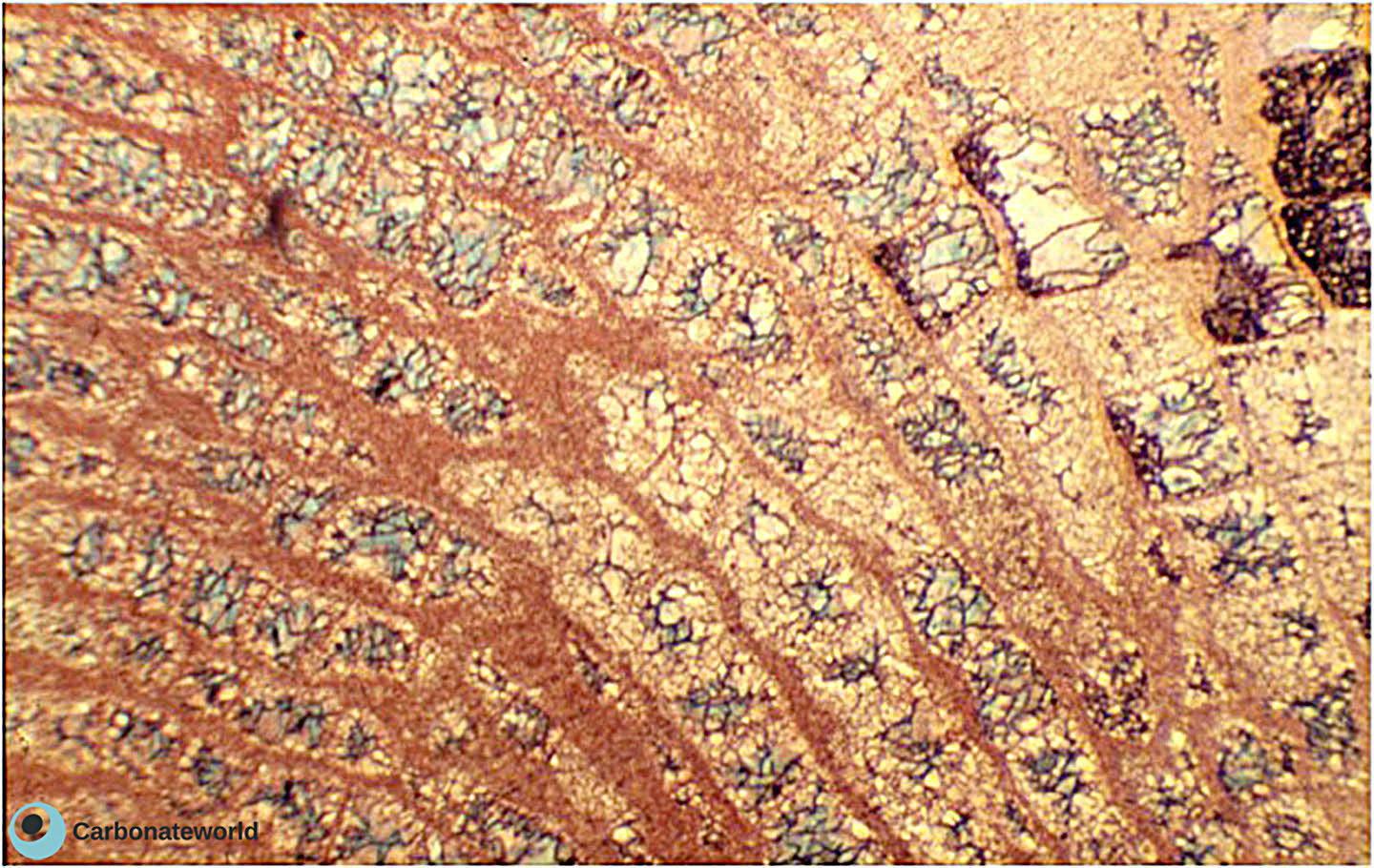
5. Zoned cement
Zoned cement and ferroan calcite (blue) filling a vein. Field of view approximately 1.6 mm.
Mississippian Oolite Group, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
6. Syntaxial cement
Syntaxial cement overgrowth of non-ferroan calcite (centre) followed by burial ferroan calcite cement (blue) in the interparticle space. Note how much thicker the syntaxial cement is on the echinoderm grain compared with the non ferroan cement surrounding the ooids. Syntaxial cements formed rapidly compared with fringe cements. Field of view approximately 1.6 mm.
Mississippian Oolite Group, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
7. Zoned cement
Zoned calcite cement (non ferroan pink, ferroan calcite blue) within Mississippian ooidal grainstone. Field of view approximately 1.6 mm.
Mississippian Oolite Group, South Wales, UK

HIDE INFO

SHOW INFO
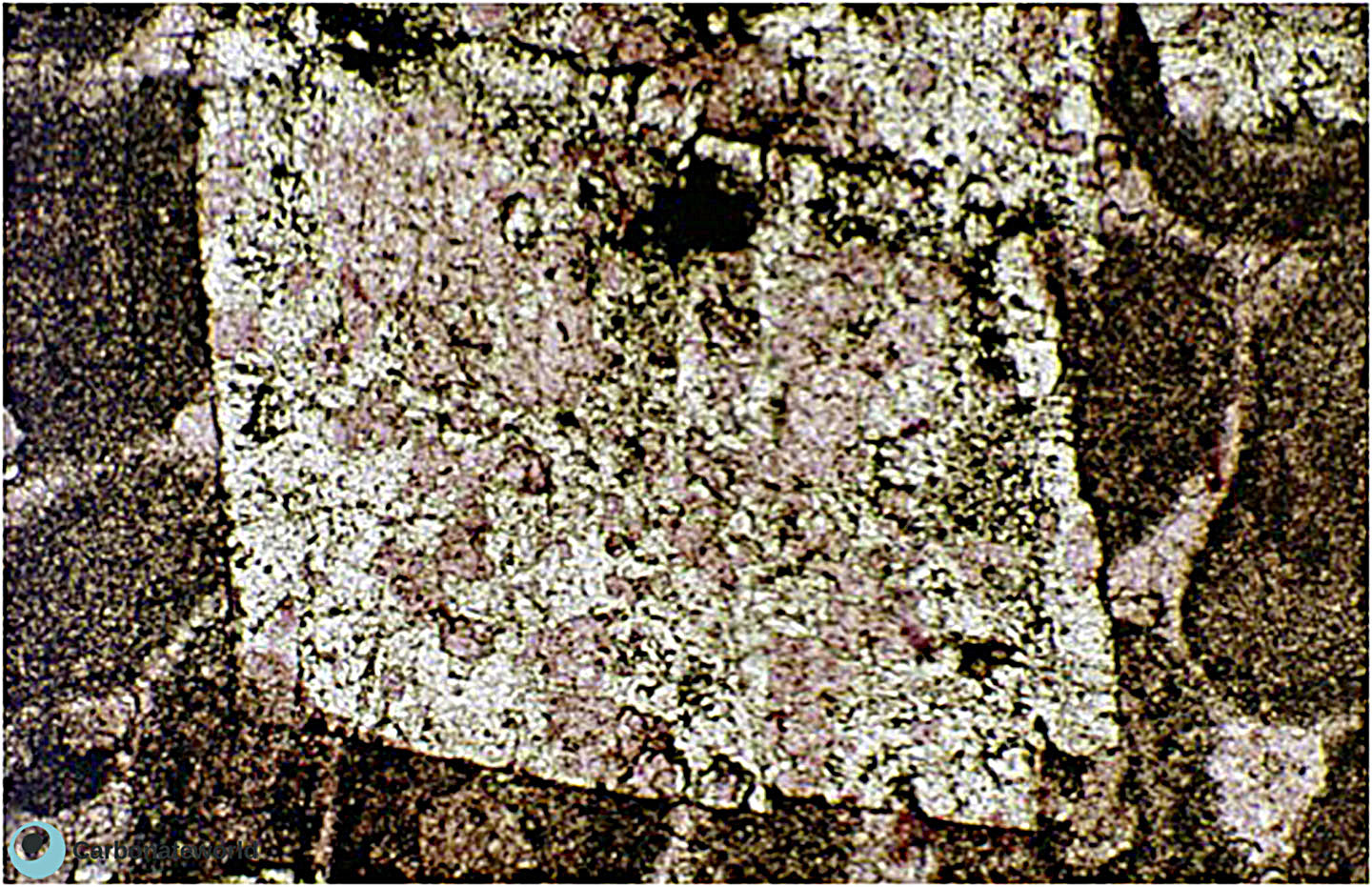



Calcite due to dedolomitization

Zoned calcite

Secondary porosity due to dissolution

Dickite

Coral calcite walls

Ferroan calcite
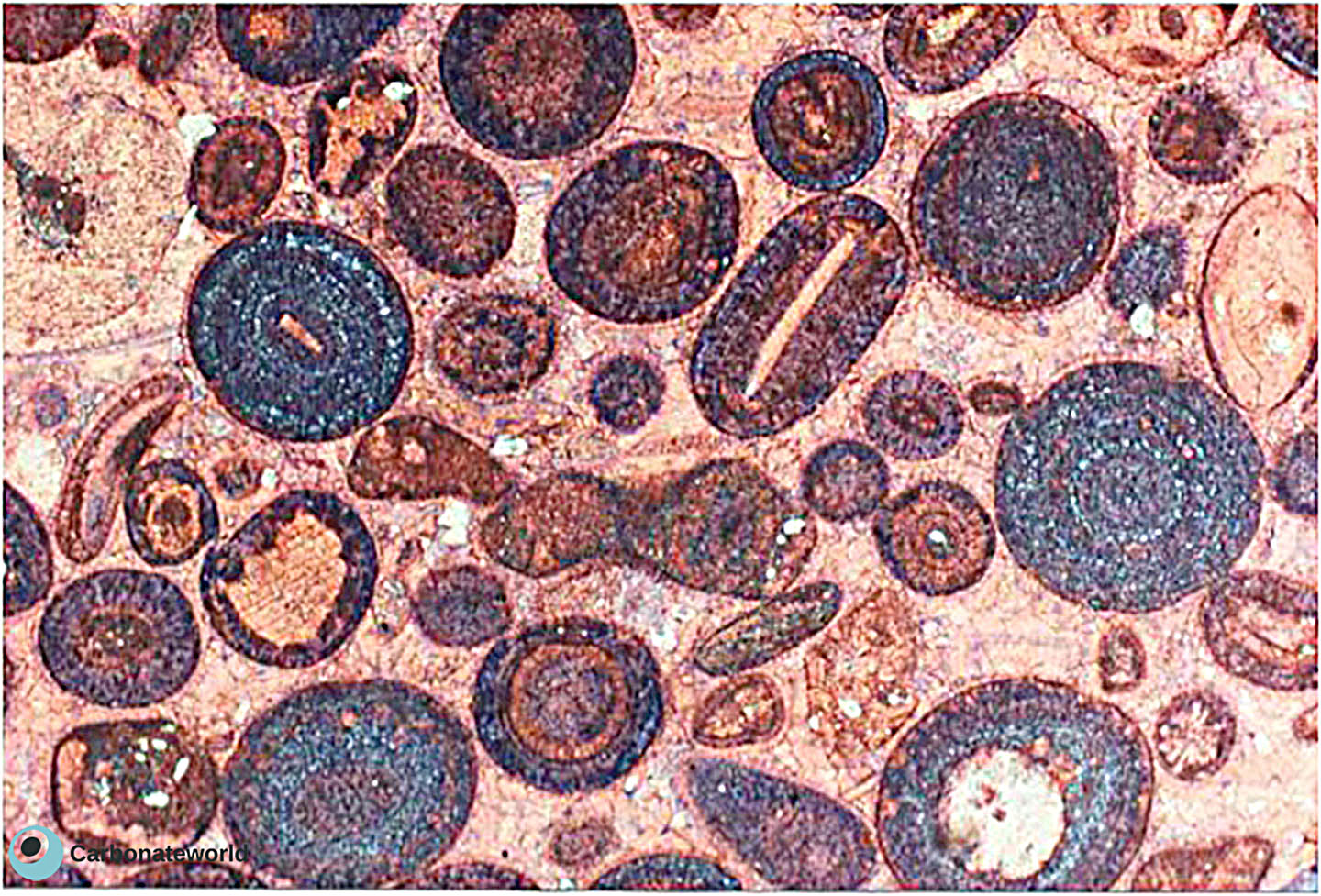

Non ferroan calcite cement

Ferroan calcite replacing ooids

Zoned calcite cement with ferroan and non ferroan growth phases

Vein filled by ferroan calcite
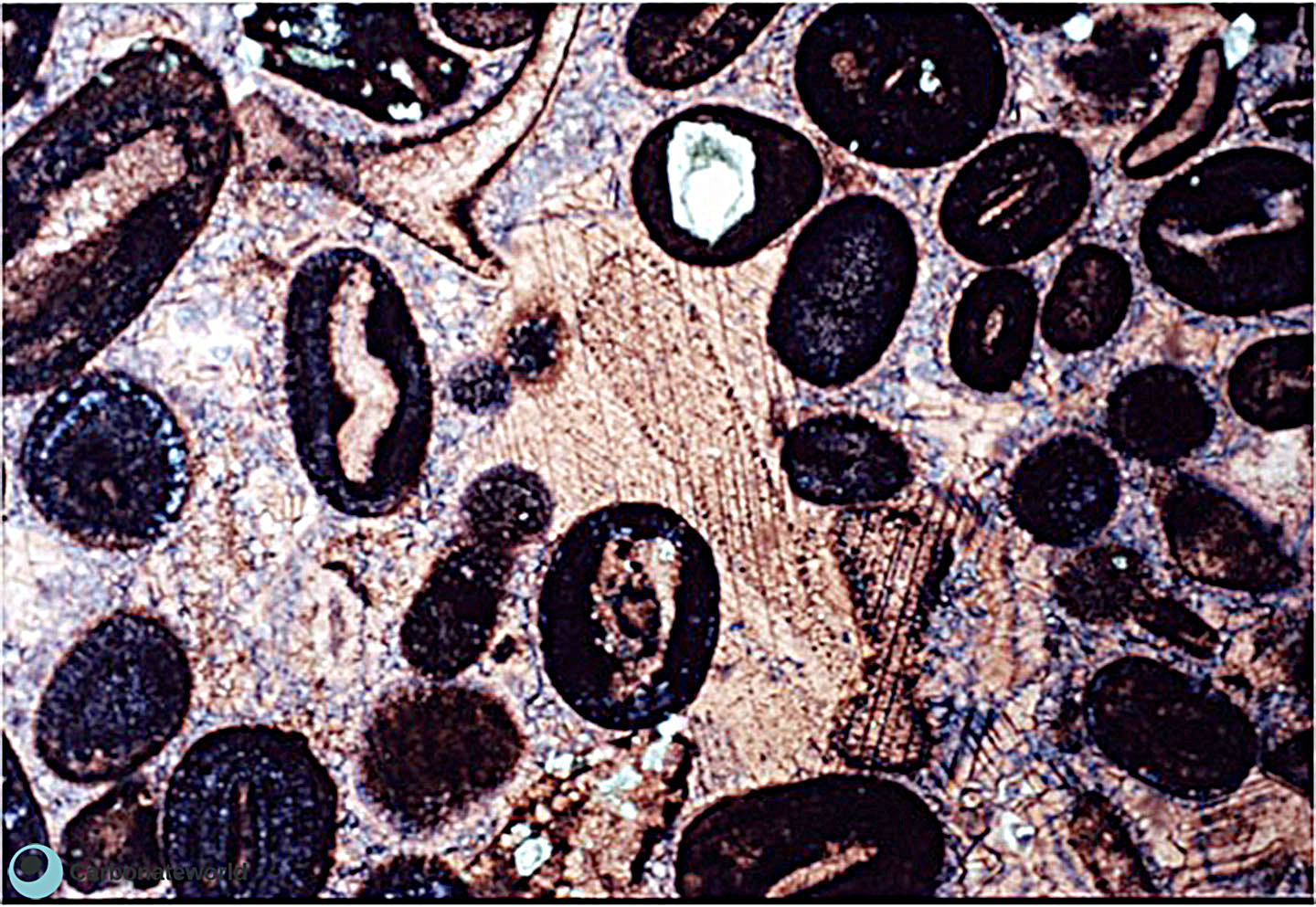

Syntaxial non ferroan calcite cement

Ferroan calcite cement
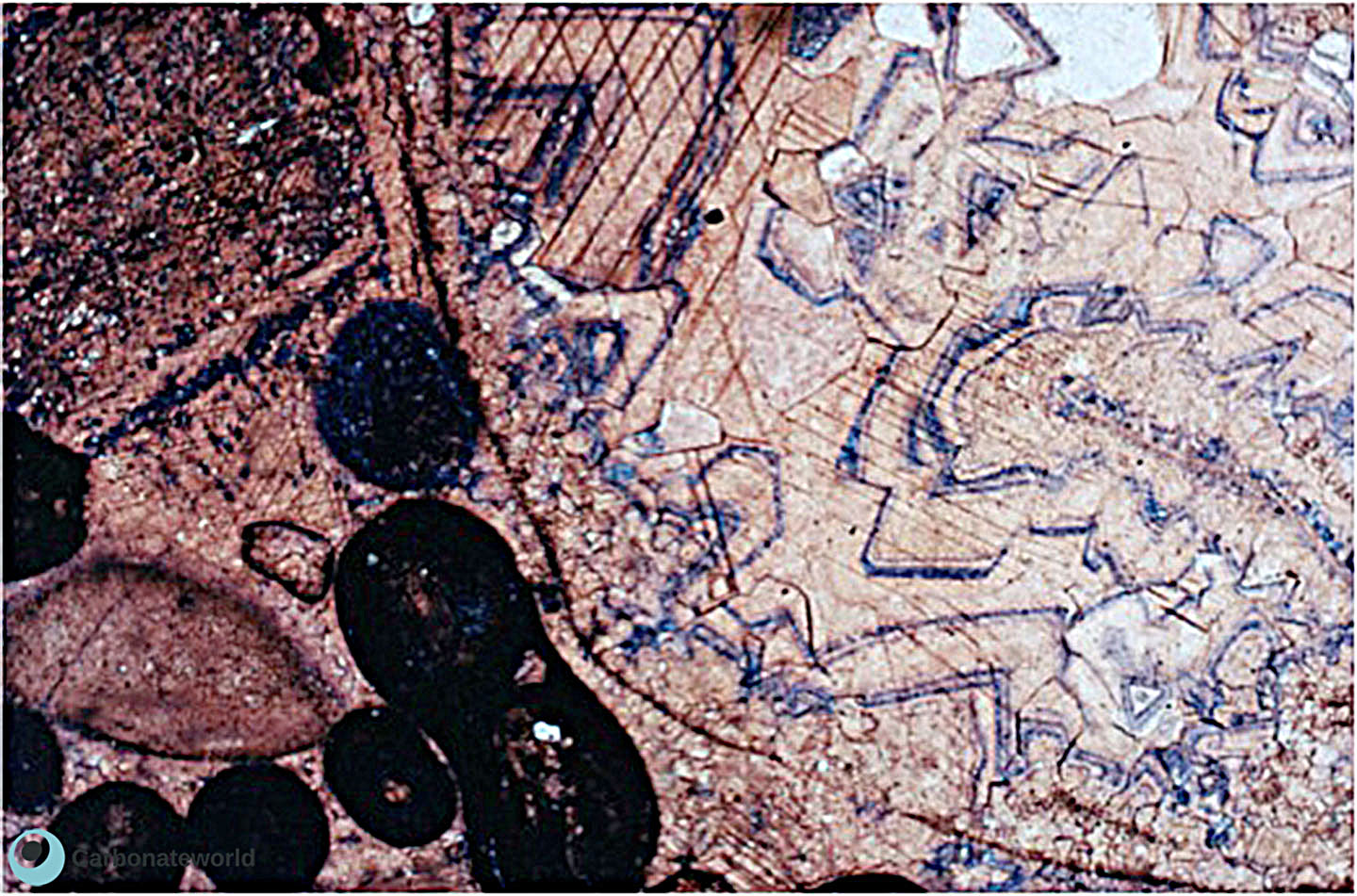

Zoned non ferroan to ferroan calcite

Ferroan calcite neomorphosed ooid